Abstract
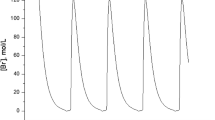
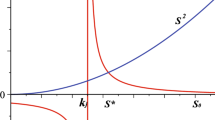
The tryptophan (trp) operon in Escherichia coli codes for the proteins responsible for the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan from chorismic acid, and has been one of the most well-studied gene networks since its discovery in the 1960s. The tryptophanase (tna) operon codes for proteins needed to transport and metabolize it. Both of these have been modeled individually with delay differential equations under the assumption of mass-action kinetics. Recent work has provided strong evidence for bistable behavior of the tna operon. The authors of Orozco-Gómez et al. (Sci Rep 9(1):5451, 2019) identified a medium range of tryptophan in which the system has two stable steady-states, and they reproduced these experimentally. In this paper, we will show how a Boolean model can capture this bistability. We will also develop and analyze a Boolean model of the trp operon. Finally, we will combine these two to create a single Boolean model of the transport, synthesis, and metabolism of tryptophan. In this amalgamated model, the bistability disappears, presumably reflecting the ability of the trp operon to produce tryptophan and drive the system toward homeostasis. All of these models have longer attractors that we call “artifacts of synchrony”, which disappear in the asynchronous automata. This curiously matches the behavior of a recent Boolean model of the arabinose operon in E. coli, and we discuss some open-ended questions that arise along these lines.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert R, Othmer H (2003) The topology of the regulatory interactions predicts the expression pattern of the segment polarity genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Theor Biol 223(1):1–18
Bliss R, Painter P, Marr A (1982) Role of feedback inhibition in stabilizing the classical operon. J Theor Biol 97(2):177–193
Davidich M, Bornholdt S (2008) Boolean network model predicts cell cycle sequence of fission yeast. PLOS ONE 3(2):e1672
Didier G, Remy E, Chaouiya C (2011) Mapping multivalued onto Boolean dynamics. J Theor Biol 270(1):177–184
Dimitrova E, Jarrah A, Laubenbacher R, Stigler B (2007) A Gröbner fan method for biochemical network modeling. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on Symbolic and algebraic computation. ACM, pp 122–126
Fauré A, Naldi A, Chaouiya C, Thieffry D (2006) Dynamical analysis of a generic Boolean model for the control of the mammalian cell cycle. Bioinformatics 22(14):e124–e131
Gong F, Ito K, Nakamura Y, Yanofsky C (2001) The mechanism of tryptophan induction of tryptophanase operon expression: tryptophan inhibits release factor-mediated cleavage of TnaC-peptidyl-tRNAPro. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(16):8997–9001
Goodwin B (1965) Oscillatory behavior in enzymatic control processes. Adv Enzym Regul 3:425–437
Grayson D, Stillman M (2002) Macaulay2, a software system for research in algebraic geometry. https://faculty.math.illinois.edu/Macaulay2/
Gu P, Yang F, Li F, Liang Q, Qi Q (2013) Knocking out analysis of tryptophan permeases in Escherichia coli for improving L-tryptophan production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(15):6677–6683
Jacob F, Perrin D, Sánchez C, Monod J (1960) L’opéron: groupe de gènes à expression coordonnée par un opérateur. C R Acad Sci 250:1727–1729
Jenkins A, Macauley M (2017) Bistability and asynchrony in a Boolean model of the L-arabinose operon in Escherichia coli. Bull Math Biol 79(8):1778–1795
Laubenbacher R, Stigler B (2004) A computational algebra approach to the reverse engineering of gene regulatory networks. J Theor Biol 229(4):523–537
Laubenbacher R, Sturmfels B (2009) Computer algebra in systems biology. Am Math Mon 882–891
Li F, Long T, Lu Y, Ouyang Q, Tang C (2004) The yeast cell-cycle network is robustly designed. Proc Acad Natl Sci 101(14):4781–4786
Li G, Young K (2014) A cAMP-independent carbohydrate-driven mechanism inhibits tnaA expression and TnaA enzyme activity in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 160(9):2079–2088
Li G, Young K (2015) A new suite of tnaA mutants suggests that Escherichia coli tryptophanase is regulated by intracellular sequestration and by occlusion of its active site. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–17
Macauley M, Robeva R (2020) Algebraic models, inverse problems, and pseudomonomials from biology. Lett Biomath 7(1):81–104
Mackey M, Santillán M, Yildirim N (2004) Modeling operon dynamics: the tryptophan and lactose operons as paradigms. C R Biol 327(3):211–224
Matsushiro A, Sato K, Ito J, Kida S, Imamoto F (1965) On the transcription of the tryptophan operon in Escherichia coli: I. The tryptophan operator. J Mol Biol 11(1):54–63
Mendoza L, Thieffry D, Alvarez-Buylla E (1999) Genetic control of flower morphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana: a logical analysis. Bioinformatics 15(7):593–606
Mendoza L, Xenarios I (2006) A method for the generation of standardized qualitative dynamical systems of regulatory networks. Theor Biol Med Model 3:13
Murrugarra D, Veliz-Cuba A, Aguilar B, Arat S, Laubenbacher R (2012) Modeling stochasticity and variability in gene regulatory networks. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol 2012(1):1–11
Müssel C, Hopfensitz M, Kestler H (2010) BoolNet-an R package for generation, reconstruction and analysis of Boolean networks. Bioinformatics 26(10):1378–1380
Nelson D, Cox M, Lehninger AL (2005) Principles of biochemistry, vol 1, no 1.1, 4th edn. WH Freeman and Company, New York, p 2
Orozco-Gómez D, Sosa-Hernández J, Gallardo-Navarro Ó, Santana-Solano J, Santillán M (2019) Bistable behaviour and medium-dependent post-translational regulation of the tryptophanase operon regulatory pathway in Escherichia coli. Sci Rep 9(1):5451
Remy É, Ruet P, Thieffry D (2008) Graphic requirements for multistability and attractive cycles in a Boolean dynamical framework. Adv Appl Math 41(3):335–350
Richard A (2010) Negative circuits and sustained oscillations in asynchronous automata networks. Adv Appl Math 44(4):378–392
Robert R (1980) Iterations sur des ensembles finis et automates cellulaires contractants. Linear Algebra Appl 29:393–412
Robeva R, Hodge T (2013) Mathematical concepts and methods in modern biology: using modern discrete models. Academic Press
Robeva R, Macauley M (2018) Algebraic and combinatorial computational biology. Elsevier
Saez-Rodriguez J et al (2007) A logical model provides insights into T cell receptor signaling. PLoS Comput Biol 3(8):e163
Santillán M, Mackey M (2001) Dynamic regulation of the tryptophan operon: a modeling study and comparison with experimental data. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(4):1364–1369
Shmulevich I, Dougherty E (2010) Probabilistic Boolean networks: the modeling and control of gene regulatory networks. SIAM, Philadelphia
Simao E, Remy E, Thieffry D, Chaouiya C (2005) Qualitative modelling of regulated metabolic pathways: application to the tryptophan biosynthesis in E. coli. Bioinformatics 21(2):190–196
Stoll G, Naldi A, Noël V, Viara E, Barillot E, Kroemer G, Thieffry D, Calzone L (2022) UPMaBoSS: a novel framework for dynamic cell population modeling. Front Mol Biosci 9:800152
Stoll G, Viara E, Barillot E, Calzone L (2012) Continuous time Boolean modeling for biological signaling: application of Gillespie algorithm. BMC Syst Biol 6(1):116
Thomas R, d’Ari R (1990) Biological feedback. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Veliz-Cuba A, Stigler B (2011) Boolean models can explain bistability in the lac operon. J Comput Biol 18(6):783–794
Yanofsky C, Horn V, Gollnick P (1991) Physiological studies of tryptophan transport and tryptophanase operon induction in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173(19):6009–6017
Yanofsky C, Kelley R, Horn V (1984) Repression is relieved before attenuation in the trp operon of Escherichia coli as tryptophan starvation becomes increasingly severe. J Bacteriol 158(3):1018–1024
Yildirim N (2012) Mathematical modeling of the low and high affinity arabinose transport systems in Escherichia coli. Mol BioSyst 8(4):1319–1324
Yildirim N, Mackey M (2003) Feedback regulation in the lactose operon: a mathematical modeling study and comparison with experimental data. Biophys J 84(5):2841–2851
Yildirim N, Santillan M, Horike D, Mackey M (2004) Dynamics and bistability in a reduced model of the lac operon. Chaos 14(2):279–292
Zander D, Samaga D, Straube R, Bettenbrock K (2017) Bistability and nonmonotonic induction of the lac operon in the natural lactose uptake system. Biophys J 112(9):1984–1996
Zheng D, Constantinidou C, Hobman J, Minchin S (2004) Identification of the CRP regulon using in vitro and in vivo transcriptional profiling. Nucleic Acids Res 32(19):5874–5893
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The second author thanks the Simons Foundation (Collaboration Grant #358242).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deal, I., Macauley, M. & Davies, R. Boolean Models of the Transport, Synthesis, and Metabolism of Tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Bull Math Biol 85, 29 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-023-01122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-023-01122-x
Keywords
- Boolean model
- Escherichia coli
- Operon
- Tryptophan
- Bistability
- Basin of attraction
- Artifact of synchrony
- Computational algebra