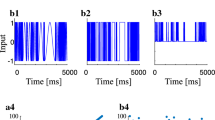
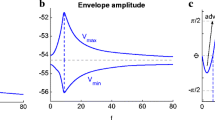
Abstract
Neuronal spike variability is a statistical property associated with the noise environment. Considering a linearised Hodgkin–Huxley model, we investigate how large spike variability can be induced in a typical stellate cell when submitted to constant and noise current amplitudes. For low noise current, we observe only periodic firing (active) or silence activities. For intermediate noise values, in addition to only active or inactive periods, we also identify a single transition from an initial spike-train (active) to silence dynamics over time, where the spike variability is low. However, for high noise current, we find intermittent active and silence periods with different values. The spike intervals during active and silent states follow the exponential distribution, which is similar to the Poisson process. For non-maximal noise current, we observe the highest values of inter-spike variability. Our results suggest sub-threshold oscillations as a possible mechanism for the appearance of high spike variability in a single neuron due to noise currents.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan N, Basu AP (1995) The exponential distribution: theory, methods and applications. Routledge, London
Burkitt AN (2006) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I. Homogeneous synaptic input. Biol Cybern 95:1–19
Cao B, Wang R, Gu H, Li Y (2020) Coherence resonance for neuronal bursting with spike undershoot. Cogn Neurodyn 15:77–90
Cleanthous A, Christodoulou C (2012) Learning optimisation by high firing irregularity. Brain Res 1434:115–122
Coutureau E, Di Scala G (2009) Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(5):753–761
Ditlevsen S, Lansky P (2005) Estimation of the input parameters in the Ornstein–Uhlenbeck neuronal model. Phys Rev E 71:011907
Engel TA, Schimansky-Geier L, Herz AVM, Schreiber S, Erchova I (2008) Subthreshold membrance-potential resonances shape spike-train patterns in the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 100(3):1579–1589
Erchova I, Kreck G, Heinemann U, Herz AVM (2004) Dynamics of rat entorhinal cortex layer II and III cells: characteristics of membrane potential resonance at rest predict oscillation properties near threshold. J Physiol 560(1):89–110
Faisal AA, Selen LPJ, Wolpert DM (2008) Noise in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(4):292–303
Fransén E (2005) Functional role of entorhinal cortex in working memory processing. Neural Netw 18(9):1141–1149
Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F (1998) Stochastic resonance. Rev Mod Phys 70(1):223–287
Gerstner W, Kistler WM (2002) Spiking neuron models: single neurons, populations, plasticity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gerstner W, Kistler WM, Naud R, Paninski L (2014) Neuronal dynamics: From single neurons to networks and models of cognition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gong Y, Hao Y, Xie Y, Ma X, Yang C (2009) Non-Gaussian noise optimized spiking activity of Hodgkin–Huxley neurons on random complex networks. Biophys Chem 144(1–2):88–93
Guo D, Li C (2012) Stochastic resonance in Hodgkin–Huxley neuron induced by unreliable synaptic transmission. J Theor Biol 308:105–114
Hänggi P, Jung P, Zerbe C, Moss F (1993) Can colored noise improve stochastic resonance? J Stat Phys 70:25–47
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117(4):500–544
Honeycutt R (1992) Stochastic Runge–Kutta algorithms. I. White noise. Phys Rev A 45(2):600–603
Izhikevich EM (2001) Resonate-and-fire neurons. Neural Netw 14:883–894
Kobayashi R (2009) The influence of firing mechanisms on gain modulation. J Stat Mech: Theory Exp 8:P01017
Kobayashi R, Kitano K (2016) Impact of slow K\(^{+}\) currents on spike generation can be described by an adaptive threshold model. J Comput Neurosci 40:347–362
Kobayashi R, Tsubo Y, Shinomoto S (2009) Made-to-order spiking neuron model equipped with a multi-timescale adaptive threshold. Front Comput Neurosci 3:9
Lánský P, Rospars JP (1995) Ornstein–Uhlenbeck model neuron revisited. Biol Cybern 72:397–406
Lánský P, Smith CE (1989) The effect of a random initial value in neural first-passage-time models. Math Biosci 93(2):191–215
Lengler J, Steger A (2017) Note on the coefficient of variation of neuronal spike trains. Biol Cybern 111(3–4):229–235
Li M, Xie K, Kuang H, Liu J, Wang D, Fox GE, Shi Z, Chen L, Zhao F, Mao Y, Tsien JZ (2018) Neural coding of cell assemblies via spike-timing self-information. Cereb Cortex 28(7):2563–2576
Lu L, Jia Y, Ge M, Xu Y, Li A (2020) Inverse stochastic resonance in Hodgkin–Huxley neural system driven by Gaussian and non-Gaussian colored noises. Nonlinear Dyn 100:877–889
Mino H, Durand DM (2008) Stochastic resonance can induce oscillation in a recurrent Hodgkin–Huxley neuron model with added Gaussian noise. In: 30th conference of proceedings in IEEE engineering medicine and biological society
Nobile AG, Ricciardi LM, Sacerdote L (1985) Exponential trends of Ornstein–Uhlenbeck first-passage-time densities. J Appl Probab 22(2):360–369
Nozaki D, Mar DJ, Grigg P, Collins JJ (1999) Effects of colored noise on stochastic resonance in sensory neurons. Phys Rev Lett 82:2402
Ostojic S (2014) Two types of asynchronous activity in networks of excitatory and inhibitory spiking neurons. Nat Neurosci 17(4):594–600
Protachevicz PR, Santos MS, Seifert EG, Gabrick EC, Borges DS, Borges RR, Trobia J, Szezech JD Jr, Iarosz K, Caldas IL, Antonopoulos CG, Xu Y, Viana RL, Batista AM (2020) Noise induces continuous and noncontinuous transitions in neuronal interspike intervals range. Indian Acad Sci Conf Ser 3(12):105–109
Richardson MJE, Gerstner W (2005) Synaptic shot noise and conductance fluctuations affect the membrane voltage with equal significance. Neural Comput 17:923–947
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J Neurosci 18(10):3870–3896
Shinomoto S, Kim H, Shimokawa T, Matsuno N, Funahashi S, Shima K, Fujita I, Tamura H, Doi T, Kawano K, Inaba N, Fukushima K, Kurkin S, Kurata K, Taira M, Tsutsui K-I, Komatsu H, Ogawa T, Koida K, Tanji J, Toyama K (2009) Relating neuronal firing patterns to functional differentiation of cerebral cortex. PLoS Comput Biol 5:e1000433
Softky WR, Kock C (1993) The highly irregular firing of cortical cells is inconsistent with temporal integration of random EPSPs. J Neurosci 13(1):334–350
Svirskis G, Rinzel J (2000) Influence of temporal correlation of synaptic input on the rate and variability of firing in neurons. Biophys J 79(2):629–637
Umbach G, Kantak P, Jacobs J, Kahana M, Pfeiffer BE, Sperling M, Lega B (2020) Time cells in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex support episodic memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(45):28463–28474
Van Cauter T, Camon J, Alvernhe A, Elduayen C, Sargolini F, Save E (2013) Distinct roles of medial and lateral entorhinal cortex in spatial cognition. Cereb Cortex 23(2):451–459
Vázquez-Rodríguez B, Avena-Koenigsberger A, Sporns O, Griffa A, Hagmann P, Larralde H (2017) Stochastic resonance at criticality in an network model of the human cortex. Sci Rep 7(13020):1–12
Verechtchaguina T, Schimansky-Geier L, Sokolov IM (2004) Spectra and waiting-time densities in firing resonant and nonresonant neurons. Phys Rev E 70(031916):1–8
Verechtchaguina T, Sokolov IM, Schimansky-Geier L (2007) Interspike interval densities of resonate and fire neurons. Biosystems 89(1–3):63–68
Wilbur WJ, Rinzel J (1983) A theoretical basis for large coefficient of variation and bimodality in neuronal interspike interval distributions. J Theor Biol 105(2):345–368
Yarom Y, Hounsgaard J (2011) Voltage fluctuations in neurons: signal or noise? Physiol Rev 91(3):917–929
Zhao J, Qin Y, Yanqiu Che, Ran H, Li J (2020) Effects of network topologies on stochastic resonance in feedforward neural network. Cogn Neurodyn 14:399–409
Acknowledgements
This work was possible by partial financial support from the following Brazilian government agencies: São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) under Grant Nos. 2020/04624-2 and 2018/03211-6, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) under Grant Nos. 407299/2018-1 and 302665/2017-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this work and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. No conflict of interest exists.
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Protachevicz, P.R., Bonin, C.A., Iarosz, K.C. et al. Large coefficient of variation of inter-spike intervals induced by noise current in the resonate-and-fire model neuron. Cogn Neurodyn 16, 1461–1470 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-022-09789-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-022-09789-z