Abstract
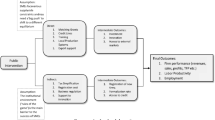
Drawing on the extant research on offshoring in international business, entrepreneurship and strategy literature, we develop a model of offshoring of service activities by small and medium-sized firms (SMEs). Using the intellectual capital perspective as a theoretical framework, we hypothesize that the unique configuration of human, social and organizational capital of SMEs will be linked to offshoring of services to international providers. Using data from 119 SMEs in three industry sectors in the US and South Korea, we empirically test the hypothesized relationships and find at least some support for our predictions. Specifically, while we found no country-specific differences in offshoring, SMEs with more social capital and less human capital are more likely to engage in offshoring of service activities. However, the relationship between human and organizational capital and offshoring of such activities is contingent on the size of the SMEs. Implications for theory and practice are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, B. S., & Eshima, Y. (2013). The influence of firm age and intangible resources on the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation and firm growth among Japanese SMEs. Journal of Business Venturing, 28(3), 413–429.
Barney, J. B. (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of Management, 17(1), 99–120.
Becker, G. S. (1964). Human capital theory. NY: Columbia.
Becker, G. S. (1993). Human capital: A theoretical and practical analysis with special reference to education. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Beugre, C. D., & Acar, W. (2008). Offshoring and cross-border interorganizational relationships: A justice model. Decision Sciences, 39(3), 445–468.
Bhalla, A., Sodhi, M. S., & Son, B. (2008). Is more IT offshoring better? An exploratory study of western companies offshoring to South East Asia. Journal of Operations Management, 26(2), 322–335.
Boehe, D. (2013). Collaborate at home to win abroad: How does access to local network resources influence export behavior? Journal of Small Business Management, 51(2), 167–182.
Brouthers, K. D., Brouthers, L. E., & Werner, S. (2008). Resource-based advantages in an international context. Journal of Management, 34(2), 189–217.
Bunyaratavej, K., Doh, J., Hahn, E. D., Lewin, A. Y., & Massini, S. (2011). Conceptual issues in services offshoring research: A multidisciplinary review. Group and Organization Management, 36(1), 70–102.
Burt, R. S. (1992). Structural holes: The social structure of competition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Caniato, F., Elia, S., Luzzini, D., Piscitello, L., & Ronchi, S. (2015). Location drivers, governance model and performance in service offshoring. International Journal of Production Economics, 163, 189–199.
Cardon, M. S., & Stevens, C. E. (2004). Managing human resources in small organizations: What do we know? Human Resource Management Review, 14(3), 295–323.
Cha, H. S., Pingry, D. E., & Thatcher, M. E. (2008). Managing the knowledge supply chain: An organizational learning model of information technology offshore outsourcing. MIS Quarterly, 32(2), 281–306.
Chollet, B., Géraudel, M., & Mothe, C. (2014). Generating business referrals for SMEs: The contingent value of CEOs social capital. Journal of Small Business Management, 52(1), 79–101.
CIA World Factbook. (2016). https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook. Accessed 24 Sept 2016.
Ciravegna, L., Lopez, L., & Kundu, S. (2014). Country of origin and network effects on internationalization: A comparative study of SMEs from an emerging and developed economy. Journal of Business Research, 67(5), 916–923.
Coleman, S. (2007). The role of human and financial capital in the profitability and growth of women-owned small firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 45(3), 303–319.
Contractor, F., Kumar, V., Kundu, S., & Pedersen, T. (2010). Reconceptualizing the firm in a world of outsourcing and offshoring: The organizational and geographical relocation of high-value company functions. Journal of Management Studies, 47(8), 1417–1433.
Contractor, F., & Mudambi, S. (2008). The influence of human capital investment on the exports of services and goods: An analysis of the top 25 services outsourcing countries. Management International Review, 48(4), 433–445.
Cooper, A. C., Gimeno-Gascon, F. J., & Woo, C. Y. (1994). Initial human and financial capital as predictors of new venture performance. Journal of Business Venturing, 9(5), 371–395.
Cortina, J. M. (1993). What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. Journal of Applied Psychology, 78(1), 98–104.
Crinò, R. (2009). Offshoring, multinationals and labour market: A review of the empirical literature. Journal of Economic Surveys, 23(2), 197–249.
Cronbach, L. J., & Shavelson, R. J. (2004). My current thoughts on coefficient alpha and successor procedures. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64(3), 391–418.
Desouza, K. C., & Awazu, Y. (2006). Knowledge management at SMEs: Five peculiarities. Journal of Knowledge Management, 10(1), 32–43.
Dhanaraj, C., & Beamish, P. W. (2003). A resource-based approach to the study of export performance. Journal of Small Business Management, 41(3), 242–261.
Di Gregorio, D., Musteen, M., & Thomas, D. E. (2008). International new ventures: The cross-border nexus of individuals and opportunities. Journal of World Business, 43(2), 186–196.
Di Gregorio, D., Musteen, M., & Thomas, D. E. (2009). Offshoring as a source of international competitive advantage for SMEs. Journal of International Business Studies, 40(6), 969–988.
Doh, J. P. (2005). Offshore outsourcing: Implications for international business and strategic management theory and practice. Journal of Management Studies, 42(3), 695–704.
Dossani, R., & Kenney, M. (2007). The next wave of globalization: Relocating service provision to India. World Development, 35(5), 772–791.
Edwards, T., Delbridge, R., & Munday, M. (2005). Understanding innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises: A process manifest. Technovation, 25(10), 1119–1120.
Ernst, D. (2005). Complexity and internationalisation of innovation: Why is chip design moving to Asia? International Journal of Innovation Management, 9(1), 47–73.
Erramilli, M. K., Agarwal, S., & Dev, C. S. (2002). Choice between non-equity entry modes: An organizational capability perspective. Journal of International Business Studies, 33(2), 223–242.
Fariñas, J. C., López, A., & Martín-Marcos, A. (2014). Assessing the impact of domestic outsourcing and offshoring on productivity at the firm level. Applied Economics, 46(15), 1814–1828.
Farrell, D., Laboissiere, M. A., & Rosenfeld, J. (2006). Sizing the emerging global labor market: Rational behavior from both companies and countries can help it work more efficiently. Academy of Management Perspectives, 20(4), 23–34.
Friedman, T. L. (2005). The world is flat: A brief history of the twenty-first century. New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Gemser, G., Brand, M., & Sorge, A. (2012). Internationalisation strategies of technology-driven small-and medium-sized enterprises. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 24(3), 311–326.
George, G., Wiklund, J., & Zahra, S. A. (2005). Ownership and the internationalization of small firms. Journal of Management, 31(2), 210–233.
Gilley, K., McGee, J. E., & Rasheed, A. A. (2004). Perceived environmental dynamism and managerial risk aversion as antecedents of manufacturing outsourcing: The moderating effects of firm maturity. Journal of Small Business Management, 42(2), 117–133.
Golovko, E., & Valentini, G. (2014). Selective learning-by-exporting: Firm size and product versus process innovation. Global Strategy Journal, 4(3), 161–180.
Graf, M., & Mudambi, S. M. (2005). The outsourcing of IT enabled business processes: A conceptual model of the location decision. Journal of International Management, 11(2), 253–268.
Gupta, M., & Cawthon, G. (1996). Managerial implication of flexible manufacturing for small/medium enterprises. International Journal of Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurships and Technology Development, 16(2), 77–83.
Harisson, A. E., & McMillan, M. S. (2006). Dispelling some myths about offshoring. Academy of Management Perspectives, 20(4), 6–22.
Hatch, N. W., & Dyer, J. H. (2004). Human capital and learning as a source of sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management Journal, 25(12), 1155–1178.
He, X., Brouthers, K. D., & Filatotchev, I. (2013). Resource-based and institutional perspectives on export channel selection and export performance. Journal of Management, 39(1), 27–47.
Herrmann, P., & Datta, D. K. (2005). Relationships between top management team characteristics and international diversification: An empirical investigation. British Journal of Management, 16(1), 69–78.
Hitt, M. A., Biermant, L., Shimizu, K., & Kochhar, R. (2001). Direct and moderating effects of human capital on strategy and performance in professional service firms: A resource-based perspective. Academy of Management Journal, 44(1), 13–28.
Hoetker, G. (2007). The use of logit and probit models in strategic management research: Critical issues. Strategic Management Journal, 28(4), 331–343.
Hoogendoorn, B., Guerra, D., & Zwan, P. (2015). What drives environmental practices of SMEs? Small Business Economics, 44(4), 759–781.
Howells, J. R. (1990). The internationalization of R&D and the development of global research network. Regional Studies, 24(6), 495–512.
Howells, J. R. (1995). Going global: The use of ICT networks in research and development. Research Policy, 24(2), 169–184.
International Labor Comparisons (2012). https://www.bls.gov/fls/country.htm. Accessed 23 Jan 2016.
Itami, H., & Roehl, T. (1987). Mobilizing intangible assets. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Jain, N. K., Kundu, S. K., & Niederman, F. A. (2008). Offshoring propensity in information technology services: A firm and country level analysis. Management International Review, 48(4), 447–461.
Jarillo, J. C. (1989). Entrepreneurship and growth: The strategic use of external resources. Journal of Business Venturing, 4(2), 133–148.
Jensen, P. D. Ø. (2009). A learning perspective on the offshoring of advanced services. Journal of International Management, 15(2), 181–193.
Jensen, P. D. Ø., & Pedersen, T. (2010). The globalization of high-value activities: Why do firms offshore advanced tasks? In J. Pla-Barber & J. Alegre (Eds.), Reshaping the boundaries of the firm in an era of global interdependence, Progress in International Business Research (Vol. 5, pp. 3–27). Cheltenham: Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Jones, O., & Macpherson, A. (2006). Inter-organizational learning and strategic renewal in SMEs: Extending the 4I framework. Long Range Planning, 39(2), 155–175.
Josefy, M., Kuban, S., Ireland, R. D., & Hitt, M. A. (2015). All things great and small: Organizational size, boundaries of the firm, and a changing environment. Academy of Management Annals, 9(1), 715–802.
Kang, S., & Snell, S. A. (2009). Intellectual capital architectures and ambidextrous learning: A framework for human resource management. Journal of Management Studies, 46(1), 65–92.
Kedia, B. L., & Lahiri, S. (2007). International outsourcing of services: A partnership model. Journal of International Management, 13(1), 22–37.
Kedia, B. L., & Mukherjee, D. (2009). Understanding offshoring: A research framework based on disintegration, location and externalization advantages. Journal of World Business, 44(3), 250–261.
Kenney, M., & Dossani, R. (2005). Offshoring and the future of U.S. engineering: An overview. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.134.4075&rep=rep1&type=pd. Accessed 30 June 2016.
Kim, B.-S., Kang, M. S., & Min, J. H. (2013). Evaluating transaction soundness between large enterprises and SMEs: A model for quantitative win-win growth index. Korea Business Review, 17(1), 225–242.
Kinkel, S., & Maloca, S. (2009). Drivers and antecedents of manufacturing offshoring and backshoring—a German perspective. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management, 15(3), 154–165.
Klaas, B. S. (2003). Professional employer organizations and their role in small and medium enterprises: The impact of HR outsourcing. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 28(1), 43–61.
Kotha, S., Rindova, V. P., & Rothaermel, F. T. (2001). Assets and actions: Firm-specific factors in the internationalization of US Internet firms. Journal of International Business Studies, 32(4), 769–791.
Krishnaswamy, C. R., & Pashley, M. M. (2007). Attitudes towards offshore outsourcing and U.S. bank risks. Paper presented at the Duke CIBER Research Conference and Workshop on Offshoring, Cary, NC.
Lahiri, S., Kedia, B. L., & Mukherjee, D. (2012). The impact of management capability on the resource–performance linkage: Examining Indian outsourcing providers. Journal of World Business, 47(1), 145–155.
Leonidou, L. C., & Katsikeas, C. S. (1996). The export development process: An integrative review of empirical models. Journal of International Business Studies, 27(3), 517–551.
Levina, N., & Su, N. (2008). Global multisourcing strategy: The emergence of a supplier portfolio in services offshoring. Decision Sciences, 39(3), 541–570.
Levine, L. (2012). Offshoring (or offshore outsourcing) and job loss among U.S. workers. Congressional Research Service Report for Congress. http://digitalcommons.ilr.cornell.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1991&context=key_workplace. Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Lewin, A. Y., Massini, S., & Peeters, C. (2009). Why are companies offshoring innovation? The emerging global race for talent. Journal of International Business Studies, 40(6), 901–925.
Lewin, A. Y., & Peeters, C. (2006). Offshoring work: Business hype or the onset of fundamental transformation? Long Range Planning, 39(3), 221–239.
Li, C., Lin, C., & Huang, H. (2014). Top management team social capital, exploration-based innovation, and exploitation-based innovation in SMEs. Technology Analysis and Strategic Management, 26(1), 69–85.
Lu, J. W., & Beamish, P. W. (2001). The internationalization and performance of SMEs. Strategic Management Journal, 22(6–7), 565–586.
Madrid-Guijarro, A., Garcia, D., & Van Auken, H. (2009). Barriers to innovation among Spanish manufacturing SMEs. Journal of Small Business Management, 47(4), 465–488.
Manning, S., Lewin, A. Y., & Schuerch, M. (2011). The stability of offshore outsourcing relationships: The role of relation specificity and client control. Management International Review, 51(3), 381–406.
Manning, S., Massini, S., & Lewin, A. Y. (2008). A dynamic perspective on next-generation offshoring: The global sourcing of science and engineering talent. Academy of Management Perspectives, 22(3), 35–54.
Martinez-Noya, A., & García-Canal, E. (2011). Technological capabilities and the decision to outsource/outsource offshore R&D services. International Business Review, 20(3), 264–277.
McEvily, B., & Zaheer, A. (1999). Bridging ties: A source of firm heterogeneity in competitive capabilities. Strategic Management Journal, 20(12), 1133–1156.
Mihalache, O. R., Jansen, J. J., Van Den Bosch, F. A., & Volberda, H. W. (2012). Offshoring and firm innovation: The moderating role of top management team attributes. Strategic Management Journal, 33(13), 1480–1498.
Miller, D. (1983). The correlates of entrepreneurship in three types of firms. Management Science, 29(7), 770–791.
Mukherjee, D., Gaur, A. S., & Datta, A. (2013). Creating value through offshore outsourcing: An integrative framework. Journal of International Management, 19(4), 377–389.
Mukherjee, D., & Kedia, B. L. (2012). Offshoring and MNC strategy. In H. Merchant & A. Verbeke (Eds.), Handbook of research on international strategic management. Cheltenham: Elgar Publishing.
Musteen, M. (2016). Behavioral factors in offshoring decisions: A qualitative analysis. Journal of Business Research, 69(9), 3439–3446.
Musteen, M., & Ahsan, M. (2013). Beyond cost: The role of intellectual capital in offshoring and innovation in young firms. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 37(2), 421–434.
Musteen, M., Datta, D. K., & Butts, M. M. (2014). Do international networks and foreign market knowledge facilitate SME internationalization? Evidence from the Czech Republic. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 38(4), 749–774.
Musteen, M., Francis, J., & Datta, D. K. (2010). The influence of international networks on internationalization speed and performance: A study of Czech SMEs. Journal of World Business, 45(3), 197–205.
Mutinelli, M., & Piscitello, L. (1998). The entry mode choice of MNEs: An evolutionary approach. Research Policy, 27(5), 491–506.
Nahapiet, J., & Ghoshal, S. (1998). Social capital, intellectual capital, and the organizational advantage. Academy of Management Review, 23(2), 242–266.
Narula, R. (2004). R&D collaboration by SMEs: New opportunities and limitations in the face of globalisation. Technovation, 24(2), 153–161.
Neirotti, P., Paolucci, E., & Raguseo, E. (2013). Is it all about size? Comparing organisational and environmental antecedents of IT assimilation in small and medium-sized enterprises. International Journal of Technology Management, 61(1), 82–108.
Newbert, S. L. (2007). Empirical research on the resource-based view of the firm: An assessment and suggestions for future research. Strategic Management Journal, 28(2), 121–146.
Nieto, M. J., & Rodríguez, A. (2011). Offshoring of R&D: Looking abroad to improve innovation performance. Journal of International Business Studies, 42(3), 345–361.
Nunnally, J. C. (1978). Psychometric theory (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Park, D., & Krishnan, H. A. (2001). Supplier selection practices among small firms in the United States: Testing three models. Journal of Small Business Management, 39(3), 259–271.
Patibandla, M., & Petersen, B. (2002). Role of transnational corporations in the evolution of a high-tech industry: The case of India’s software industry. World Development, 30(9), 1561–1577.
Peeters, C., Dehon, C., & Garcia-Prieto, P. (2015). The attention stimulus of cultural differences in global services sourcing. Journal of International Business Studies, 46(2), 241–251.
Peeters, C., Massini, S., & Lewin, A. Y. (2014). Sources of variation in the efficiency of adopting management innovation: The role of absorptive capacity routines, managerial attention and organizational legitimacy. Organization Studies, 35(9), 1343–1371.
Peng, M. W. (2001). The resource-based view and international business. Journal of Management, 27(6), 803–829.
Podsakoff, P. M., & Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in organizational research: Problems and prospects. Journal of Management, 12(4), 531–544.
Prajogo, D., & McDermott, C. M. (2014). Antecedents of service innovation in SMEs: Comparing the effects of external and internal factors. Journal of Small Business Management, 52(3), 521–540.
Preisendörfer, P., & Voss, T. (1990). Organizational mortality of small firms: The effects of entrepreneurial age and human capital. Organization Studies, 11(1), 107–129.
Rilla, N., & Squicciarini, M. (2011). R&D (re) location and offshore outsourcing: A management perspective. International Journal of Management Reviews, 13(4), 393–413.
Rodríguez, A., & Nieto, M. J. (2016). Does R&D offshoring lead to SME growth? Different governance modes and the mediating role of innovation. Strategic Management Journal, 37(8), 1734–1753.
Rothwell, R. (1991). External networking and innovation in small and medium-sized manufacturing firms in Europe. Technovation, 11(2), 93–112.
Roza, M., Van den Bosch, F. A., & Volberda, H. W. (2011). Offshoring strategy: Motives, functions, locations, and governance modes of small, medium-sized and large firms. International Business Review, 20(3), 314–323.
Rungtusanatham, M., Salvador, F., Forza, C., & Choi, T. Y. (2003). Supply-chain linkages and operational performance—a resource-based-view perspective. International Journal of Operations and Production Management, 23(9), 1084–1099.
Sambharya, R. B. (1996). Foreign experience of top management teams and international diversification strategies of U.S. multinational corporations. Strategic Management Journal, 17(9), 739–746.
Saxenian, A. (2002). From brain drain to brain circulation: Transnational communities and regional upgrading in India and China. Studies in Comparative International Development, 40(2), 35–61.
Schmeisser, B. (2013). A systematic review of literature on offshoring of value chain activities. Journal of International Management, 19(4), 390–406.
Schroeder, R. G., Bates, K. A., & Junttila, M. A. (2002). A resource-based view of manufacturing strategy and the relationship to manufacturing performance. Strategic Management Journal, 23(2), 105–117.
Seghers, A., Manigart, S., & Vanacker, T. (2012). The impact of human and social capital on entrepreneurs knowledge of finance alternatives. Journal of Small Business Management, 50(1), 63–86.
Smith, D. (2006). Offshoring: Political myths and economic reality. The World Economy, 29(3), 249–256.
Stephan, M., & Silvia, M. (2008). A dynamic perspective on next-generation offshoring: The global sourcing of science and engineering talent. Academy of Management Perspectives, 22(3), 35–54.
Stringfellow, A., Teagarden, M. B., & Nie, W. (2008). Invisible costs in offshoring services work. Journal of Operations Management, 26(2), 164–179.
Subramaniam, M., & Youndt, M. A. (2005). The influence of intellectual capital on the types of innovative capabilities. Academy of Management Journal, 48(3), 450–463.
Sydler, R., Haefliger, S., & Pruksa, R. (2014). Measuring intellectual capital with financial figures: Can we predict firm profitability? European Management Journal, 32(2), 244–259.
Tagoe, N., Nyarko, E., & Anuwa-Amarh, E. (2005). Financial challenges facing urban SMEs under financial sector liberalization in Ghana. Journal of Small Business Management, 43(3), 331–343.
Teece, D. J. (2014). A dynamic capabilities-based entrepreneurial theory of the multinational enterprise. Journal of International Business Studies, 45(1), 8–37.
Teirlinck, P., & Spithoven, A. (2013). Research collaboration and R&D outsourcing: Different R&D personnel requirements in SMEs. Technovation, 33(4), 142–153.
Terziovski, M. (2010). Innovation practice and its performance implications in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the manufacturing sector: A resource-based view. Strategic Management Journal, 31(8), 892–902.
Tiwana, A., & Keil, M. (2007). Does peripheral knowledge complement control? An empirical test in technology outsourcing alliances. Strategic Management Journal, 28(6), 623–634.
Tomczyk, D., Lee, J., & Winslow, E. (2013). Entrepreneurs personal values, compensation, and high growth firm performance. Journal of Small Business Management, 51(1), 66–82.
Van Beveren, J., & Thomson, H. (2002). The use of electronic commerce by SMEs in Victoria, Australia. Journal of Small Business Management, 40(3), 250–253.
van de Vrande, V., de Jong, J. P. J., Vanhaverbeke, W., & de Rochemont, M. (2009). Open innovation in SMEs: Trends, motives and management challenges. Technovation, 29(6), 423–437.
Vecina, M., Sanz, N., Santiago, L., & Gomez, M. (2012). Offshoring components and their effect on employment: Firms deciding about how and where. Applied Economics, 44(8), 1009–1020.
Vivek, S. D., Richey, R. G., & Dalela, V. (2009). A longitudinal examination of partnership governance in offshoring: A moving target. Journal of World Business, 44(1), 16–30.
Weigelt, C., & Sarkar, M. (2012). Performance implications of outsourcing for technological innovations: Managing the efficiency and adaptability trade-off. Strategic Management Journal, 33(2), 189–216.
Welsh, J. A., & White, J. F. (1981). A small business is not a little big business. Harvard Business Review, 59(4), 18–32.
Werner, W. (2009). Service offshoring. Intereconomics, 44(2), 96–104.
Wernerfelt, B. (2013). Small forces and large firms: Foundations of the RBV. Strategic Management Journal, 34(6), 635–643.
Westhead, P., Wright, M., & Ucbasaran, D. (2001). The internationalization of new and small firms: A resource-based view. Journal of Business Venturing, 16(4), 333–358.
Wiener, M., Vogel, B., & Amberg, M. (2010). Information systems offshoring—a literature review and analysis. Information Systems, 27(1), 455–492.
Wolff, J. A., & Pett, T. L. (2000). Internationalization of small firms: An examination of export competitive patterns, firm size, and export performance. Journal of Small Business Management, 38(2), 34–47.
Yli-Renko, H., Autio, E., & Sapienza, H. J. (2001). Social capital, knowledge acquisition, and knowledge exploitation in young technology-based firms. Strategic Management Journal, 22(6), 587–613.
Yli-Renko, H., Autio, E., & Tontti, V. (2002). Social capital, knowledge, and the international growth of technology-based new firms. International Business Review, 11(3), 279–304.
Yoon, S. C. (2014). The impacts of offshoring on productivity: Evidence in Korean manufacturing. Journal of International Trade and Insurance, 15(1), 199–219.
Youndt, M. A., Subramanian, M., & Snell, S. A. (2004). Intellectual capital profiles: An examination of investments and returns. Journal of Management Studies, 41(2), 335–361.
Youngdahl, W. E., Ramaswamy, K., & Dash, K. C. (2010). Service offshoring: The evolution of offshore operations. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 30(8), 798–820.
Zahra, S. A., Hayton, J. C., & Salvato, C. (2004). Entrepreneurship in family vs. non-family firms: A resource-based analysis of the effect of organizational culture. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 28(4), 363–381.
Zhao, H., & Hsu, C. C. (2007). Social ties and foreign market entry: An empirical inquiry. Management International Review, 47(6), 815–844.
Acknowledgements
This research was in part funded by the San Diego State University Center for International Business Education and Research (CIBER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Survey Items
Appendix: Survey Items
Intellectual capital
(1 = strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree)
Human capital (adapted from Subramaniam and Youndt 2005)
-
Our employees are highly skilled
-
Our employees are widely considered the best in our industry
-
Our employees are creative and bright
-
Our employees develop new ideas and knowledge
Social capital (adapted from Yli-Renko et al. 2002)
-
We rely extensively on personal contacts to find new business opportunities
-
We work closely with our business partners (e.g. suppliers, vendors, customers)
-
We rely on external contacts and networking in growing our business
Organizational capital (adapted from Subramaniam and Youndt 2005)
Our organization uses patents and licenses as a way to store knowledge
Much of our organization’s knowledge is contained in manuals, databases, etc.
Our organization embeds much of its knowledge and information in structures, systems, and processes
Entrepreneurial orientation (adapted from Miller 1983)
(1-strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree)
-
Our firm shows a great deal of tolerance for high-risk projects.
-
Our firm uses only ‘tried and true’ procedures, systems, or methods.
-
Our firm rewards taking calculated risks.
-
Our firm challenges, rather than responds to its major competitors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musteen, M., Ahsan, M. & Park, T. SMEs, Intellectual Capital, and Offshoring of Service Activities: An Empirical Investigation. Manag Int Rev 57, 603–630 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11575-017-0315-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11575-017-0315-1