Abstract
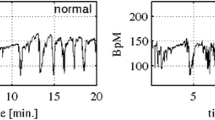
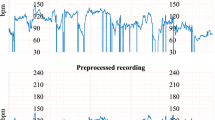
A new scheme was presented in this study for the evaluation of fetal well-being from the cardiotocogram (CTG) recordings using support vector machines (SVM) and the genetic algorithm (GA). CTG recordings consist of fetal heart rate (FHR) and the uterine contraction (UC) signals and are widely used by obstetricians for assessing fetal well-being. Features extracted from normal and pathological FHR and UC signals were used to construct an SVM based classifier. The GA was then used to find the optimal feature subset that maximizes the classification performance of the SVM based normal and pathological CTG classifier. An extensive clinical CTG data, classified by three expert obstetricians, was used to test the performance of the new scheme. It was demonstrated that the new scheme was able to predict the fetal state as normal or pathological with 99.3 % and 100 % accuracy, respectively. The results reveal that, the GA can be used to determine the critical features to be used in evaluating fetal well-being and consequently increase the classification performance. When compared to widely used ANN and ANFIS based methods, the proposed scheme performed considerably better.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacDonald, D., Grant, A., Sheridan-Pereira, M., Boylan, P., and Chalmers, I., The Dublin randomized controlled trial of intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 152:524–539, 1985.
Goddard, R., Electronic fetal monitoring is not necessary for low risk labours. Brit. Med. J. 322:1436–1437, 2001.
Rooth, G., Huch, A., and Huch, R., Guidelines for the use of fetal monitoring. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 25:159–167, 1987.
Bernardes, J., Costa-Pereira, A., Ayres-de-Campos, D., van-Geijn, H. P., and Pereira-Leite, L., Evaluation of interobserver agreement of cardiotocograms. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 57:33–37, 1997.
Palomaki, O., Luukkaala, T., Luoto, R., and Tuimala, R., Intrapartum cardiotocography - the dilemma of interpretational variation. J Perinat Med 34:298–302, 2006.
Jongsma, H. W., and Nijhuis, J. G., Classification of fetal and neonatal heart rate patterns in relation to behavioural states. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 21:293–299, 1986.
Georgoulas, G., Stylios, C. D., Nokas, G., and Groumpos, P. P., Classification of fetal heart rate during labour using hidden Markov models. Proc IEEE Int Joint Conf. Neural Netw. 3:2471–2474, 2004.
Signorini, M. G., de-Angelis, A., Magenes, G., Sassi, R., Arduini, D., and Cerutti, S., Classification of fetal pathologies through fuzzy inference systems based on a multiparametric analysis of fetal heart rate. Comput. Cardiol. 27:435–438, 2000.
Georgoulas, G., and Stylios, C. D., Predicting the risk of metabolic acidosis for newborns based on fetal heart rate signal classification using support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53:875–884, 2006.
Spilka, J., Chudacek, V., Koucky, M., Lhotska, L., Huptych, M., Janku, P., Georgoulas, G., and Stylios, C. D., Using nonlinear features for fetal heart rate classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 7:350–357, 2012.
Georgoulas, G., Stylios, C. D., and Groumpos, P. P., Feature extraction and classification of fetal heart rate using wavelet analysis and support vector machine. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 15:411–432, 2005.
Vaisman, S., Salem, S. Y., Holcberg, G., and Geva, A. B., Passive fetal monitoring by adaptive wavelet denoising method. Comput. Biol. Med. 42:171–179, 2012.
Cattani, C., Doubrovina, O., Rogosin, S., Voskresensky, S. L., and Zelianko, E., On the creation of a new diagnostic model for fetal well-being on the base of wavelet analysis of cardiotocograms. J. Med. Syst. 30:489–494, 2006.
Magenes, G., Signorini, M. G., and Arduini, D., Classification of cardiotocographic records by neural networks. Proc. IEEE-INNS-ENNS Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw. (IJCNN’00) 3:637–641, 2000.
Liszka-Hackzell, J. J., Categorization of fetal heart rate patterns using neural networks. J. Med. Syst. 25:269–276, 2001.
Magenes, G., Signorini, M.G., Sassi, R., Arduini, D., Multiparametric analysis of fetal heart rate: comparison of neural and statistical classifiers. Proceedings of Medicon 2001, Pula, Croatia, 360–363, (2001).
Ocak, H., and Ertunc, H. M., Prediction of fetal State from the cardiotocogram recordings using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. Neural Comput. Appl., 2012. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1110-3.
Shah, S., and Kusiak, A., Cancer gene search with data-mining and genetic algorithms. Comput. Biol. Med. 37:251–261, 2007.
Hassan, R., Nath, B., and Kirley, M., A fusion model of HMM, ANN and GA for stock market forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 33:171–180, 2007.
Yu, S. N., and Lee, M. Y., Bispectral analysis and genetic algorithm for congestive heart failure recognition based on heart rate variability. Comput. Biol. Med. 42:816–825, 2012.
Elveren, E., and Yumusak, N., Tuberculosis disease diagnosis using artificial neural network trained with genetic algorithm. J. Med. Syst. 35:329–332, 2011.
Kocer, S., and Canal, M. R., Classifying epilepsy diseases using artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm. J. Med. Syst. 35:489–498, 2011.
Vapnik, V., and Cortes, C., Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20:273–297, 1989.
Ubeyli, E. D., Multiclass support vector machines for diagnosis of erythemato-squamous diseases. Expert Syst. Appl. 35:1733–1740, 2008.
Sahin, D., Ubeyli, E. D., Ilbay, G., Sahin, M., and Yasar, A. B., Diagnosis of airway obstruction or restrictive spirometric patterns by multiclass support vector machines. J. Med. Syst. 34:967–973, 2010.
Abibullaev, B., and An, J., Decision support algorithm for diagnosis of ADHD using electroencephalograms. J. Med. Syst. 36:2675–2688, 2012.
Chen, H. L., Yang, B., Wang, G., Wang, S. J., Liu, J., and Liu, D. Y., Support vector machine based diagnostic system for breast cancer using swarm intelligence. J. Med. Syst. 36:2505–2519, 2012.
Goldberg, D. E., Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning. Addison-Wesley, 1989
Melanie, M., An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. MIT Press, 1996.
Holland, J., Genetic algorithms. Scientific American, 66–72, 1992.
Frank, A., Asuncion, A., UCI Machine Learning Repository. [http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml]. Irvine, CA: University of California, School of Information and Computer Science, 2000.
Ayres-de-Campos, D., Bernardes, J., Garrido, A., Marques-de-Sa, J., and Pereira-Leite, L., SisPorto 2.0: a program for automated analysis of cardiotocograms. J. Matern-Fetal Med 5:311–318, 2000.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ocak, H. A Medical Decision Support System Based on Support Vector Machines and the Genetic Algorithm for the Evaluation of Fetal Well-Being. J Med Syst 37, 9913 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9913-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-012-9913-4