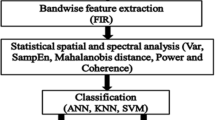
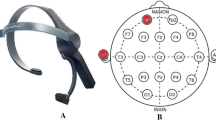
Abstract
Our ability to measure time is vital for daily life, technology use, and even mental health; however, separating pure time perception from other mental processes (like emotions) is a research challenge requiring precise tests to isolate and understand brain activity solely related to time estimation. To address this challenge, we designed an experiment utilizing hypnosis alongside electroencephalography (EEG) to assess differences in time estimation, namely underestimation and overestimation. Hypnotic induction is designed to reduce awareness and meta-awareness, facilitating a detachment from the immediate environment. This reduced information processing load minimizes the need for elaborate internal thought during hypnosis, further simplifying the cognitive landscape. To predict time perception based on brain activity during extended durations (5 min), we employed artificial intelligence techniques. Utilizing Support Vector Machines (SVMs) with both radial basis function (RBF) and polynomial kernels, we assessed their effectiveness in classifying time perception-related brain patterns. We evaluated various feature combinations and different algorithms to identify the most accurate configuration. Our analysis revealed an impressive 80.9% classification accuracy for time perception detection using the RBF kernel, demonstrating the potential of AI in decoding this complex cognitive function.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Abbasi SF, Ahmad J, Tahir A, Awais M, Chen C, Irfan M, Siddiqa HA, Waqas AB, Long X, Yin B (2020) EEG-based neonatal sleep-wake classification using multilayer perceptron neural network. IEEE Access 8:183025–183034
Albayrak M (2009) The detection of an epileptiform activity on EEG signals by using data mining process. Technol Appl Sci 4(1):1–12
Allman MJ, Meck WH (2012) Pathophysiological distortions in time perception and timed performance. Brain 135(3):656–677
Alotaiby T, Abd El-Samie FE, Alshebeili SA, Ahmad I (2015) A review of channel selection algorithms for EEG signal processing. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2015(1):1–21
Arnal LH (2012) Predicting “when” using the motor system’s beta-band oscillations. Front Hum Neurosci 6:225
Arnal LH, Doelling KB, Poeppel D (2015) Delta–beta coupled oscillations underlie temporal prediction accuracy. Cereb Cortex 25(9):3077–3085
Basgol H, Ayhan I, Ugur E (2021) Time perception: A review on psychological, computational and robotic models. IEEE Trans. Cognit. Dev. Syst. 14(2):301–315
Bashivan P, Rish I, Yeasin M, Codella N (2015) Learning representations from EEG with deep recurrent-convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06448
Bayazit O, Üngür G (2018) Neuroelectric responses of sportsmen and sedentaries under cognitive stress. Cogn Neurodyn 12(3):295–301
Behzadifard B, Sabaghypour S, Farkhondeh Tale Navi F, Nazari MA (2022) Training the brain to time: the effect of neurofeedback of SMR–Beta1 rhythm on time perception in healthy adults. Exp Brain Res 240(7–8):2027–2038
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29(4):1165–1188
Block RA, Gruber RP (2014) Time perception, attention, and memory: a selective review. Acta Physiol (oxf) 149:129–133
Born M (1962) Einstein's theory of relativity. Courier Corporation
Bortoletto M, Cook A, Cunnington R (2011) Motor timing and the preparation for sequential actions. Brain Cogn 75(2):196–204
Carver CS (2004) Self-regulation of action and affect. In: Baumeister RF, Vohs KD (eds) Handbook of self-regulation: research, regulation, theory, and applications. The Guillford Press, p 39
Chen Y, Zhang Z, Guang X, Guo X, Yuan H, Zhang T (2007) Attentional modulation of time perception: an ERP study. Acta Psychol Sin 39(06):1002
Chen Y, Huang X, Luo Y, Peng C, Liu C (2010) Differences in the neural basis of automatic auditory and visual time perception: ERP evidence from an across-modal delayed response oddball task. Brain Res 1325:100–111
Cirelli LK, Bosnyak D, Manning FC, Spinelli C, Marie C, Fujioka T, Ghahremani A, Trainor LJ (2014) Beat-induced fluctuations in auditory cortical beta-band activity: using EEG to measure age-related changes. Front Psychol 5:742
Cooper LF, Erickson MH (2004) Time distortion in hypnosis. An Experimental and Clinical Investigation
Correa Á, Lupiáñez J, Tudela P (2005) Attentional preparation based on temporal expectancy modulates processing at the perceptual level. Psychon Bull Rev 12(2):328–334
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press
da Silva K, Curvina M, Araújo S, Rocha K, Marinho FV, Magalhães FE, Teixeira S, Bastos V, Ribeiro P, Silva-Júnior F (2021) Male practitioners of physical activity present lower absolute power of beta band in time perception test. Neurosci Lett 764:136210
Daud S, Sudirman R (2015) Butterworth bandpass and stationary wavelet transform filter comparison for electroencephalography signal. In: 2015 6th international conference on intelligent systems, modelling and simulation
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21
Dini H, Ghassemi F, Sendi M (2020) Investigation of brain functional networks in children suffering from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brain Topogr 33(6):733–750
Droit-Volet S, Brunot S, Niedenthal P (2004) BRIEF REPORT Perception of the duration of emotional events. Cogn Emot 18(6):849–858
Eagleman DM (2008) Human time perception and its illusions. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18(2):131–136
Effron DA, Niedenthal PM, Gil S, Droit-Volet S (2006) Embodied temporal perception of emotion. Emotion 6(1):1
Forgas JP, Baumeister RF, Tice DM (2009) The psychology of self-regulation: An introductory review. Psychology of Self-Regulation: Cognitive, Affective, and Motivational Processes 11:1–17
Fraisse P (1978) Time and rhythm perception. In Perceptual coding (pp. 203–254). Elsevier
Frank A (2011) About time: Cosmology and culture at the twilight of the big bang. Simon and Schuster
Fujioka T, Trainor LJ, Large EW, Ross B (2012) Internalized timing of isochronous sounds is represented in neuromagnetic beta oscillations. J Neurosci 32(5):1791–1802
Gabard-Durnam LJ, Mendez Leal AS, Wilkinson CL, Levin AR (2018) The Harvard Automated Processing Pipeline for Electroencephalography (HAPPE): standardized processing software for developmental and high-artifact data. Front Neurosci 12:97
Gallistel CR, Gibbon J (2000) Time, rate, and conditioning. Psychol Rev 107(2):289
Gardner AB, Krieger AM, Vachtsevanos G, Litt B, Kaelbing LP (2006) One-class novelty detection for seizure analysis from intracranial EEG. J Mach Learn Res 7(6):1025–1044
Ghaderi AH, Moradkhani S, Haghighatfard A, Akrami F, Khayyer Z, Balcı F (2018) Time estimation and beta segregation: an EEG study and graph theoretical approach. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0195380
Gibbon J, Church RM, Meck WH (1984) Scalar timing in memory. Ann N Y Acad Sci 423(1):52–77
Gil S, Niedenthal PM, Droit-Volet S (2007) Anger and time perception in children. Emotion 7(1):219
Gräber S, Hertrich I, Daum I, Spieker S, Ackermann H (2002) Speech perception deficits in Parkinson’s disease: underestimation of time intervals compromises identification of durational phonetic contrasts. Brain Lang 82(1):65–74
Graf P, Grondin S (2006) Time perception and time-based prospective memory. Timing the future: The case for a time-based prospective memory, 1–24
Grondin S (2010) Timing and time perception: A review of recent behavioral and neuroscience findings and theoretical directions. Atten Percept Psychophys 72(3):561–582
Gulberti A, Moll CKE, Hamel W, Buhmann C, Koeppen J, Boelmans K, Zittel S, Gerloff C, Westphal M, Schneider T (2015) Predictive timing functions of cortical beta oscillations are impaired in Parkinson’s disease and influenced by L-DOPA and deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus. NeuroImage Clin 9:436–449
Halsband U, Mueller S, Hinterberger T, Strickner S (2009) Plasticity changes in the brain in hypnosis and meditation. Contemp Hypn 26(4):194–215
Han J, Dong F, Xu Y (2009) Entropy feature extraction on flow pattern of gas/liquid two-phase flow based on cross-section measurement. J Phys Conf Ser 147:012041
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman JH, Friedman JH (2009) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer
Heap M, Aravind K (2002) Hartland’s medical and dental hypnosis.. London: Churchill Livingston. In: Harcourt Health Sciences
Hicks RE, Miller GW, Gaes G, Bierman K (1977) Concurrent processing demands and the experience of time-in-passing. Am J Psychol 90(3):431–446
Hildenbrand AK, Nicholls EG, Aggarwal R, Brody-Bizar E, Daly BP (2014) Symptom Checklist-90-Revised (SCL-90-R). Encycloped Clin Psychol. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118625392.wbecp495
Hjorth B (1970) EEG analysis based on time domain properties. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 29(3):306–310
Hosseini Houripasand M, Sabaghypour S, Farkhondeh Tale Navi F, Nazari MA (2023) Time distortions induced by high-arousing emotional compared to low-arousing neutral faces: an event-related potential study. Psychol Res 87:1836–1847
Huang X, Altahat S, Tran D, Sharma D (2012) Human identification with electroencephalogram (EEG) signal processing. In: 2012 International symposium on communications and information technologies (ISCIT)
Im S-H, Varma S (2018) Distorted time perception during flow as revealed by an attention-demanding cognitive task. Creat Res J 30(3):295–304
Ivry RB, Schlerf JE (2008) Dedicated and intrinsic models of time perception. Trends Cogn Sci 12(7):273–280
Jenke R, Peer A, Buss M (2014) Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 5(3):327–339
Jo H-G, Hinterberger T, Wittmann M, Schmidt S (2015) Do meditators have higher awareness of their intentions to act? Cortex 65:149–158
Kaiser JF (1990) On a simple algorithm to calculate the'energy'of a signal. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing
Katz MJ (1988) Fractals and the analysis of waveforms. Comput Biol Med 18(3):145–156
Klug M, Gramann K (2021) Identifying key factors for improving ICA-based decomposition of EEG data in mobile and stationary experiments. Eur J Neurosci 54(12):8406–8420
Kononowicz TW, van Rijn H (2015) Single trial beta oscillations index time estimation. Neuropsychologia 75:381–389
Kononowicz TW, Van Rijn H, Meck WH (2018) Timing and time perception: A critical review of neural timing signatures before, during, and after the to-be-timed interval. Stevens’ Handbook Exp Psychol Cognitive Neurosci 1:1–38
Kulashekhar S, Pekkola J, Palva JM, Palva S (2016) The role of cortical beta oscillations in time estimation. Hum Brain Mapp 37(9):3262–3281
Lawson RA, Yarnall AJ, Duncan GW, Breen DP, Khoo TK, Williams-Gray CH, Barker RA, Collerton D, Taylor J-P, Burn DJ (2016) Cognitive decline and quality of life in incident Parkinson’s disease: the role of attention. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 27:47–53
Lin Y-W, Zhou Y, Faghri F, Shaw MJ, Campbell RH (2019) Analysis and prediction of unplanned intensive care unit readmission using recurrent neural networks with long short-term memory. PLoS ONE 14(7):e0218942
Liu Z (2011) A method of SVM with normalization in intrusion detection. Procedia Environ Sci 11:256–262
Marcano-Cedeño A, Quintanilla-Domínguez J, Cortina-Januchs M, Andina D (2010) Feature selection using sequential forward selection and classification applying artificial metaplasticity neural network. In: IECON 2010–36th annual conference on IEEE industrial electronics society
Maris E, Oostenveld R (2007) Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG-and MEG-data. J Neurosci Methods 164(1):177–190
Matell MS, Meck WH (2000) Neuropsychological mechanisms of interval timing behavior. BioEssays 22(1):94–103
Memar P, Faradji F (2017) A novel multi-class EEG-based sleep stage classification system. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 26(1):84–95
Michielli N, Acharya UR, Molinari F (2019) Cascaded LSTM recurrent neural network for automated sleep stage classification using single-channel EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 106:71–81
Mitrani L, Shekerdjiiski S, Gourevitch A, Yanev S (1977) Identification of short time intervals under LSD25 and mescaline. Act Nerv Super 19(2):103–104
Morillon B, Kell CA, Giraud A-L (2009) Three stages and four neural systems in time estimation. J Neurosci 29(47):14803–14811
Muller T, Nobre AC (2014) Perceiving the passage of time: neural possibilities. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1326(1):60–71
Naish PL (2001) Hypnotic time perception: busy beaver or tardy timekeeper? Contemp Hypn 18(2):87–99
Nasiri JA, Naghibzadeh M, Yazdi HS, Naghibzadeh B (2009) ECG arrhythmia classification with support vector machines and genetic algorithm. In: 2009 Third UKSim European Symposium on Computer Modeling and Simulation
Newton I (1962) Sir Isaac Newton’s mathematical principles of natural philosophy and his system of the world. Univ of California Press
Ng KK, Penney TB (2014) Probing interval timing with scalp-recorded electroencephalography (EEG). Neurobiol Interval Tim 829:187–207
Nobre AC, Rohenkohl G, Stokes MG (2012) Nervous anticipation: Top-down biasing across space and time
Noulhiane M, Mella N, Samson S, Ragot R, Pouthas V (2007) How emotional auditory stimuli modulate time perception. Emotion 7(4):697
Ocak H (2013) A medical decision support system based on support vector machines and the genetic algorithm for the evaluation of fetal well-being. J Med Syst 37(2):1–9
Ogden RS, Dobbins C, Slade K, McIntyre J, Fairclough S (2022) The psychophysiological mechanisms of real-world time experience. Sci Rep 12(1):1–10
O’Hanlon JF, McGrath JJ, McCauley ME (1974) Body temperature and temporal acuity. J Exp Psychol 102(5):788
Owusu E, Zhan Y, Mao QR (2014) An SVM-AdaBoost facial expression recognition system. Appl Intell 40(3):536–545
Pahuja S, Veer K (2022) Recent approaches on classification and feature extraction of EEG signal: a review. Robotica 40(1):77–101
Patle A, Chouhan DS (2013) SVM kernel functions for classification. In: 2013 International Conference on Advances in Technology and Engineering (ICATE)
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238
Petrosian A (1995). Kolmogorov complexity of finite sequences and recognition of different preictal EEG patterns. In: Proceedings eighth IEEE symposium on computer-based medical systems
Pisner DA, Schnyer DM (2020) Support vector machine. In Machine learning (pp 101–121). Elsevier
Ramezani M, Feizi-Derakhshi M-R, Balafar M-A, Asgari-Chenaghlu M, Feizi-Derakhshi A-R, Nikzad-Khasmakhi N, Ranjbar-Khadivi M, Jahanbakhsh-Nagadeh Z, Zafarani-Moattar E, Akan T (2022) Automatic personality prediction: an enhanced method using ensemble modeling. Neural Comput Appl 34(21):18369–18389
Ronconi L, Vitale A, Federici A, Pini E, Molteni M, Casartelli L (2020) Altered neural oscillations and connectivity in the beta band underlie detail-oriented visual processing in autism. NeuroImage Clinical 28:102484
Rudd M, Vohs KD, Aaker J (2012) Awe expands people’s perception of time, alters decision making, and enhances well-being. Psychol Sci 23(10):1130–1136
Ryu V, Kook S, Lee SJ, Ha K, Cho H-S (2015) Effects of emotional stimuli on time perception in manic and euthymic patients with bipolar disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 56:39–45
Scherer S, Kane J, Gobl C, Schwenker F (2013) Investigating fuzzy-input fuzzy-output support vector machines for robust voice quality classification. Comput Speech Lang 27(1):263–287
Schirmer A (2004) Timing speech: a review of lesion and neuroimaging findings. Cogn Brain Res 21(2):269–287
Schirmer A (2011) How emotions change time. Front Integr Neurosci 5:58
Şen B, Peker M, Çavuşoğlu A, Çelebi FV (2014) A comparative study on classification of sleep stage based on EEG signals using feature selection and classification algorithms. J Med Syst 38(3):1–21
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal 27(3):379–423
Sharma A, Amarnath M, Kankar P (2016) Feature extraction and fault severity classification in ball bearings. J Vib Control 22(1):176–192
Sitaula C, Basnet A, Mainali A, Shahi TB (2021) Deep learning-based methods for sentiment analysis on Nepali COVID-19-related tweets. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2158184
Sohn M-H, Carlson RA (2003) Implicit temporal tuning of working memory strategy during cognitive skill acquisition. Am J Psychol 116(2):239–256
Stafford RQ, MacDonald BA, Jayawardena C, Wegner DM, Broadbent E (2014) Does the robot have a mind? Mind perception and attitudes towards robots predict use of an eldercare robot. Int J Soc Robot 6(1):17–32
Tagawa M, Takei Y, Kato Y, Suto T, Hironaga N, Ohki T, Takahashi Y, Fujihara K, Sakurai N, Ujita K (2022) Disrupted local beta band networks in schizophrenia revealed through graph analysis: A magnetoencephalography study. Psychiat Clin Neurosci 76(7):309–320
Terhune DB, Croucher M, Marcusson-Clavertz D, Macdonald JS (2014) Time contracts when the mind wanders. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 126:125–126
Tipples J (2008) Negative emotionality influences the effects of emotion on time perception. Emotion 8(1):127
Treisman M (1963) Temporal discrimination and the indifference interval: Implications for a model of the" internal clock". Psychol Monogr Gen Appl 77(13):1
Treisman M, Faulkner A, Naish PL, Brogan D (1990) The internal clock: Evidence for a temporal oscillator underlying time perception with some estimates of its characteristic frequency. Perception 19(6):705–742
Valizadeh A, Tass P (2023) Decoupling of interacting neuronal populations by time-shifted stimulation through spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Plos Comput Biol 19(2):1010853
Vapnik VN (1995). Constructing learning algorithms. In The nature of statistical learning theory (pp. 119–166). Springer
Vohs KD, Schmeichel BJ (2003) Self-regulation and extended now: Controlling the self alters the subjective experience of time. J Pers Soc Psychol 85(2):217
Wearden J (2016) The psychology of time perception. Springer
Weitzenhoffer AM, Hilgard ER (1962) Stanford hypnotic susceptibility scale, form C, vol 27. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, CA
Wickens CD (2012) Workload assessment and prediction. MANPRINT: an approach to systems integration, 257
Wiener M, Parikh A, Krakow A, Coslett H (2018) An intrinsic role of beta oscillations in memory for time estimation. Sci Rep 8(1):1–17
Wittmann M, van Wassenhove V (2009) The experience of time: neural mechanisms and the interplay of emotion, cognition and embodiment. R Soc London 364:1809–1813
Zakay D, Block RA (1997) Temporal cognition. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 6(1):12–16
Zhou J, Wang G, Liu J, Wu D, Xu W, Wang Z, Ye J, Xia M, Hu Y, Tian Y (2020) Automatic sleep stage classification with single channel EEG signal based on two-layer stacked ensemble model. IEEE Access 8:57283–57297
Funding
The present study was extracted from the Hoda Taghilou doctoral dissertation. She has not received any funding for her project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MAN conceptualized the study. HT, MAN, MR, and THN designed the study. HT recruited participants and recorded EEG. MR conducted all the hypnotic inductions and the assessments of hypnotic susceptibility. AV was the supervisor of machine learning. Hoda Taghilou wrote the first draft of the manuscript and analyzed the data in collaboration with MAN and AV. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study received ethics approval from the ethics committee of Tabriz University with the code IR.TABRIZU.REC.1399.070.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Taghilou, H., Rezaei, M., Valizadeh, A. et al. Predicting an EEG-Based hypnotic time estimation with non-linear kernels of support vector machine algorithm. Cogn Neurodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10088-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10088-y