Abstract
Purpose
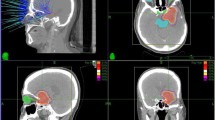
The aim of our study was to retrospectively evaluate the feasibility and clinical benefit of cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery (CSRS) in patients treated at Florence University for recurrent, pre-irradiated brain lesions.
Materials and methods
Thirteen patients were retreated with cyberknife. Mean age was 47.1 years (range 33–77 years). Karnofsky performance status ranged from 60 to 100 (median 80). Eleven (84.6 %) out of 13 patients had metastatic lesions: four (36.4 %) had primary lung, three (27.2 %) had primary breast cancer and four (36.4 %) other types of solid malignancies. Two (15.4 %) out of 13 patients had recurrent of glioblastoma.
Results
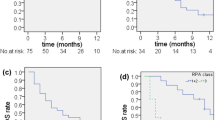
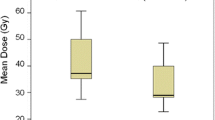
In terms of compliance with CSRS, the majority of patients did not develop any acute side effects. However, two (15.4 %) out of 13 patients developed acute grade 2 toxicity requiring an increase of steroid medication. At the time of the last follow-up, response rates were as follows: complete response in one case (16.6 %), partial response in three (50 %) and stable disease in two (33.4 %).
Conclusions
Re-irradiation with CSRS is a feasible and effective option for pre-irradiated, recurrent brain lesions to obtain clinical benefit without excessive acute toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posner JB, Chernik NL (1978) Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol 19:579–592
Rwigema JC, Wegner RE, Mintz AH et al (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery to the resection cavity of brain metastases: a retrospective analysis and literature review. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89:329–337
Niibe Y, Hayakawa K (2010) Oligometastases and oligo-recurrence: the new era of cancer therapy. Jap J Clin Oncol 40:107–111
Tsao MN, Lloyd NS, Wong RK et al (2005) Radiotherapeutic management of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 31:256–273
Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK (2010) Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:655–661
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs. stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock B et al (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with “radioresistant” brain metastases. Neurosurgery 51:656–665
Chang EL, Selek U, Hassenbusch SJ III et al (2005) Outcome variation among socalled “radioresistant” brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 56:936–945
Abusaris H, Storchi PR, Brandwijk RP, Nuyttens JJ (2011) Second re-irradiation: efficacy, dose and toxicity in patients who received three courses of radiotherapy with overlapping fields. Radiother Oncol 99:235–239
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):219–222
Nakamura JL, Verhey LJ, Smith V (2001) Dose conformity of gamma knife radiosurgery and risk factors for complications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:1313–1319
MacDonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Cooper JS, Steinfeld AD, Lerch IA (1999) Cerebral metastases: value of reirradiation in selected patients. Radiology 174:883–885
Wong WW, Schild SE, Sawyer TE, Shaw EG (1996) Analysis of outcome in patients reirradiated for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34:585–590
Loeffler JS, Kooy HM, Wen PY et al (1990) The treatment of recurrent brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Clin Oncol 8:576–582
Manning MA, Cardinale RM, Benedict SH et al (2000) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy as an alternative to radiosurgery for the treatment of patients with brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:603–608
Chao ST, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA et al (2008) Salvage stereotactic radiosurgery effectively treats recurrences from whole-brain radiation therapy. Cancer 113:2198–2204
Patel M, Siddiqui F, Jin JY et al (2009) Salvage reirradiation for recurrent glioblastoma with radiosurgery: radiographic response and improved survival. J Neurooncol 92:185–191
Auchter RM, Lamond JP, Alexander E et al (1996) A multi-institutional outcome and prognostic factor analysis of radiosurgery for resectable single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:27–35
Alexander E 3rd, Moriarty TM, Davis R et al (1995) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, noninvasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:34–40
Ma L, Petti P, Wang B et al (2011) Apparatus dependence of normal brain tissue dose in stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases. J Neurosurg 114:1580–1584
Karam I, Nichol A, Woods R, Tyldesley S (2011) Population-based outcomes after whole brain radiotherapy and re-irradiation in patients with metastatic breast cancer in the trastuzumab era. Radiat Oncol 28:181
Ammirati M, Cobbs CS, Linskey ME et al (2010) The role of retreatment in the management of recurrent/progressive brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 96:85–96
Dritschilo A, Bruckman JE, Cassady JR, Belli JA (1981) Tolerance of brain to multiple courses of radiation therapy. I. Clinical experiences. Br J Radiol 54:782–786
Wong CS, Hao Y (1999) Long-term recovery kinetics of radiation damage in rat spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:171–179
Abusaris H, Storchi PR, Brandwijk RP, Nuyttens JJ (2011) Second re-irradiation: efficacy, dose and toxicity in patients who received three courses of radiotherapy with overlapping fields. Radiother Oncol 99:235–239
Gwak HS, Yoo HJ, Youn SM et al (2009) Radiosurgery for recurrent brain metastases after whole-brain radiotherapy: factors affecting radiation-induced neurological dysfunction. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 45:275–283
Joseph J, Adler JR, Cox RS, Hancock SL (1996) Linear accelerator-based stereotaxic radiosurgery for brain metastases: the influence of number of lesions on survival. J Clin Oncol 14(4):1085–1092
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U et al (2007) Survival and quality of life after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 81:287–294
Conflict of interest
Daniela Greto, Lorenzo Livi, Pierluigi Bonomo, Laura Masi, Beatrice Detti, Icro Meattini, Monica Mangoni, Raffaella Doro, Virginia Favuzza, Samantha Cipressi, Carmine Iermano, Ivano Bonucci, Mauro Loi and Gianpaolo Biti declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greto, D., Livi, L., Bonomo, P. et al. Cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery for the re-irradiation of brain lesions: a single-centre experience. Radiol med 119, 721–726 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0383-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-014-0383-2