Abstract
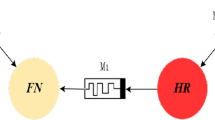
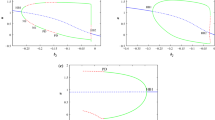
In this study, the hybrid conductance-based adaptive exponential integrate and fire (CadEx) neuron model is proposed to determine the effect of magnetic flux on conductance-based neurons. To begin with, bifurcation analysis is carried out in relation to the input current, resetting parameter, and adaptation time constant in order to comprehend dynamical transitions. We exemplify that the existence of period-1, period-2, and period-4 cycles depends on the magnitude of input current via period doubling and period halving bifurcations. Furthermore, the presence of chaotic behavior is discovered by varying the adaptation time constant via the period doubling route. Following that, we examine the network behavior of CadEx neurons and discover the presence of a variety of dynamical behaviors such as desynchronization, traveling chimera, traveling wave, imperfect chimera, and synchronization. The appearance of synchronization is especially noticeable when the magnitude of the magnetic flux coefficient or the strength of coupling strength is increased. As a result, achieving synchronization in CadEx is essential for neuron activity, which can aid in the realization of such behavior during many cognitive processes.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data generated during the current study will be made available at reasonable request.
References
Altan A, Karasu S (2020) Recognition of COVID-19 disease from X-ray images by hybrid model consisting of 2D curvelet transform, chaotic salp swarm algorithm and deep learning technique. Chaos Solitons Fractals 140:110071
Brette R, Gerstner W (2005) Adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire model as an effective description of neuronal activity. J Neurophysiol 94(5):3637–3642
Buonocore A, Caputo L, Pirozzi E, Carfora MF (2016) A leaky integrate-and-fire model with adaptation for the generation of a spike train. Math Biosci Eng 13(3):483
Cavallari S, Panzeri S, Mazzoni A (2014) Comparison of the dynamics of neural interactions between current-based and conductance-based integrate-and-fire recurrent networks. Front Neural Circuits 8:12
Ding S, Wang N, Bao H, Chen B, Wu H, Xu Q (2023) Memristor synapse-coupled piecewise-linear simplified Hopfield neural network: dynamics analysis and circuit implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166:112899
Feng J (2003) Computational neuroscience: a comprehensive approach. Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York
Gerster M, Berner R, Sawicki J, Zakharova A, Škoch A, Hlinka J, Lehnertz K, Schöll E (2020) FitzHugh–Nagumo oscillators on complex networks mimic epileptic-seizure-related synchronization phenomena. Chaos 30(12):123130
Górski T, Depannemaecker D, Destexhe A (2021) Conductance-based adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire model. Neural Comput 33(1):41–66
Ibrahim MM, Kamran MA, Mannan MMN, Jung IH, Kim S (2021) Lag synchronization of coupled time-delayed FitzHugh–Nagumo neural networks via feedback control. Sci Rep 11(1):1–15
Izhikevich EM (2003) Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(6):1569–1572
Jun M, Li-Jian Y, Ying W, Cai-Rong Z (2010) Spiral wave in small-world networks of Hodgkin–Huxley neurons. Commun Theor Phys 54(3):583
Kafraj MS, Parastesh F, Jafari S (2020) Firing patterns of an improved Izhikevich neuron model under the effect of electromagnetic induction and noise. Chaos Solitons Fractals 137:109782
Kanagaraj S, Durairaj P, Karthikeyan A, Rajagopal K (2022) Effect of propagation noise on the network dynamics of a flux coupled conductance-based neuron model. Eur Phys J Plus 137(11):1223
Kanagaraj S, Durairaj P, Prince AA, Rajagopal K (2022) Local and network dynamics of a non-integer order resistor–capacitor shunted Josephson junction oscillators. Electronics 11(18):2812
Ladenbauer J, Augustin M, Shiau L, Obermayer K (2012) Impact of adaptation currents on synchronization of coupled exponential integrate-and-fire neurons. PLoS Comput Biol 8(4):e1002478
Li Z, Tang W, Zhang B, Yang R, Miao X (2023) Emerging memristive neurons for neuromorphic computing and sensing. Sci Technol Adv Mater 24(1):2188878
Li Z, Zhou H, Wang M, Ma M (2021) Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn 104(2):1455–1473
Liu YH, Wang XJ (2001) Spike-frequency adaptation of a generalized leaky integrate-and-fire model neuron. J Comput Neurosci 10(1):25–45
Lu L, Yang L, Zhan X, Jia Y (2020) Cluster synchronization and firing rate oscillation induced by time delay in random network of adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire neural system. Eur Phys J B 93(11):1–9
Lv M, Ma J (2016) Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205:375–381
Lv M, Wang C, Ren G, Ma J, Song X (2016) Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn 85:1479–1490
Lv G, Zhang N, Ma K, Weng J, Zhu P, Chen F, He G (2021) Functional brain network dynamics based on the Hindmarsh–Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn 104(2):1475–1489
Nelson M, Rinzel J (1998) The Hodgkin–Huxley model. In: The book of genesis. Springer, New York, pp 29–49
Parastesh F, Rajagopal K, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T, Pham VT, Hussain I (2019) Birth and death of spiral waves in a network of Hindmarsh–Rose neurons with exponential magnetic flux and excitable media. Appl Math Comput 354:377–384
Paul Asir M, Sathiyadevi K, Philominathan P, Premraj D (2022) A nonlinear memductance induced intermittent and anti-phase synchronization. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 32(7):073125
Premraj D, Suresh K, Banerjee T, Thamilmaran K (2018) Bifurcation delay in a network of locally coupled slow-fast systems. Phys Rev E 98(2):022206
Premraj D, Suresh K, Thamilmaran K (2019) Effect of processing delay on bifurcation delay in a network of slow-fast oscillators. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 29(12):123127
Qi Y, Watts AL, Kim JW, Robinson PA (2013) Firing patterns in a conductance-based neuron model: bifurcation, phase diagram, and chaos. Biol Cybern 107(1):15–24
Rajagopal K, Khalaf AJM, Parastesh F, Moroz I, Karthikeyan A, Jafari S (2019) Dynamical behavior and network analysis of an extended Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn 98(1):477–487
Ramadoss J, Aghababaei S, Parastesh F, Rajagopal K, Jafari S, Hussain I (2021) Chimera state in the network of fractional-order Fitzhugh–Nagumo neurons. Complexity 2021
Rocsoreanu C, Georgescu A, Giurgiteanu N (2012) The FitzHugh–Nagumo model: bifurcation and dynamics, vol 10. Springer, Berlin
Rontogiannis A, Provata A (2021) Chimera states in FitzHugh–Nagumo networks with reflecting connectivity. Eur Phys J B 94(5):1–12
Routhu G, Phalguni Singh N, Reddy ESK (2023) Investigation of memristor-based neural networks on pattern recognition. Eng Proc 34(1):9
Santos MS, Protachevicz PR, Iarosz KC, Caldas IL, Viana RL, Borges FS, Grebogi C (2019) Spike-burst chimera states in an adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire neuronal network. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 29(4):043106
Sathiyadevi K, Chandrasekar VK, Senthilkumar DV, Lakshmanan M (2018) Imperfect amplitude mediated chimera states in a nonlocally coupled network. Front Appl Math Stat 4:58
Schöll E (2016) Synchronization patterns and chimera states in complex networks: interplay of topology and dynamics. Eur Phys J Spec Top 225(6):891–919
Storace M, Linaro D, de Lange E (2008) The Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model: bifurcation analysis and piecewise-linear approximations. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 18(3):033128
Teka W, Marinov TM, Santamaria F (2014) Neuronal spike timing adaptation described with a fractional leaky integrate-and-fire model. PLoS Comput Biol 10(3):e1003526
Tolba MF, Elsafty AH, Armanyos M, Said LA, Madian AH, Radwan AG (2019) Synchronization and FPGA realization of fractional-order Izhikevich neuron model. Microelectron J 89:56–69
Trappenberg T (2009) Fundamentals of computational neuroscience. OUP Oxford, Oxford
Wang Z, Guo L, Adjouadi M (2014) A generalized leaky integrate-and-fire neuron model with fast implementation method. Int J Neural Syst 24(05):1440004
Wang Q, Shi X, Chen G (2011) Delay-induced synchronization transition in small-world Hodgkin-Huxley neuronal networks with channel blocking. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-B 16(2):607
Wang S, Song L, Chen W, Wang G, Hao E, Li C, Hu Y, Pan Y, Nathan A, Hu G, Gao S (2023) Memristor-based intelligent human-like neural computing. Adv Electron Mater 9(1):2200877
Wu F, Wang C, Xu Y, Ma J (2016) Model of electrical activity in cardiac tissue under electromagnetic induction. Sci Rep 6(1):28
Yang S, Wei X, Deng B, Liu C, Li H, Wang J (2018) Efficient digital implementation of a conductance-based globus pallidus neuron and the dynamics analysis. Physica A 494:484–502
Yang X, Zhang G, Li X, Wang D (2021) Diverse dynamic behaviors and firing activities of the modified fractional-order Hindmarsh–Rose neuronal model induced by fractional-order. Complexity 2021
Yağ İ, Altan A (2022) Artificial intelligence-based robust hybrid algorithm design and implementation for real-time detection of plant diseases in agricultural environments. Biology 11(12):1732
Yu X, Bao H, Chen M, Bao B (2023) Energy balance via memristor synapse in Morris-Lecar two-neuron network with FPGA implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 171:113442
Yu D, Wang G, Li T, Ding Q, Jia Y (2023) Filtering properties of Hodgkin–Huxley neuron on different time-scale signals. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 117:106894
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge this work is funded by the Center for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology (CIT), India, vide funding number CIT/CNS/2023/RP-005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kanagaraj, S., Moroz, I., Durairaj, P. et al. Imperfect chimera and synchronization in a hybrid adaptive conductance based exponential integrate and fire neuron model. Cogn Neurodyn 18, 473–484 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-023-10000-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-023-10000-0