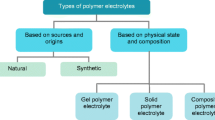
Abstract
An attempt has been made to synthesize a polymer electrolyte based on biopolymer pectin with ammonium thiocyanate (NH4SCN) salt by solution casting technique. Amorphous/crystalline nature of the polymer electrolyte has been studied by X-ray diffraction technique. The complexation between polymer and salt has been confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. A shift in glass transition temperature of the pectin: NH4SCN electrolytes have been observed from the differential scanning calorimetry thermograms. Ionic conductivity of the electrolytes was measured through impedance spectroscopic technique. The frequency and temperature dependence of ionic conductivity has been studied. The highest conductivity of 1.5 × 10−3 S cm−1 was observed for 40 mol% pectin: 60 mol% NH4SCN sample. Transference number measurement was carried out to confirm the nature of the charge transport species in the polymer electrolyte. Electrochemical stability of the highest conducting sample was studied by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV). The value is found to be 3.69 V. Using highest proton-conducting membrane, a proton battery has been constructed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001 (18pp)
Pratap R, Singh B, Chandra S (2006) Polymeric rechargeable solid state proton battery. J Power Sources 161:702–706
Peighambardoust SJ, Rowshanzamir S, Amjadi M (2010) Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int J Hydrogen Energ 35:9349–9384
Gao H, Lian K (2011) High rate all-solid electrochemical capacitors using proton conducting polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 196:8855–8857
Thakur VK, Ding G, Ma J, Lee PS, Xuehong L (2012) Hybrid materials and polymer electrolytes for electrochromic device applications. Adv Mater 24:4071–4096
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A (1998) PEO-based composite polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 110:1–14
Tipton AL, Lonergan MC, Ratner MA, Shriver DF, Wong TTY, Han K (1994) Conductivity and dielectric constant of PPO and PPO-based solid electrolytes from Dc to 6 GHz. J Phys Chem 98:4148–4154
Hema M, Selvasekarapandian S, Arunkumar D, Sakunthala A, Nithya H (2009) FTIR, XRD and ac impedance spectroscopic study on PVA based polymer electrolyte doped with NH4X (X = Cl, Br, I). J Non-Cryst Solids 355:84–90
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Karthikeyan S, Nithya V, Ramya CS, Prabu M (2012) Structural, vibrational, thermal, and conductivity studies on proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone). Ionics 18:91–99
Nithya S, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Inbavalli D, Sikkinthar S, Sanjeeviraja C (2014) AC impedance studies on proton-conducting PAN: NH4SCN polymer electrolytes. Ionics 20:1391–1398
Chiellini E, Solaro R (1996) Biodegradable polymeric materials. Adv Mater 8(4):305–313
Tan W, Majid SR, Khiar ASA, Arof AK (2006) Ionic conductivity of chitosan membranes and application for electrochemical devices. Polym Adv Technol 17:523–527
Ahmad Khiar AS, Arof AK (2010) Conductivity studies of starch based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16:123–129
Johari NA, Kudin TIT, Ali AMM, Winie T, Yahya MZA (2009) Studies on cellulose acetate-based gel polymer electrolytes for proton batteries. Mater Res Innov 13(3):232–234
Raphael E, Avellaneda CO, Manzolli B, Pawlicka A (2009) Agar-based films for application as polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 55:1455–1459
Mishra RK, Datt M, Banthia AK, Majeed ABA (2012) Development of novel pectin based membranes as proton conducting material. Int J Plast Technol 16(1):80–88
Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S, Boopathi G, Aristatil G, Arun A, Madeswaran S (2016) Proton-conducting I-Carrageenan-based biopolymer electrolyte for fuel cell applications. Ionics 23:2775–2780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1901-0
Mohamed SN, Johari NA, Ali AMM, Harun MK, Yahya MZA (2008) Electrochemical studies on epoxidised natural rubber-based gel polymer electrolytes for lithium–air cells. J Power Sources 183:351–354
May CD (1990) Industrial pectins: sources, production and applications. Carbohydr Polym 12:79–99
Mishra RK, Datt M, Pal K, Banthia AK (2008) Preparation and characterization of amidated pectin based hydrogels for drug delivery system. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:2275–2280
Nimisha KV, Mohan A, Janardanan C (2016) Pectin–Tin(IV) molybdosilicate: an ecofriendly cationic exchanger and its potential for sorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Resource-Efficient Technologies 2:S153–S164
Assaf SM, Abul-Haija YM, Fares MM (2011) Versatile pectin grafted poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) modulated targeted drug release. J Macromol Sci, Pure Appl Chem 48:493–502
Mishra RK, Banthia AK, Majeed ABA (2012) Pectin based formulations for biomedical applications: a review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 5(4):1–7
Mishra RK, Anis A, Mondal S, Dutt M, Banthia AK (2009) Preparation and characterization of amidated pectin based polymer electrolyte membranes. Chin J Polym Sci 27(5):639–646
Andrade JR, Raphael E, Pawlicka A (2009) Plasticized pectin based gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 54:6479–6483
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Sornalatha M, Sujithra KS, Monisha S (2016) Proton-conducting biopolymer electrolytes based on pectin doped with NH4X (X=Cl, Br). Ionics 23:2799–2808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1852-5
Zulkefli FN, Navaratnam S, Ahmad AH (2016) Proton conducting biopolymer electrolytes based on starch incorporated with ammonium thiocyanate. Adv Mater Res 1112:275–278
Shukur M F, Azmi M S, Zawawi S M M, Majid N A, Illias H A, Kadir M F Z (2013) Conductivity studies of biopolymer electrolytes based on chitosan incorporated with NH4Br. Phys Scr T157 014049: (5pp)
Chung C, Lee M, Choe EK (2004) Characterization of cotton fabric scouring by FT-IR ATR spectroscopy. Carbohydr Polym 58:417–420
Singthong J, Cui SW, Ningsanond S, Douglas Goff H (2004) Structural characterization, degree of esterification and some gelling properties of Krueo Ma Noy (Cissampelos pareira) pectin. Carbohydr Polym 58:391–400
Zhang H, Xuan X, Wang J, Wamg H (2003) FT-IR investigation of ion association in PEO–MSCN (M=Na, K) polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 164:73–79
Leones R, Mbs B, Sentanin F, Cesarino I, Pawlicka A, Ass C,MmS (2014) Pectin-based polymer electrolytes with Ir (III) complexes. Mole Crys Liq Crys 604:117–125
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37(8):1371–1376
Kadir MFZ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2010) Plasticized chitosan–PVA blend polymer electrolyte based proton battery. Electrochim Acta 55:1475–1482
Chaichi M, Hashemi M, Badii F, Mohammadi A (2017) Preparation and characterization of a novel bionanocompostie edible film based on pectin and crystalline nanocellulose. Carbohy Polym 157:167–175
Premalatha M, Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Selvalakshmi S (2016) Characterization of blend polymer PVA-PVP complexed with ammonium thiocyanate. Ionics 22:1299–1310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1672-7
Karthikeyan S, Sikkanthar S, Selvasekarapandian S, Arunkumar D, Nithya H, Kawamura J (2016) Structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium hexaflurophosphate polymer electrolyte system. J Polym Res 23:51–60
Perumal P, Christopher Selvin P, Selvasekarapandian S (2018) Characterization of biopolymer pectin with lithium chloride and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics Doi/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2507-5
Ramesh S, Arof AK (2001) Ionic conductivity studies of plasticized poly (vinyl chloride) polymer electrolytes. Mater Sci Eng B 85:11–15
Macdonald J R (1987) Impedance spectroscopy. Johnwiley & sons, Newyork. 12–23
Prabu M, Selvasekarapandian S, Kulkarni AR, Hirankumar G, Sakunthala A (2010) Ionic conductivity studies on LiSmO2 by impedance spectroscopy. Ionics 16:317–321
Boukamp BA (1986) Solid State Ionics 20: 301
Premalatha M, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Selvalakshmi S, Vinoth Pandi D (2017) Tamarind seed polysaccharide (TSP)-based Li-ion conducting membranes. Ionics 23:2677–2684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-1989-x
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Milton Franklin Benial A, Premalatha M (2016) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate and lithium nitrate for advanced electrochemical devices. Ionics 23:2697–2706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1886-8
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Milton Franklin Benial A,. Aristatilc G, Manic N, Premalatha M, Vinoth Pandi D (2016) Investigation of bio polymer electrolyte based on celluloseacetate-ammonium nitrate for potential use in electrochemical devices Carbohydrate Polymers 157: 38–47
Jonscher AK (1977) The universal dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Dutta P, Biswas S (2002) Characterization of plasticized solid polymer electrolyte by XRD and AC impedance methods. Mater Res Bull 37:193–200
Amstrong RD, Dickinson T, Wills PM (1974) The A.C. impedance of powdered and sintered solid ionic conductors. J Electroanal Chem 53(3):389–405
Hodge IM, Ingram MD, West AR (1976) Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of polycrystalline solid electrolytes. J Electroanal Chem 74:125–143
Adachi K, Urakawa O (2002) Dielectric study of concentration fluctuations in concentrated polymer solutions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 307–310 & 667–670
MacCallum JR, Vincent CA (1989) Polymer electrolyte review-2. Elsevier, London
Raja V, Sharma AK, Narasimha Rao VVR (2004) Impedance spectroscopic and dielectric analysis of PMMA-CO-P4VPNO polymer films. Mater Lett 58(26):3242–3247
Schmidt-Rohr K, Kulik AS, Beckham HW, Ohlemacher A, Pawelzik U, Boeffel C, Spiess HW (1994) Molecular nature of the beta. Relaxation in poly (methyl methacrylate) investigated by multidimensional NMR. Macromolecules 27:4733–4745
Cassu SN, Felisberti MI (1999) Poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (vinylpyrrolidone) blends: 2. Study of relaxations by dynamic mechanical analysis. Polymer 40:4845–4851
Manjuladevi R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Mangalam R, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinyl alcohol)- poly (acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 308:90–100
Wagner JB, Wagner C (1957) Electrical conductivity measurements on cuprous halides. J Chem Phys 26:1597–1601
Winnie T, Arof AK (2006) Transport properties of hexanoyl chitosan-based gel electrolyte. Ionics 12:149–152
Subba Reddy CV, Sharma AD, Narasimha Rao VVR (2003) Conductivity and discharge characteristics of polyblend (PVP+PVA+KIO3) electrolyte. J Power Sources 114:338–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muthukrishnan, M., Shanthi, C., Selvasekarapandian, S. et al. Synthesis and characterization of pectin-based biopolymer electrolyte for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25, 203–214 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2568-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2568-5