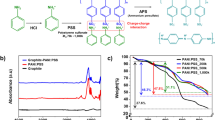
Abstract
In order to improve the charge transfer rate and Li+ diffusion coefficient of LiFePO4 (LFP), the material was surface treated with polyacrylonitrile/polyaniline (PAN/PANI). PAN/PANI polymers were synthesized by a self-assembly process, and LFP@PAN/PANI were prepared by a wet-coating process. LFP@PAN/PANI exhibits superior electrochemical performance compared to bare LFP, with a discharge capacity of 3088.97 mAh at low temperature and high rate condition (−20 °C, 26650-type cylindrical battery, 5 C rate), and a relatively high low-temperature discharge plateau (2.68 V). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) proves that the Li+ diffusion coefficient of LFP@PAN/PANI is an order of magnitude higher than that of bare LFP. The above performance is improved because the polar cyano group of the polymer can interact with the electrolyte and Li+, and the polyaniline makes the polymer have high conductivity. Therefore, the composite of the two polymers endows LFP with excellent Li+ activity and high conductivity.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang F, Sun Y, Yuan Y, Huang J, Hou M, Lu J (2021) Designing inorganic electrolytes for solid-state Li-ion batteries: a perspective of LGPS and garnet. Mater Today 50:418–441
Yang X, Peng C, Hou M, Zhang D, Yang B, Xue D, Lei Y, Liang F (2022) Rational design of electrolyte solvation structures for modulating 2e-/4e-transfer in sodium-air batteries. Adv Funct Mater 32(23):2201258
Yang X, Su F, Hou M, Zhang D, Dai Y, Liang F (2021) Plasma tailored reactive nitrogen species in MOF derived carbon materials for hybrid sodium-air batteries. Dalton Trans 50(20):7041–7047
Pomerantseva E, Bonaccorso F, Feng X, Cui Y, Gogotsi Y (2019) Energy storage: the future enabled by nanomaterials. Science 366(6468):eaan8285
Goodenough JB, Kim Y (2009) Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries. Chem Mater 22(3):587–603
Hannan MA, Hoque MM, Mohamed A, Ayob A (2017) Review of energy storage systems for electric vehicle applications: issues and challenges. Renew Sust Energ Rev 69:771–789
Wang JJ, Sun XL (2015) Olivine LiFePO4: the remaining challenges for future energy storage. Energy Environ Sci 8(4):1110–1138
Jung JCY, Sui PC, Zhang J (2021) A review of recycling spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials using hydrometallurgical treatments. J Energy Storage 35:102217
Wang Y, An N, Wen L, Wang L, Jiang X, Hou F, Yin Y, Liang J (2021) Recent progress on the recycling technology of Li-ion batteries. J Energy Chem 55:391–419
Wu XL, Guo YG, Su J, Xiong JW, Zhang YL, Wan LJ (2013) Carbon-nanotube-decorated nano-LiFePO4 @C cathode material with superior high-rate and low-temperature performances for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 3(9):1155–1160
Liao L, Zuo P, Ma Y, Chen X, An Y, Gao Y, Yin G (2012) Effects of temperature on charge/discharge behaviors of LiFePO4 cathode for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 60:269–273
Zhang WJ (2011) Structure and performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials: a review. J Power Sources 196(6):2962–2970
Yang CC, Jang JH, Jiang JR (2016) Study of electrochemical performances of lithium titanium oxide-coated LiFePO4/C cathode composite at low and high temperatures. Appl Energy 162:1419–1427
Alsamet MAMM, Burgaz E (2021) Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized LiFePO4 by using consecutive combination of sol-gel and hydrothermal methods. Electrochim Acta 367:137530
Zhang B, Wang S, Li Y, Sun P, Yang C, Wang D, Liu L (2020) Review: Phase transition mechanism and supercritical hydrothermal synthesis of nano lithium iron phosphate. Ceram Int 46(18):27922–27939
Ellis B, Kan WH, Makahnouk WRM, Nazar LF (2007) Synthesis of nanocrystals and morphology control of hydrothermally prepared LiFePO4. J Mater Chem 17(30):3248–3254
Stenina IA, Minakova PV, Kulova TL, Desyatov AV, Yaroslavtsev AB (2021) LiFePO4/carbon nanomaterial composites for cathodes of high-power lithium ion batteries. Inorg Mater 57(6):620–628
Wang H, Lai A, Huang D, Chu Y, Hu S, Pan Q, Liu Z, Zheng F, Huang Y, Li Q (2021) Y-F co-doping behavior of LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. New J Chem 45(12):5695–5703
Zhang Y, Shao Z, Zhang Y (2020) Preparation of Mo-doping LiFePO4/C by carbon reduction method. Mater Manuf Process 36(4):419–425
Gao Y, Xiong K, Zhang H, Zhu B (2021) Effect of Ru doping on the properties of LiFePO4/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Omega 6(22):14122–14129
Guo J, Liang C, Cao J, Jia S (2020) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of lithium iron phosphate/carbon composites based on controlling the secondary morphology of precursors. Int J Hydrog Energy 45(58):33016–33027
Cao J, Liu R, Guo H, Tian S, Zhang K, Ren X, Wang Y, Liang G (2022) High-temperature solid-phase synthesis of lithium iron phosphate using polyethylene glycol grafted carbon nanotubes as the carbon source for rate-type lithium-ion batteries. J Electroanal Chem 907:116049
Yao J, Wu F, Qiu X, Li N, Su Y (2011) Effect of CeO2-coating on the electrochemical performances of LiFePO4/C cathode material. Electrochim Acta 56(16):5587–5592
Wang H, Liu S, Huang Y (2014) Preparation and characterization of SnO2 and carbon co-coated LiFePO4 cathode materials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(4):3281–3284
Kim JK, Manuel J, Lee MH, Scheers J, Lim DH, Johansson P, Ahn JH, Matic A, Jacobsson P (2012) Towards flexible secondary lithium batteries: polypyrrole-LiFePO4 thin electrodes with polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem 22(30):15045–15049
Raj H, Sil A (2019) PEDOT:PSS coating on pristine and carbon coated LiFePO4 by one-step process: the study of electrochemical performance. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(14):13604–13616
Liu H, Wang GX, Wexler D, Wang JZ, Liu HK (2008) Electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 cathode material coated with ZrO2 nanolayer. Electrochem Commun 10(1):165–169
Chang HH, Chang CC, Su CY, Wu HC, Yang MH, Wu NL (2008) Effects of TiO2 coating on high-temperature cycle performance of LiFePO4-based lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 185(1):466–472
Avci E, Mazman M, Uzun D, Biçer E, Şener T (2013) High performance LiFePO4/CN cathode material promoted by polyaniline as carbon-nitrogen precursor. J Power Sources 240:328–337
Wurster V, Engel C, Graebe H, Ferber T, Jaegermann W, Hausbrand R (2019) Characterization of the interfaces in LiFePO4/PEO-LiTFSI composite cathodes and to the adjacent layers. J Electrochem Soc 166(3):A5410–A5420
Yi W, Sun C, Jiang W, Zhai Y, Gao Y (2022) Effect of different carbon and nitrogen co-doping on electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/CN. Mater Lett 324:132713
Bhadra S, Khastgir D, Singha NK, Lee JH (2009) Progress in preparation, processing and applications of polyaniline. Prog Polym Sci 34(8):783–810
Cao Y, Qi X, Hu K, Wang Y, Gan Z, Li Y, Hu G, Peng Z, Du K (2018) Conductive polymers encapsulation to enhance electrochemical performance of Ni-rich cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(21):18270–18280
Raghavan P, Zhao X, Shin C, Baek DH, Choi JW, Manuel J, Heo MY, Ahn JH, Nah C (2010) Preparation and electrochemical characterization of polymer electrolytes based on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)/polyacrylonitrile blend/composite membranes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 195(18):6088–6094
Tsao CH, Hsu CH, Kuo PL (2016) Ionic conducting and surface active binder of poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly(acrylonitrile) for high power lithium-ion battery. Electrochim Acta 196:41–47
Gong L, Nguyen MHT, Oh ES (2013) High polar polyacrylonitrile as a potential binder for negative electrodes in lithium ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 29:45–47
Chung SY, Kim YM, Kim JG, Kim YJ (2008) Multiphase transformation and Ostwald’s rule of stages during crystallization of a metal phosphate. Nat Phys 5(1):68–73
Xia Y, Lu Y (2009) Conductive polymers/polyacrylonitrile composite fibers: fabrication and properties. Polym Compos 31(2):340–346
Karbownik I, Rac O, Fiedot M, Suchorska Woźniak P, Teterycz H (2015) In situ preparation of silver-polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite fibres. Eur Polym J 69:385–395
Mottaghitalab V, Spinks GM, Wallace GG (2005) The influence of carbon nanotubes on mechanical and electrical properties of polyaniline fibers. Synth Met 152(1-3):77–80
Karbownik I, Rac Rumijowska O, Fiedot Tobola M, Rybicki T, Teterycz H (2019) The preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile-polyaniline (PAN/PANI) fibers. Materials (Basel) 12(4):664
Shi P, Liu ZY, Zhang XQ, Chen X, Yao N, Xie J, Jin CB, Zhan YX, Ye G, Huang JQ, Ifan ELS, Maria Magdalena T, Zhang Q (2022) Polar interaction of polymer host–solvent enables stable solid electrolyte interphase in composite lithium metal anodes. Journal of Energy. Chemistry 64:172–178
Wang Y, Zhang D, Chang C, Deng L, Huang K (2014) Controllable growth of LiFePO4 microplates of (010) and (001) lattice planes for Li ion batteries: a case of the growth manner on the Li ion diffusion coefficient and electrochemical performance. Mater Chem Phys 148(3):933–939
Chen J, Whittingham M (2006) Hydrothermal synthesis of lithium iron phosphate. Electrochem Commun 8(5):855–858
Gao Y (2019) Enhanced high-rate and low-temperature electrochemical properties of LiFePO4/polypyrrole cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Int J Electrochem Sci 14(4):3408–3417
Liu XY, Peng HJ, Zhang Q, Huang JQ, Liu XF, Wang L, He X, Zhu W, Wei F (2013) Hierarchical carbon nanotube/carbon black scaffolds as short- and long-range electron pathways with superior Li-ion storage performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2(2):200–206
Liu W, Zhong X, Han J, Qin W, Liu T, Zhao C, Chang Z (2018) Kinetic study and pyrolysis behaviors of spent LiFePO4 batteries. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(1):1289–1299
Zhao X, Liu B, Yang J, Hou J, Wang Y, Zhu Y (2020) Synthesizing LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 with microsized peanut-like structure for enhanced electrochemical properties of lithium ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 832:154464
Abraham K, M. (1990) Li+-conductive solid polymer electrolytes with liquid-like conductivity. J Electrochem Soc 137(5):1657–1658
Kanagaraj AB, Chaturvedi P, Alkindi TS, Susantyoko RA, An BH, Patole SP, Shanmugam K, AlMheiri S, AlDahmani S, AlFadaq H, Choi DS (2018) Mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of LiFePO4/MWCNTs composite electrodes. Mater Lett 230:57–60
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Ministry of Science and Technology major special projects (Grant number: SQ2020YFF0400789) for the financial support to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Guo, H., Gu, H. et al. Influence of PAN/PANI polymer on low-temperature rate performance of LiFePO4. Ionics 29, 2175–2189 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-04983-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-04983-3