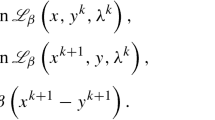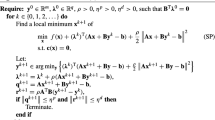Abstract
The alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) has recently received a lot of attention especially due to its capability to harness the power of the new parallel and distributed computing environments. However, ADMM could be notoriously slow especially if the penalty parameter, assigned to the augmented term in the objective function, is not properly chosen. This paper aims to accelerate ADMM by integrating that with the Barzilai–Borwein gradient method and an acceleration technique known as line search. Line search accelerates an iterative method by performing a one-dimensional search along the line segment connecting two successive iterations. We pay a special attention to the large-scale nonnegative least squares problems, and our experiments using real datasets indicate that the integration not only accelerate ADMM but also robustifies that against the penalty parameter.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For computational efficiency, the code does not include a diminishing stepsize that was suggested in the paper to assure the convergence.
References
Barzilai, J., Borwein, J.M.: Two-point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8(1), 141–148 (1988)
Bauschke, H., Deutsch, F., Hundal, H., Park, S.H.: Accelerating the convergence of the method of alternating projections. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 355(9), 3433–3461 (2003)
Birgin, E.G., Martínez, J.M., Raydan, M.: Algorithm 813: SPG—software for convex-constrained optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 27(3), 340–349 (2001)
Björck, A.: Numerical Methods for Least Squares Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia (1996)
Boyd, S., Parikh, N., Chu, E., Peleato, B., Eckstein, J.: Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 3(1), 1–122 (2011)
Bro, R., De Jong, S.: A fast non-negativity-constrained least squares algorithm. J. Chemom. 11(5), 393–401 (1997)
Byrd, R.H., Lu, P., Nocedal, J., Zhu, C.: A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 16(5), 1190–1208 (1995)
Chen, D., Plemmons, R.J.: Nonnegativity constraints in numerical analysis. In: Symposium on the Birth of Numerical Analysis, pp. 109–140 (2009)
Craft, D., McQuaid, D., Wala, J., Chen, W., Salari, E., Bortfeld, T.: Multicriteria VMAT optimization. Med. Phys. 39(2), 686–696 (2012)
Dai, Y.H., Fletcher, R.: Projected Barzilai–Borwein methods for large-scale box-constrained quadratic programming. Numer. Math. 100(1), 21–47 (2005)
Dai, Y.H., Liao, L.Z.: R-linear convergence of the barzilai and borwein gradient method. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 22(1), 1–10 (2002)
Dax, A.: Successive refinement of large multicell models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22(5), 865–887 (1985)
Dax, A.: Line search acceleration of iterative methods. Linear Algebra Appl. 130, 43–63 (1990)
De Pierro, A., Lopes, J.: Accelerating iterative algorithms for symmetric linear complementarity problems. Int. J. Comput. Math. 50(1–2), 35–44 (1994)
Deasy, J.O., Blanco, A.I., Clark, V.H.: CERR: a computational environment for radiotherapy research. Med. Phys. 30(5), 979–985 (2003)
Deutsch, F.: Accelerating the convergence of the method of alternating projections via a line search: a brief survey. Stud. Comput. Math. 8, 203–217 (2001)
Eckstein, J.: Augmented Lagrangian and alternating direction methods for convex optimization: a tutorial and some illustrative computational results. RUTCOR Research Report RRR 32–2012, (2012)
Ehrgott, M., Güler, Ç., Hamacher, H.W., Shao, L.: Mathematical optimization in intensity modulated radiation therapy. 4OR 6(3), 199–262 (2008)
Fang, E.X., He, B., Liu, H., Yuan, X.: Generalized alternating direction method of multipliers: new theoretical insights and applications. Math. Program. Comput. 7(2), 149–187 (2015)
Fletcher, R.: Low storage methods for unconstrained optimization. Lect. Appl. Math. (AMS) 26, 165–179 (1990)
Fletcher, R.: On the Barzilai–Borwein method. In: Qi, L., Teo, K., Yang, X. (eds.) Optimization and Control with Applications, pp. 235–256. Springer, New York (2005)
Fortin, M., Glowinski, R.: Augmented Lagrangian Methods: Applications to the Numerical Solution of Boundary-Value Problems. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2000)
Fukushima, M.: Application of the alternating direction method of multipliers to separable convex programming problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 1(1), 93–111 (1992)
Glunt, W., Hayden, T., Raydan, M.: Molecular conformations from distance matrices. J. Comput. Chem. 14(1), 114–120 (1993)
Glunt, W., Hayden, T.L., Raydan, M.: Preconditioners for distance matrix algorithms. J. Comput. Chem. 15(2), 227–232 (1994)
He, B., Yang, H.: Some convergence properties of a method of multipliers for linearly constrained monotone variational inequalities. Oper. Res. Lett. 23(3), 151–161 (1998)
He, B., Yang, H., Wang, S.: Alternating direction method with self-adaptive penalty parameters for monotone variational inequalities. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 106(2), 337–356 (2000)
Kim, D., Sra, S., Dhillon, I.S.: A non-monotonic method for large-scale non-negative least squares. Optim. Methods Softw. 28(5), 1012–1039 (2013)
Kontogiorgis, S., Meyer, R.R.: A variable-penalty alternating directions method for convex optimization. Math. Program. 83(1–3), 29–53 (1998)
Lawson, C.L., Hanson, R.J.: Solving Least Squares Problems. SIAM, Philadelphia, (1995)
Luenberger, D.G., Ye, Y.: Linear and Nonlinear Programming, vol. 116. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Molina, B., Raydan, M.: Preconditioned Barzilai–Borwein method for the numerical solution of partial differential equations. Numer. Algorithms 13(1), 45–60 (1996)
Raydan, M.: On the Barzilai and Borwein choice of steplength for the gradient method. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 13(3), 321–326 (1993)
Raydan, M.: The Barzilai and Borwein gradient method for the large scale unconstrained minimization problem. SIAM J. Optim. 7(1), 26–33 (1997)
Shepard, D.M., Ferris, M.C., Olivera, G.H., Mackie, T.R.: Optimizing the delivery of radiation therapy to cancer patients. SIAM Rev. 41(4), 721–744 (1999)
Xing, L., Hamilton, R., Spelbring, D., Pelizzari, C., Chen, G., Boyer, A.: Fast iterative algorithms for three-dimensional inverse treatment planning. Med. Phys. 25(10), 1845–1849 (1998)
Xing, L., Li, R.: Inverse planning in the age of digital linacs: station parameter optimized radiation therapy (sport). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 489, 12065–12070 (2014)
Yang, Y., Xing, L.: Clinical knowledge-based inverse treatment planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 49(22), 5101 (2004)
Yu, C.X.: Intensity-modulated arc therapy with dynamic multileaf collimation: an alternative to tomotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 40(9), 1435 (1995)
Zarepisheh, M., Li, R., Ye, Y., Xing, L.: Simultaneous beam sampling and aperture shape optimization for sport. Med. Phys. 42(2), 1012–1022 (2015)
Zarepisheh, M., Long, T., Li, N., Tian, Z., Romeijn, H.E., Jia, X., Jiang, S.B.: A DVH-guided IMRT optimization algorithm for automatic treatment planning and adaptive radiotherapy replanning. Med. Phys. 41(6), 061,711 (2014)
Zarepisheh, M., Uribe-Sanchez, A.F., Li, N., Jia, X., Jiang, S.B.: A multicriteria framework with voxel-dependent parameters for radiotherapy treatment plan optimization. Med. Phys. 41(4), 041,705 (2014)
Zhang, J., Morini, B.: Solving regularized linear least-squares problems by the alternating direction method with applications to image restoration. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 40, 356–372 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by NIH (1R01 CA176553 and R01E0116777).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarepisheh, M., Xing, L. & Ye, Y. A computation study on an integrated alternating direction method of multipliers for large scale optimization. Optim Lett 12, 3–15 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1116-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-017-1116-y