Abstract
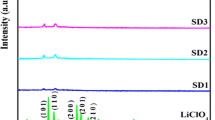
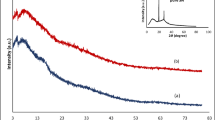
In this paper, we report the effects of two different type of salts which are magnesium trifluoromethanesulfonate (MgTf2) and magnesium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (Mg(TFSI)2) on ionic conductivity studies, transference number measurements, and electrochemical properties of gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) systems. Both systems used poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) (PVdC-co-AN) as the host polymer with the incorporation of plastic crystal succinonitrile (SN) and plasticizer ethylene carbonate (EC) in the ratio of (1:1). The system containing Mg(TFSI)2 exhibits higher in ionic conductivity of ~ (10−7–10−6) S cm−1 compared to the system containing MgTf2 of ~ (10−8–10−7) S cm−1. The conductivity temperature dependence studies of both GPE systems seem to obey the VTF relation. The ionic transference numbers were found to be > 0.9 for all GPEs while the highest cationic transference numbers obtained were 0.56 and 0.59 for MgTf2 system and Mg(TFSI)2 system, respectively. In linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) studies, wider electrochemical stability window was observed for the GPE containing Mg(TFSI)2 than that containing MgTf2 while cyclic voltammetry (CV) confirmed the conduction of Mg2+ ions in the GPEs. The structural and complex formations of the GPEs were confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis and both systems are shown to be amorphous in nature. The Mg/GPE/MgMn2O4 cells were assembled by using the most optimum GPE film from both systems and their charge-discharge performance was studied.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon J-M, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Pandey GP, Hashmi SA (2009) Experimental investigations of an ionic-liquid-based, magnesium ion conducting, polymer gel electrolyte. J Power Sources 187:627–634
Asmara SN, Kufian MZ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2011) Preparation and characterization of magnesium ion gel polymer electrolytes for application in electrical double layer capacitors. Electrochim Acta 57:91–97
Oh J, Ko J, Kim D (2004) Preparation and characterization of gel polymer electrolytes for solid state magnesium batteries. Electrochim Acta 50:903–906
Saha P, Kanchan M, Velikokhatnyi OI (2014) Progress in materials science rechargeable magnesium battery: current status and key challenges for the future. Prog Mater Sci 66:1–86
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2000) Solid-state Mg/MnO2cell employing a gel polymer electrolyte of magnesium triflate. J Power Sources 91:157–160
Saikia D, Wu HY, Pan YC, Lin CP, Huang KP, Chen KN, Fey GTK, Kao HM (2011) Highly conductive and electrochemically stable plasticized blend polymer electrolytes based on PVdF-HFP and triblock copolymer PPG-PEG-PPG diamine for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources 196:2826–2834
Raghavan P, Choi JW, Ahn JH, Cheruvally G, Chauhan GS, Ahn HJ, Nah C (2008) Novel electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-in situ SiO2 composite membrane-based polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 184:437–443
Raghavan P, Zhao X, Kim J et al (2008) Ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes based on electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) with nano-sized ceramic fillers. Electrochim Acta 54:228–234
Yang C-M, Kim H-S, Na B-K, Kum KS, Cho BW (2006) Gel-type polymer electrolytes with different types of ceramic fillers and lithium salts for lithium-ion polymer batteries. J Power Sources 156:574–580
Fan L, Wang X, Long F (2009) All-solid-state polymer electrolyte with plastic crystal materials for rechargeable lithium-ion battery. J Power Sources 189:775–778
Yoshimoto N, Yakushiji S, Ishikawa M, Morita M (2003) Rechargeable magnesium batteries with polymeric gel electrolytes containing magnesium salts. Electrochim Acta 48:2317–2322
Wang J, Song S, Gao S, Muchakayala R, Liu R, Ma Q (2017) Mg-ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte membranes containing biodegradable chitosan: preparation, structural, electrical and electrochemical properties. Polym Test 62:278–286
Manjuladevi R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Mangalam R, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly (vinyl alcohol) - poly (acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 308:90–100
Alarco P-J, Abu-Lebdeh Y, Abouimrane A, Armand M (2004) The plastic-crystalline phase of succinonitrile as a universal matrix for solid-state ionic conductors. Nat Mater 3:476–481
Taib NU, Hayati N (2014) Plastic crystal–solid biopolymer electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Memb Sci 468:149–154
Pistoia G, De Rossi M, Scrosati B (1970) Study of the behavior of ethylene carbonate as a nonaqueous battery solvent. J Electrochem Soc 117:500
Hambali D, Zainuddin Z, Osman Z (2016) Characteristics of novel plastic crystal gel polymer electrolytes based on PVdC-co-AN. Ionics 23:285–294
Evans J, Vincent CA, Bruce PG (1987) Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 28:2324–2328
Lee DK, Allcock HR (2010) The effects of cations and anions on the ionic conductivity of poly [bis (2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethoxy) phosphazene] doped with lithium and magnesium salts of trifluoromethanesulfonate and bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imidate. Solid State Ionics 181:1721–1726
Pradhan DK, Samantaray BK, Choudhary RNP et al (2007) Effect of plasticizer on structural and electrical properties of nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 2:861–871
Fernández-Sánchez C, McNeil CJ, Rawson K (2005) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy studies of polymer degradation: application to biosensor development. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 24:37–48
Osman Z, Samin SM, Othman L, Md Isa KB (2012) Ionic transport in PMMA-NaCF3SO3 gel polymer electrolyte. Adv Mater Res 545:259–263
Marzantowicz M, Dygas JR, Krok F, Tomaszewska A, Florjańczyk Z, Zygadło-Monikowska E, Lapienis G (2009) Star-branched poly(ethylene oxide) LiN(CF3SO2)2: a promising polymer electrolyte. J Power Sources 194:51–57
He D, Kim DW, Park JS, Cho SY, Kang Y (2013) Electrochemical properties of semi-interpenetrating polymer network solid polymer electrolytes based on multi-armed oligo(ethyleneoxy) phosphate. J Power Sources 244:170–176
Jayaraman R, Vickraman P, Subramanian NMV, Justin AS (2016) A.C. impedance, XRD, DSC, FTIR studies on PbTiO3 dispersoid pristine PVdF-co-HFP and PEMA blended PVdF-co-HFP microcomposite electrolytes. J Non-Cryst Solids 435:27–32
Echeverri M, Kim N, Kyu T (2012) Ionic conductivity in relation to ternary phase diagram of poly(ethylene oxide), succinonitrile, and lithium bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide blends. Macromolecules 45:6068–6077
Lascaud S, Perrier M, Vallee A, Besner S, Prud'homme J, Armand M (1994) Phase diagrams and conductivity behavior of poly(ethylene oxide)-molten salt rubbery electrolytes. Macromolecules 27:7469–7477
Rajendran S, Mahendran O, Kannan R (2002) Ionic conductivity studies in composite solid polymer electrolytes based on methylmethacrylate. J Phys Chem Solids 63:303–307
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2000) Effect of plasticizers on magnesium-poly (ethyleneoxide) polymer electrolyte. J Electron Chem 495:42–50
Pradeepa P, Edwin S, Sowmya G et al (2016) Optimization of hybrid polymer electrolytes with the effect of lithium salt concentration in PEO/PVdF-HFP blends. Mater Sci Eng B 205:6–17
Ratner MA, Shriver DF (1988) Ion transport in solvent-free polymers. Chem Rev 88:109–124
Piszcz M, Zhang H, Marczewski M, Żukowska GZ, Lemańska K, Sukiennik M, Siekierski M (2017) Vibrational spectroscopic studies combined with viscosity analysis and VTF calculation for hybrid polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 303:78–88
Kumar R, Rhee H (2012) Effect of succinonitrile on electrical, structural, optical, and thermal properties of [poly(ethylene oxide)-succinonitrile]/LiI–I2 redox-couple solid polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 76:159–164
Zhou Y, Xiang W, Chen S, Fang S, Zhou X, Zhang J, Lin Y (2009) Influences of poly(ether urethane) introduction on poly(ethylene oxide) based polymer electrolyte for solvent-free dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 54:6645–6650
Kalaignan GP, Kang MS, Kang YS (2006) Effects of compositions on properties of PEO-KI-I2 salts polymer electrolytes for DSSC. Solid State Ionics 177:1091–1097
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2009) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with nanosized magnesium oxide. J Power Sources 190:563–572
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2002) Poly (methylmethacrylate)—magnesium triflate gel polymer electrolyte for solid state magnesium battery application. Electrochim Acta 47:1013–1022
Zhou DY, Wang GZ, Li WS, Li GL, Tan CL, Rao MM, Liao YH (2008) Preparation and performances of porous polyacrylonitrile-methyl methacrylate membrane for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 184:477–480
Lee K-H, Lee Y-G, Park J-K, Seung D-Y (2000) Effect of silica on the electrochemical characteristics of the plasticized polymer electrolytes based on the P(AN-co-MMA) copolymer. Solid State Ionics 133:257–263
Kumar D, Hashmi S a. (2010) Ion transport and ion-filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195:5101–5108
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2011) Performance studies on composite gel polymer electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium battery application. J Phys Chem Solids 72:1408–1413
Kuo H-H, Chen W-C, Wen T-C, Gopalan A (2002) A novel composite gel polymer electrolyte for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Power Sources 110:27–33
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia and University of Malaya for the scholarship and grants, PG038-2015A, PG093-2015A, and FP044-2017A awarded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hambali, D., Zainol, N.H., Othman, L. et al. Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) (PVdC-co-AN): a comparative study between magnesium trifluoromethanesulfonate (MgTf2) and magnesium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (Mg(TFSI)2). Ionics 25, 1187–1198 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2666-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2666-4