Abstract
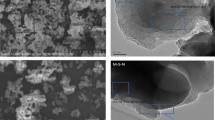
Magnetic Fe-containing ordered mesoporous carbons (Fe/OMCs) with high surface areas and pore volume were synthesized through a simple soft-template route, wherein phenolic resin was used as a carbon precursor, triblock copolymer F127 as a template agent, tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as a silica precursor and hydrated iron nitrate as an iron source. The effects of carbonization temperature, loading degree of TEOS on the structural parameters of these Fe/OMCs were evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and N2 sorption analysis. The ordering, the specific surface area and the total pore volumes increased with the increase of carbonization temperature from 600 to 850 °C. And the specific surface area and the total pore volumes increased with the increase of TEOS loading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim BC, Lee J, Um W, et al. Magnetic Mesoporous Materials for Removal of Environmental Wastes[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 192:1 140–1 147
Tian Y, Liu P, Wang XF, Lin HS. Adsorption of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solutions onto Ordered Mesoporous Carbons[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 171: 1 263–1 269
Wang XF, Liu P, Tian Y. Ordered Mesoporous Carbons for Ibuprofen Drug Loading and Release Behavior[J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2011, 142: 334–340
Tian Y, Wang XF, Pan YF. Simple Synthesis of Ni-containing Ordered Mesoporous Carbons and Their Adsorption/Desorption of Methylene Orange[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 192: 1 140–1 147
Zhai YP, Dou YQ, Liu XX, et al. One-pot Synthesis of Magnetically Separable Ordered Mesoporous Carbon[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19:3 292–3 300
Fulvio PF, Jaroniec M, Liang CD, et al. Polypyrrole-based Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Replicas of SBA-15 and SBA-16 Containing Magnetic[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112: 13 126–13 133
Guo LM, Cui XZ, et al. Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Spheres with Magnetic Cores and Their Performance as Separable Bilirubin Adsorbents [J]. Chem. -Asian J., 2009, 4: 1 480–1 485
Fuertes AB, Centeno TA. Mesoporous Carbons with Graphitic Structures Fabricated by Using Porous Silica Materials as Templates and Iron-impregnated Polypyrrole as Precursor [J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15: 1 079–1 083
Park IS, Choi M, Kim TW, et al. Synthesis of Magnetically Separable Ordered Mesoporous Carbons Using Furfuryl Alcohol and Cobalt Nitrate in a Silica Template [J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2006, 16: 3 409–3 416
Wang XF, Liu P, Tian Y, et al. Novel Synthesis of Fe-containing Mesoporous Carbons and Their Release of Ibuprofen[J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2011, 145: 98–103
Dong XP, Chen HR, Zhao WR, et al. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Mesostructured -Fe2O3/Carbon Composites by a Co-casting Method [J]. Chem. Mater., 2007, 19: 3 484–3 490
Lee JW, Jin SM, Hwang YS, et al. Simple Synthesis of Mesoporous Carbon with Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Rods[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43: 2 536–2 543
Zhang TM, Zhao DL, Yin L, et al. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Iron Nanoparticles Confined in Highly Ordered Mesoporous Carbons[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 508: 147–151
Li JS, Gu J, Li HJ, et al. Synthesis of Highly Ordered Fe-containing Mesoporous Carbon Materials Using Soft Templating Routes[J]. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2010, 128: 144–149
Tian Y, Liu P, Wang J, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic FeNi Mesoporous Carbon by Simple One Pot Method [J]. Mater. Lett., 2012, 82: 19–21
Wang ZL, Liu XJ, Lv MF, Meng J. Simple Synthesis of Magnetic Mesoporous FeNi/Carbon Composites with A Large Capacity for the Immobilization of Biomolecules[J]. Carbon, 2010, 48: 3 182–3 189
Zhai YP, Dou YQ, Liu XX, et al. Soft-template Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Carbon/nanoparticle Nickel Composites with A High Surface Area[J]. Carbon, 2011, 49: 545–555
Meng Y, Gu D, Zhang FQ, et al. Ordered Mesoporous Polymers and Homologous Carbon Frameworks: Amphiphilic Surfactant Templating and Direct Transformation[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44: 7 053–7 059
Huber DL. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Iron Nanoparticles[J]. Small, 2005, 1: 482–501
Yao JY, Li LX, Song HH, et al. Synthesis of Magnetically Separable Ordered Mesoporous Carbons from F127/[Ni(H2O)6](NO3)2/Resorcinol-formaldehyde Composites[J]. Carbon, 2009, 47: 436–444
Weisweiler W, Subramanian N, Terwiesch B. Catalytic Influence of Metal Melts on the Graphitization of Monolithic Glasslike Carbon[J]. Carbon, 1971, 9: 755–758
Bonnet F, Ropital F, Berthier Y, Marcus P. Filamentous Carbon Formation Caused by Catalytic Metal Particles from Iron Oxide[J]. Mater. Corros., 2003, 54: 870–880
Cushing BL, Kolesnichenko VL, Connor JCO. Recent Advances in the Liquid-phase Syntheses of Inorganic Nanoparticles[J]. Chem. Rev., 2004, 104: 3 893–3 946
Celik O, Dag OA. New Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline System: Oligo (Ethylene Oxide) Surfactants with [M(H2O)n]Xm Transition Metal Complexes[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40: 3 799–3 803
Zhao DY, Feng JL, Huo QS, et al. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science, 1998, 279: 548–552
Liu RL, Shi YF, Wan Y, et al. Triconstituent Co-assembly to Ordered Mesostructured Polymer-silica and Carbon-silica Nanocomposites and Large-pore Mesoporous Carbons with High Surface areas[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128: 11 652–11 662
Deng YH, Yu T, Wan Y, et al. Ordered Mesoporous Silicas and Carbons with Large Accessible Pores Templated from Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymer poly(Ethylene Oxide)-b-polystyrene[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129: 1 690–1 697
Sterk L, Górka J, Jaroniec M. Polymer-templated Mesoporous Carbons with Nickel Nanoparticles[J]. Colloid Surface A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2010, 362: 20–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50802017), the Higher Education Talents Introducing Fund of Guangdong Province (2011 Annual), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012010009416), the Foundation for Distinguished Young Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong (2012LYM_0085) and the Planned Project of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2012B020316007, 2012A020602058)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Zhong, G. & Wang, X. Simple synthesis of magnetic mesoporous carbons with high surface areas by soft-template method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 28, 668–672 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0749-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0749-7