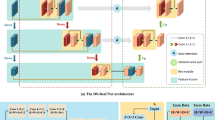
Abstract
Transformer-based methods have led to the revolutionizing of multiple computer vision tasks. Inspired by this, we propose a transformer-based network with a channel-enhanced attention module to explore contextual and spatial information in non-contrast (NC) and contrast-enhanced (CE) computed tomography (CT) images for pulmonary vessel segmentation and artery-vein separation. Our proposed network employs a 3D contextual transformer module in the encoder and decoder part and a double attention module in skip connection to effectively finish high-quality vessel and artery-vein segmentation. Extensive experiments are conducted on the in-house dataset and the ISICDM2021 challenge dataset. The in-house dataset includes 56 NC CT scans with vessel annotations and the challenge dataset consists of 14 NC and 14 CE CT scans with vessel and artery-vein annotations. For vessel segmentation, Dice is 0.840 for CE CT and 0.867 for NC CT. For artery-vein separation, the proposed method achieves a Dice of 0.758 of CE images and 0.602 of NC images. Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrated that the proposed method achieved high accuracy for pulmonary vessel segmentation and artery-vein separation. It provides useful support for further research associated with the vascular system in CT images. The code is available at https://github.com/wuyanan513/Pulmonary-Vessel-Segmentation-and-Artery-vein-Separation.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Resten A, Maitre S, Musset D (2005) CT imaging of peripheral pulmonary vessel disease. Eur Radiol 15:2045–2056
Lahousse L, Tiemeier H, Ikram MA, Brusselle GG (2015) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cerebrovascular disease: a comprehensive review. Respir Med 109(11):1371–1380
Wang M et al (2023) CE-NC-VesselSegNet: supervised by contrast-enhanced CT images but utilized to segment pulmonary vessels from non-contrast-enhanced CT images. Biomed Signal Process Control 82:104565
Hida K, Ohga N, Kurosu T, Totsuka Y, Shindoh M (2009) Crosstalk between blood vessels and tumor microenvironment. Oral Sci Int 7(1):1–10
Coste F et al (2016) CT evaluation of small pulmonary vessels area in patients with COPD with severe pulmonary hypertension. Thorax 71(9):830–837
Hoeper MM, Ghofrani H-A, Grünig E, Klose H, Olschewski H, Rosenkranz S (2017) Pulmonary hypertension, Deutsches Ärzteblatt. International 114(5):73
Washko GR, Coxson HO, O’Donnell DE, Aaron SD (2017) CT imaging of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: insights, disappointments, and promise. The Lancet Respir Med 5:11
Sajja T, Devarapalli R, Kalluri H (2019) Lung cancer detection based on CT scan images by using deep transfer learning. Traitement du Signal 36(4):339–344
Wu R, Xin Y, Qian J, Dong Y (2023) A multi-scale interactive U-Net for pulmonary vessel segmentation method based on transfer learning. Biomed Signal Process Control 80:104407
Poletti J et al (2022) Automated lung vessel segmentation reveals blood vessel volume redistribution in viral pneumonia. Eur J Radiol 150:110259
Li X, Bala R, Monga V (2022) Robust deep 3D blood vessel segmentation using structural priors. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:1271–1284
Pan L et al (2023) Learning multi-view and centerline topology connectivity information for pulmonary artery-vein separation. Comput Biol Med 155:106669
Gao Y-R, Drew PJ (2014) Determination of vessel cross-sectional area by thresholding in Radon space. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34(7):1180–1187
Hojjatoleslami S, Kittler J (1998) Region growing: a new approach. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(7):1079–1084
Duan H-H, Su G-Q, Huang Y-C, Song L-T, Nie S-D (2019) Segmentation of pulmonary vascular tree by incorporating vessel enhancement filter and variational region-growing. J Xray Sci Technol 27(2):343–360
Ziou D, Tabbone S (1998) Edge detection techniques-an overview. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis C/C of Raspoznavaniye Obrazov I Analiz Izobrazhenii 8:537–559
Ozkava U, Ozturk S, Akdemir B, Sevfi L (2018) An efficient retinal blood vessel segmentation using morphological operations. In: 2018 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT). IEEE, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMSIT.2018.8567239
Kaftan JN, Kiraly AP, Bakai A, Das M, Novak CL, Aach T (2008) Fuzzy pulmonary vessel segmentation in contrast enhanced CT data. Medical Imaging 2008: Image Processing 6914:585–596 (SPIE)
Wu C, Agam G, Roy AS, Armato SG III (2004) Regulated morphology approach to fuzzy shape analysis with application to blood vessel extraction in thoracic CT scans. Med Imaging 2004 Image Process 5370:1262–1270
Meye D, Wien F (2015) Support vector machines. The Interface to libsvm in package e1071, 28(20):597
Wu Y et al (2023) Deep CNN for COPD identification by multi-view snapshot integration of 3D airway tree and lung field. Biomed Signal Process Control 79:104162
Zou Y, Chen S, Sun Q, Liu B, Zhang J (2021) DCET-Net: dual-stream convolution expanded transformer for breast cancer histopathological image classification. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, pp 1235–1240
Sünnetci KM, Alkan A (2022) Lung cancer detection by using probabilistic majority voting and optimization techniques. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 32(6):2049–2065
Zhang B et al (2022) Multi-scale segmentation squeeze-and-excitation UNet with conditional random field for segmenting lung tumor from CT images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 222:106946
Pang H et al (2022) A fully automatic segmentation pipeline of pulmonary lobes before and after lobectomy from computed tomography images. Comput Biol Med 147:105792
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 25:2
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Kohl SA, Petersen J, Maier-Hein KH (2021) nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat Methods 18(2):203–211
Wang A, Islam M, Xu M, Ren H (2022) Rethinking surgical instrument segmentation: a background image can be all you need. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, September 18–22, 2022, Proceedings, Part VII. Springer, pp 355–364
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5–9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer, pp 234–241
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S-A (2016) V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV). IEEE, pp 565–571
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, October 17–21, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 19. Springer, pp 424–432
Nardelli P et al (2018) Pulmonary artery–vein classification in CT images using deep learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(11):2428–2440
Zhai Z et al (2019) Linking convolutional neural networks with graph convolutional networks: application in pulmonary artery-vein separation. Graph Learning in Medical Imaging: First International Workshop, GLMI 2019, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2019, Shenzhen, China, October 17, 2019, Proceedings 1. Springer, pp 36–43
Qin Y et al (2021) Learning tubule-sensitive CNNs for pulmonary airway and artery-vein segmentation in CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(6):1603–1617
Gu X, Wang J, Zhao J, Li Q (2019) Segmentation and suppression of pulmonary vessels in low-dose chest CT scans. Med Phys 46(8):3603–3614
Cui H, Liu X, Huang N (2019) Pulmonary vessel segmentation based on orthogonal fused u-net++ of chest CT images. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, October 13–17, 2019, Proceedings, Part VI 22. Springer, pp 293–300
Xu S, Zhang Z, Zhou Q, Shao W, Tan W (2021) A pulmonary vascular extraction algorithm from chest CT/CTA images. J Healthcare Eng 2021:1–7
Vaswani A et al (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30:5998–6008
Duong LT, Le NH, Tran TB, Ngo VM, Nguyen PT (2021) Detection of tuberculosis from chest X-ray images: boosting the performance with vision transformer and transfer learning. Expert Syst Appl 184:115519
Niu C, Wang G (2022) Unsupervised contrastive learning based transformer for lung nodule detection. Phys Med Biol 67(20):204001
Wu H, Chen S, Chen G, Wang W, Lei B, Wen Z (2022) FAT-Net: feature adaptive transformers for automated skin lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 76:102327
Shen Z, Yang H, Zhang Z, Zheng S (2022) Automated kidney tumor segmentation with convolution and transformer network. In: Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation: MICCAI 2021 Challenge, KiTS 2021, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2021, Strasbourg, France, September 27, 2021, Proceedings: Springer, pp 1–12
Li Y et al (2022) Global transformer and dual local attention network via deep-shallow hierarchical feature fusion for retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, pp 1–14
Tan W, Huang P, Li X, Ren G, Chen Y, Yang J (2021) Analysis of segmentation of lung parenchyma based on deep learning methods. J Xray Sci Technol 29(6):945–959
Tan W, Zhou L, Li X, Yang X, Chen Y, Yang J (2021) Automated vessel segmentation in lung CT and CTA images via deep neural networks. J Xray Sci Technol 29(6):1123–1137
Tan W, Liu P, Li X, Xu S, Chen Y, Yang J (2022) Segmentation of lung airways based on deep learning methods. IET Image Proc 16(5):1444–1456
Chen Y, Kalantidis Y, Li J, Yan S, Feng J (2018) A^ 2-nets: double attention networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 31:350–359
Li Y, Yao T, Pan Y, Mei T (2022) Contextual transformer networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 4(2):1489–1500
Zhao R et al (2020) Rethinking dice loss for medical image segmentation. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). IEEE, pp 851–860
Lin T-Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2980–2988
Sunnetci KM, Kaba E, Beyazal Çeliker F, Alkan A (2023) Comparative parotid gland segmentation by using ResNet-18 and MobileNetV2 based DeepLab v3+ architectures from magnetic resonance images. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 35:e7405
Tuncer SA, Alkan A (2019) Spinal cord based kidney segmentation using connected component labeling and K-means clustering algorithm. Traitement du Signal 36:6
Wu Y, Zhao S, Qi S et al (2022) Two-stage contextual transformer-based convolutional neural network for airway extraction from CT images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.07651
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072008), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-YGJC-21), Key R&D Program Guidance Projects in Liaoning Province (2019JH8/10300051), Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC) Collaborative Research Fund (C4026-21G), Hong Kong General Research Fund (RGC-GRF 14211420), Hong Kong RGC Research Impact Fund (RIF) R4020-22, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N2124006-3, N2224001-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Qi, S., Wang, M. et al. Transformer-based 3D U-Net for pulmonary vessel segmentation and artery-vein separation from CT images. Med Biol Eng Comput 61, 2649–2663 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02872-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02872-5