Abstract
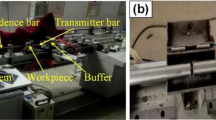
The dynamic tensile behaviors of a newly developed Ti-6Al-2Sn-2Zr-3Mo-1Cr-2Nb-Si alloy (referred as TC21 in China) over a wide range of strain rates from quasi-static to dynamic regimes (0.001–1 200 s−1) at different temperatures were experimentally investigated. A split Hopkinson tension bar apparatus and a static material testing system were utilized to study the stress-strain responses under uniaxial tension loading condition. The experimental results indicate that the tensile behavior of TC21 titanium alloy is dependent on the strain rate and temperature. The values of initial yield stress increase with increasing strain rate and decreasing temperature. The effects of strain rate and temperature on the initial yield behavior are estimated by introducing two sensitivity parameters. The phenomenological-based constitutive model, Johnson-Cook model, is suitably modified to describe the rate-temperature dependent constitutive behavior of TC21 titanium alloy. It is observed that the modified model is in good agreement with the experimental data subjected to the investigated range of strain rates and temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gysler A, Lütjering G. Influence of Test Temperature and Microstructure on the Tensile Properties of Titanium Alloys[J]. Metall. Trans. A, 1982, 13(8): 1 435–1 443
Reed-Hill R E, Iswaran C V, Kaufman M J. An Analysis of the Flow Stress of a Two- phase Alloy System Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, 27(12): 3 957–3 962
Majorell A, Srivatsa S, Picu R C. Mechanical Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V at High and Moderate Temperatures-Part I: Experimental Results[J]. Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 326(2): 297–305
Zong Y Y, Shan D B, Xu M, et al. Flow Softening and Microstructural Evolution of TC11 Titanium Alloy during Hot Deformation[J]. J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2009, 209(4): 1 988–1 994
McEldowney D J, Tamirisakandala S, Miracle D B. Heat-treatment Effects on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Powder Metallurgy Ti-6Al-4V Alloys Modified with Boron[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, 41(4): 1 003–1 015
Zhang X Y, Li M Q, Li H, et al. Deformation Behavior in Isothermal Compression of the TC11 Titanium Alloy[J]. Mater. Des., 2010, 31(6): 2 851–2 857
Sun Q J, Wang G C, Li M Q. The Super Plasticity and Microstructure Evolution of TC11 Titanium Alloy[J]. Mater. Des., 2011, 32(7): 3 893–3 899
Littlewood P D, Wilkinson A J. Local Deformation Patterns in Ti-6Al-4V under Tensile, Fatigue and Dwell Fatigue Loading[J]. Int. J. Fatigue, 2012, 43: 111–119
Gu Y, Zeng F H, Qi Y L, et al. Tensile Creep Behavior of Heat-treated TC11 Titanium Alloy at 450–550 °C[J]. Mater Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 575: 74–85
Park C H, Kim J H, Hyun Y T, et al. The Origins of Flow Softening during High-temperature Deformation of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy with a Lamellar Microstructure[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 582: 126–129
Follansbee P S, Gray G T. An Analysis of the Low Temperature, Low and High Strain-rate Deformation of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Metall. Trans. A, 1989, 20(5): 863–874
Silva M G, Ramesh K T. The Rate-dependent Deformation and Localization of Fully Dense and Porous Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 232(1–2): 11–22
Lee W S, Lin C F. Plastic Deformation and Fracture Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Loaded with High Strain Rate under Various Temperatures[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 241(1–2): 48–59
Chichili D R, Ramesh K T, Hemker K J. The High-strain-rate Response of Alpha-titanium: Experiments, Deformation Mechanisms and Modeling[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(3): 1 025–1 043
Nemat-Nasser S, Guo W G, Nesterenko V F, et al. Dynamic Response of Conventional and Hot Isostatically Pressed Ti-6Al-4V Alloys: Experiments and Modeling[J]. Mech. Mater, 2001, 33(8): 425–439
Lee D G, Lee S, Lee C S, et al. Effects of Micro Structural Factors on Quasi-static and Dynamic Deformation Behaviors of Ti-6Al-4V Alloys with Widmanstätten Structures[J]. Metall. Mater Trans. A, 2003, 34(11): 2 541–2 548
Khan A, Kazmi R, Farrokh B, et al. Effect of Oxygen Content and Micro-structure on the Thermo-mechanical Response of Three Ti-6Al-4V Alloys: Experiments and Modeling over a Wide Range of Strain-rates and Temperatures[J]. Int. J. Plasticity, 2007, 23(7): 1 105–1 125
Luntz R D, Griffin R M, Green S J, et al. High-strain-rate Tests on Titanium 6-6-2 Utilizing a Unique Rate-testing Machine[J]. Exp. Mech., 1975, 15(10): 396–402
Fundenberger J J, Philippe M J, Wagner F, et al. Modeling and Prediction of Mechanical Properties for Materials with Hexagonal Symmetry (Zinc, Titanium and Zirconium Alloys)[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45: 4 041–4 055
Gall K, Sehitoglu H, Chumlyakov Y I, et al. Tension-compression Asymmetry of the Stress-strain Response in Aged Single Crystal and Polycrystalline NiTi[J]. Acta. Mater, 1999, 47(4): 1 203–1 217
Williams J C, Baggerly R G, Paton N E. Deformation Behavior of HCP Ti-Al Single Crystals[J]. Metall. Mater Trans. A, 2002, 33(13): 837–850
Cheng S, Spencer J A, Milligan W W. Strength and Tension/compression Asymmetry in Nanostructured and Ultra Fine-grain Metals[J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(15): 4 505–4 518
Macdougall D A S, Harding J. A Constitutive Relation and Failure Criterion for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy at Impact Rates of Strain[J]. J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1999, 47(5): 1 157–1 185
Roy S, Suwas S. The Influence of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Deformation Response and Microstructural Evolution during Hot Compression of a Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V-0.1B[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 548(4): 110–125
Kotkunde N, Deole A D, Gupta A K, et al. Comparative Study of Constitutive Modeling for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy at Low Strain Rates and Elevated Temperatures[J]. Mater Des., 2014, 55: 999–1005
Huang W, Zan X, Nie X, et al. Experimental Study on the Dynamic Tensile Behavior of a Poly-crystal Pure Titanium at Elevated Temperatures[J]. Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 443(1–2): 33–41
Kapoor R, Nemat-Nasser S. Determination of Temperature Rise during High Strain Rate Deformation[J]. Mech. Mater, 1998, 27(1): 1–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Academy of Engineering Physics and Jointly Set up “NSAF” Joint Fund (No. U1430119)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zeng, X. Dynamic Tensile Behavior and Constitutive Modeling of TC21 Titanium Alloy. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 707–716 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2107-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2107-x