Abstract
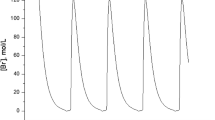
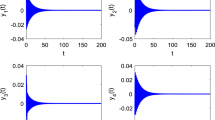
It is well known that the FitzHugh–Nagumo model is one of the simplified forms of the four-variable Hodgkin–Huxley model that can reflect most of the significant phenomena of nerve cell action potential. However, this model cannot capture the irregular action potentials of sufficiently large periods in a one-parameter family of solutions. Motivated by this, we propose a modified FitzHugh–Nagumo reaction-diffusion system by changing its recovery kinetics. First, we investigate the parameter regime to know the existence of the wavetrains. Second, we conceive the occurrence of Eckhaus bifurcations of solutions that divide the solution region into two parts. The essential spectra at different grid points explore the occurrence of bifurcations of the waves. We find that the wavetrains of sufficiently large periods cross the stability boundary. This characteristic phenomenon is absent in the standard FitzHugh–Nagumo model. Finally, we observe a reasonable agreement between the direct PDE simulations and the solutions in the traveling wave ODEs. Furthermore, the model exhibits spiral wave for monotone and non-monotone cases that agrees with the waves observed in cellular activity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bär M, Brusch L (2004) Breakup of spiral waves caused by radial dynamics: eckhaus and finite wavenumber instabilities. New J Phys 6:5
Bauer S, Röder G, Bär M: Alternans and the influence of ionic channel modifications: cardiac three–dimensional simulations and one-dimensional numerical bifurcation analysis. Chaos: An Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 17, 015104 (2007)
Bierman SM, Fairbairn JP, Petty SJ, Elston DA, Tidhar D, Lambin X (2006) Changes over time in the spatiotemporal dynamics of cyclic populations of field voles (microtus agrestis l.). Am Nat 167(4):583–590
Bordiougov G, Engel H (2006) From trigger to phase waves and back again. Phys D 215:25–37
Bordyugov G, Engel H (2006) Creating bound states in excitable media by means of nonlocal coupling. Phys Rev E 74:016205
Bordyugov G, Fischer N, Engel H, Manz N, Steinbock O (2010) Anomalous dispersion in the belousov-zhabotinsky reaction: experiments and modeling. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 239(11):766–775
Davidenko JM, Pertsov AV, Salomonsz R, Baxter W, Jalife J (1992) Stationary and drifting spiral waves of excitation in isolated cardiac muscle. Nature 355(6358):349–351
DeVille REL, Eijnden EV (2007) Wavetrain response of an excitable medium to local stochastic forcing. Nonlinearity 20(1):51
Doedel EJ, Kernevez J (1986) Auto: software for continuation and bifurcation problems in ordinary differential equations. Applied Mathematics Report, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA
Echebarria B, Röder G, Engel H, Davidsen J, Bär M (2011) Supernormal conduction in cardiac tissue promotes concordant alternans and action potential bunching. Phys Rev E 83:040902
Epstein IR, Showalter K (1996) Nonlinear chemical dynamics: oscillations, patterns, and chaos. J Phys Chem 100(31):13132–13147
Ermentrout GB, Kleinfeld D (2001) Traveling electrical waves in cortex: insights from phase dynamics and speculation on a computational role. Neuron 29(1):33–44
Ermentrout GB, Kleinfeld D (2001) Traveling electrical waves in cortex: insights from phase dynamics and speculation on a computational role. Neuron 29(1):33–44
FitzHugh R (1961) Impulse and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1:445–465
Gani MO, Ogawa T: (2014). Alternans and spiral breakup in an excitable reaction-diffusion system: a simulation study. Int Sch Res Not 2014(459675)
Gani MO, Ogawa T (2015) Instability of periodic traveling wave solutions in a modified FitzHugh-Nagumo model for excitable media. Appl Math Comput 256:968–984
Gani MO, Ogawa T (2016) Stability of periodic traveling waves in the aliev-panfilov reaction-diffusion system. Commun in Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 33:30–42
Gorelova NA, Bureš J (1983) Spiral waves of spreading depression in the isolated chicken retina. J neurobiol 14(5):353–363
Gray CM (1989) Singer W : Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proceed National Acad Sci 86(5):1698–1702
Hecke MV (2003) Coherent and incoherent structures in systems described by the 1d cgle: experiments and identification. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 174(1):134–151
Huang X et al (2004) Spiral waves in disinhibited mammalian neocortex. J Neurosci 24(44):9897–9902
Izhikevich EM : (2007). Dynamical systems in neuroscience. MIT press
Jalife J (2003) Rotors and spiral waves in atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 14(7):776–780
Kopell N, Howard LN (1973) Plane-wave solutions to reaction-diffusion equations. Stud Appl Math 52:291–328
Lechleiter J et al (1991) Spiral calcium wave propagation and annihilation in xenopus laevis oocytes. Science 252(5002):123–126
Ma J, Jia Y, Yi M, Tang J, Xia YF (2009) Suppression of spiral wave and turbulence by using amplitude restriction of variable in a local square area. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 41(3):1331–1339
Maginu K (1980) Existence and stability of periodic travelling wave solutions to nagumo’s nerve equation. J Math Biol 10(2):133–153
Meron E (1992) Pattern formation in excitable media. Phys Rep (Rev sect Phys Lett) 218:1–66
Morton KW, Mayers DF : (2005). Numerical solution of partial differential equations: an introduction. Cambridge university press
Nagumo JS, Arimoto S, Yoshizawa S (1962) An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc IRE 50:2061–2071
Oreanu CR, Georgescu A, Eanu NG : (2000) The FitzHugh-Nagumo Model: Bifurcation and Dynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Rademacher JD, Sandstede B, Scheel A (2007) Computing absolute and essential spectra using continuation. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 229(2):166–183
Ranta E, Kaitala V (1997) Travelling waves in vole population dynamics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:3503–3512
Saarloos WV (2003) Front propagation into unstable states. Phys report 386(2):29–222
Sakaguchi H, Maruyama T (2008) Elimination of pulses and spirals by external forces in luo-rudy model. J Phy Soc Japan 77:1–5
Sherratt JA (2012) Numerical continuation methods for studying periodic travelling wave (wavetrain) solutions of partial differential equations. Appl Math & Comput 218:4684–4694
Sherratt JA (2013) Numerical continuation of boundaries in parameter space between stable and unstable periodic travelling wave (wavetrain) solutions of partial differential equations. Adv Comput Math 39:175–192
Sherratt JA, Lord GJ (2007) Nonlinear dynamics and pattern bifurcations in a model for vegetation stripes in semi-arid environments. Theor popul biol 71(1):1–11
Sherratt JA, Smith MJ (2008) Periodic travelling waves in cyclic populations: field studies and reaction-diffusion models. J Royal Soc Interface 5(22):483–505
Steinberg V, Fineberg J, Moses E, Rehberg I (1989) Pattern selection and transition to turbulence in propagating waves. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 37:359–383
Vanag VK, Epstein IR (2008) Design and control of patterns in reaction-diffusion systems. Chaos :An Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 18(2):026107
Verkhratsky A, Orkand RK, Kettenmann H (1998) Glial calcium: homeostasis and signaling function. Physiol Rev 78(1):99–141
Wu JY, Guan L, Bai L, Yang Q (2001) Spatiotemporal properties of an evoked population activity in rat sensory cortical slices. J Neurophysiol 86(5):2461–2474
Yu G, Ma J, Jia Y, Tang J (2010) Dynamics of spiral wave in the coupled hodgkin-huxley neurons. Int J Modern Phys B 24(23):4555–4562
Acknowledgements
It is acknowledged the support provided by the GCOE program entitled “Formation and Development of Mathematical Sciences Based on Modeling and Analysis”, of the Meiji University, Japan, where this work was carried out.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Biological Systems (in memory of Masayasu Mimura).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gani, M.O., Kabir, M.H. & Ogawa, T. Inhibitor-Induced Wavetrains and Spiral Waves in an Extended FitzHugh–Nagumo Model of Nerve Cell Dynamics. Bull Math Biol 84, 145 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-022-01100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-022-01100-9