Abstract
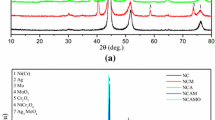
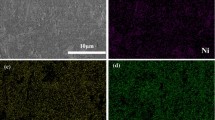
The tribological properties of Nickel-based composites containing Ti3SiC2 and Ag2W2O7 fabricated by spark plasma sintering against Si3N4 balls were investigated using a ball-on-disk tribometer from room temperature to 600 °C. The tribolayers formed on the friction surface and their effects on the tribological properties of composites at different temperatures were discussed based on the worn surface characterization. The results show that Ag2W2O7 is decomposed into metallic silver and CrWO4 during the high-temperature fabrication process. The composite with the addition of 20 wt% Ti3SiC2 and 5 wt% Ag2W2O7 exhibits a friction coefficient of 0.33–0.49 and a wear rate of 7.07×10−5–9.89×10−5 mm3/(Nm) over a wide temperature range from room temperature to 600 °C. The excellent tribological properties at a wide temperature range are attributed to the formation of a glaze layer at low temperature and a tribooxide layer at high temperature, which can provide a low shearing strength for the synergistic effects of Ag and tribooxides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DellaCorte C, Sliney H E. Tribological and Mechanical Comparison of Sintered and HIPped PM212-High Temperature Self-lubricating Composites[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 1992, 48 (11): 877–885
Li J L, Xiong D S, Huang Z J, et al. Effect of Ag and CeO2 on Friction and Wear Properties of Ni-base Composite at High Temperature[J]. Wear, 2009, 267: 576–584
Li J L, Xiong D S. Tribological Properties of Nickel-based Self-lubricating Composite at Elevated Temperature and Counterface Material Selection[J]. Wear, 2008, 265: 533–539
Rajnesh T, Xiong D S, Li J L. Effect of Load and Sliding Speed on Friction and Wear Behavior of Silver/h-BN Containing Ni-base P/M Composites[J]. Wear, 2011, 270: 423–430
Rajnesh T, Xiong D S, Li J L, et al. Elevated Temperature Tribological Behavior of Ni-based Composites Containing Nano-silver and h-BN[J]. Wear, 2010, 269: 884–890
Zhu S Y, Bi Q L, Yang J, et al. Ni3Al Matrix High Temperature Self-lubricating Composites[J]. Tribol. Int., 2011, 44: 445–453
Gupta S, Filimonov D, Zaitsev V, et al. Ambient and 550 °C Tribological Behavior of Select MAX Phases against Ni-based Superalloys[J]. Wear, 2008, 264: 270–278
Gupta S, Filimonov D, Palanisamy T, et al. Tribological Behavior of Select MAX Phases against Al2O3 at Elevated Temperatures[J]. Wear, 2008, 265: 560–565
Shi X L, Wang M, Zhai W Z, et al. Influence of Ti3SiC2 Content on Tribological Properties of NiAl Matrix Self-lubricating Composites[J]. Mater. Des., 2013, 45: 179–189
Peterson M B, Calabrese S B, Stupp B. Lubrication with Naturally Occurring Double Oxide Films[R]. Cleveland: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Glenn Research Center, 1982
Gulbiński W, Suszko T. Thin Films of MoO3–Ag2O Binary Oxides — the High Temperature Lubricants[J]. Wear, 2006, 261: 867–873
Aouadi S M, Paudel Y, Simonson W J, et al. Tribological Investigation of Adaptive Mo2N/MoS2/Ag Coatings with High Sulfur Content[J]. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203: 1 304–1 312
Gulbiński W, Suszko T, Sienicki W, et al. Tribological Properties of Silver- and Copper-doped Transition Metal (xide Coatings[J]. Wear, 2003, 254: 129–135
Stone D, Liu J, Singh D P, et al. Layered Atomic Structures of Double (xides for Low Shear Strength at High Temperatures[J]. Scripta Mater., 2010, 62: 735–742
Manakkadu S. Synthesis and Tribological Study of Selected Double Metal Oxide Nanomaterials[D]. Ann Arbor: Southern Illinois University Carbondale, 2010
Peng M C, Shi X L, Zhu Z W, et al. Facile Synthesis of Ti3SiC2 Powder by High Energy Ball-milling and Vacuum Pressureless Heat-treating Process from Ti-TiC-SiC-Al Powder Mixtures[J]. Ceram. Int., 2012, 38: 2 027–2 033
Shi X L, Peng M C, Zhu Z W, et al. Synthesis and Tribological Behaviors of Ti3SiC2 Material Prepared by Vacuum Sintering Technique[J]. J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2013, 28(3): 417–424
ASTM. Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials[S]. ASTM E92-82, 2003
ASTM. Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle[S]. ASTM B962-08, 2008
ASTM. Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-disk Apparatus[S]. ASTM G99-95, 1995
Peterson M B, Calabrese S J, Li S Z, et al. Friction of Alloys at High Temperature[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 1994, 10: 313–320
Gupta S, Barsoum M W. On the Tribology of the MAX Phases and Their Composites during Dry Sliding: A Review[J]. Wear, 2011, 271: 1 878–1 894
Zhai W Z, Lu W L, Zhang P, et al. Wear-triggered Self-healing Behavior on the Surface of Nanocrystalline Nickel Aluminum Bronze/Ti3SiC2 Composites[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 436: 1 038–1 049
Zhang P, Liu X J, Lu W L, et al. Fretting Wear Behavior of CuNiAl against 42CrMO4 under Different Lubrication Conditions[J], Tribol. Int., 2018, 117: 59–67
Yu T, Deng Q L, Dong G, et al. Influence of Ta on Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Laser Clad NiCrSiB Coating[J]. J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2013, 28(3): 437–443
Sun T, Sun D L. Friction and Wear Properties of TiAl and Ti2AlN/TiAl Composites at High-temperature[J]. J. Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2013, 28(5): 1 023–1 028
Gao P, Ji H M, Zhou Y G, et al. Selective Acetone Gas Sensors Using Porous WO3-Cr2O3 Thin Films Prepared Bysol-gel Method[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520: 3 100–3 106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51805183)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Zhou, X. & Zhang, Q. Tribological Behavior of Ni-based Self-lubricating Composites with the Addition of Ti3SiC2 and Ag2W2O7. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 698–706 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2106-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2106-y