Abstract
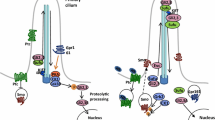
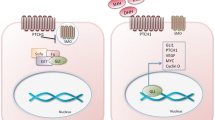
The Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted proteins plays essential roles in the development of a wide variety of animal species and underlies multiple human birth defects and cancers. To ensure the proper range of signaling, the Hh proteins are modified with lipids, assembled into water-soluble multimers, and interact with multiple cell surface proteins. In the target cells, a largely conserved intracellular signal transduction pathway, from the cell surface receptor Patched to the Glioma-associated oncogene homolog (Gli) family of transcription factors, mediates the transcriptional responses from fruit flies to mammals. A significant divergence between vertebrates and insects is the vertebrate-specific requirement of cilia for Hh signal transduction and Gli protein activation. Finally, transcription-independent cellular responses to Hh have been described in certain developmental processes. With clinical trial underway to treat Hhrelated diseases, more work is urgently needed to reach a more comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of Hh signaling in development and diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper J E (1996). The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell, 86(2): 221–232
Allen B L, Tenzen T, McMahon A P (2007). The Hedgehog-binding proteins Gas1 and Cdo cooperate to positively regulate Shh signaling during mouse development. Genes Dev, 21(10): 1244–1257
Amanai K, Jiang J (2001). Distinct roles of central missing and dispatched in sending the Hedgehog signal. Development, 128(24): 5119–5127
Apionishev S, Katanayeva N M, Marks S A, Kalderon D, Tomlinson A (2005). Drosophila Smoothened phosphorylation sites essential for Hedgehog signal transduction. Nat Cell Biol, 7(1): 86–92
Asaoka Y, Kanai F, Ichimura T, Tateishi K, Tanaka Y, Ohta M, Seto M, Tada M, Ijichi H, Ikenoue T, Kawabe T, Isobe T, Yaffe M B, Omata M (2010). Identification of a suppressive mechanism for Hedgehog signaling through a novel interaction of Gli with 14-3-3. J Biol Chem, 285(6): 4185–4194
Aza-Blanc P, Ramírez-Weber F A, Laget M P, Schwartz C, Kornberg T B (1997). Proteolysis that is inhibited by hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell, 89(7): 1043–1053
Bai C B, Auerbach W, Lee J S, Stephen D, Joyner A L (2002). Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development, 129(20): 4753–4761
Bai C B, Stephen D, Joyner A L (2004). All mouse ventral spinal cord patterning by hedgehog is Gli dependent and involves an activator function of Gli3. Dev Cell, 6(1): 103–115
Barzi M, Berenguer J, Menendez A, Alvarez-Rodriguez R, Pons S (2010). Sonic-hedgehog-mediated proliferation requires the localization of PKA to the cilium base. J Cell Sci, 123(Pt 1): 62–69
Bellaiche Y, The I, Perrimon N (1998). Tout-velu is a Drosophila homologue of the putative tumour suppressor EXT-1 and is needed for Hh diffusion. Nature, 394(6688): 85–88
Bergeron S A, Tyurina O V, Miller E, Bagas A, Karlstrom R O (2011). Brother of cdo (umleitung) is cell-autonomously required for Hedgehog-mediated ventral CNS patterning in the zebrafish. Development, 138(1): 75–85
Bitgood M J, Shen L, McMahon A P (1996). Sertoli cell signaling by Desert hedgehog regulates the male germline. Curr Biol, 6(3): 298–304
Bumcrot D A, Takada R, McMahon A P (1995). Proteolytic processing yields two secreted forms of sonic hedgehog. Mol Cell Biol, 15(4): 2294–2303
Burke R, Nellen D, Bellotto M, Hafen E, Senti K A, Dickson B J, Basler K (1999). Dispatched, a novel sterol-sensing domain protein dedicated to the release of cholesterol-modified hedgehog from signaling cells. Cell, 99(7): 803–815
Byrd N, Becker S, Maye P, Narasimhaiah R, St-Jacques B, Zhang X, McMahon J, McMahon A, Grabel L (2002). Hedgehog is required for murine yolk sac angiogenesis. Development, 129(2): 361–372
Callejo A, Torroja C, Quijada L, Guerrero I (2006). Hedgehog lipid modifications are required for Hedgehog stabilization in the extracellular matrix. Development, 133(3): 471–483
Cameron D A, Pennimpede T, Petkovich M (2009). Tulp3 is a critical repressor of mouse hedgehog signaling. Dev Dyn, 238(5): 1140–1149
Canettieri G, Di Marcotullio L, Greco A, Coni S, Antonucci L, Infante P, Pietrosanti L, De Smaele E, Ferretti E, Miele E, Pelloni M, De Simone G, Pedone E M, Gallinari P, Giorgi A, Steinkühler C, Vitagliano L, Pedone C, Schinin M E, Screpanti I, Gulino A (2010). Histone deacetylase and Cullin3-REN(KCTD11) ubiquitin ligase interplay regulates Hedgehog signalling through Gli acetylation. Nat Cell Biol, 12(2): 132–142
Capurro M I, Xu P, Shi W, Li F, Jia A, Filmus J (2008). Glypican-3 inhibits Hedgehog signaling during development by competing with patched for Hedgehog binding. Dev Cell, 14(5): 700–711
Caspary T, García-García M J, Huangfu D, Eggenschwiler J T, Wyler M R, Rakeman A S, Alcorn H L, Anderson K V (2002). Mouse Dispatched homolog1 is required for long-range, but not juxtacrine, Hh signaling. Curr Biol, 12(18): 1628–1632
Caspary T, Larkins C E, Anderson K V (2007). The graded response to Sonic Hedgehog depends on cilia architecture. Dev Cell, 12(5): 767–778
Chamoun Z, Mann R K, Nellen D, von Kessler D P, Bellotto M, Beachy P A, Basler K (2001). Skinny hedgehog, an acyltransferase required for palmitoylation and activity of the hedgehog signal. Science, 293(5537): 2080–2084
Charron F, Stein E, Jeong J, McMahon A P, Tessier-Lavigne M (2003). The morphogen sonic hedgehog is an axonal chemoattractant that collaborates with netrin-1 in midline axon guidance. Cell, 113(1): 11–23
Chen J K, Taipale J, Cooper M K, Beachy P A (2002a). Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev, 16(21): 2743–2748
Chen J K, Taipale J, Young K E, Maiti T, Beachy P A (2002b). Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(22): 14071–14076
Chen M H, Gao N, Kawakami T, Chuang P T (2005). Mice deficient in the fused homolog do not exhibit phenotypes indicative of perturbed hedgehog signaling during embryonic development. Mol Cell Biol, 25(16): 7042–7053
Chen M H, Li Y J, Kawakami T, Xu S M, Chuang P T (2004). Palmitoylation is required for the production of a soluble multimeric Hedgehog protein complex and long-range signaling in vertebrates. Genes Dev, 18(6): 641–659
Chen MH, Wilson CW, Li Y J, Law K K, Lu C S, Gacayan R, Zhang X, Hui C C, Chuang P T (2009). Cilium-independent regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is evolutionarily conserved. Genes Dev, 23(16): 1910–1928
Chen Y, Gallaher N, Goodman R H, Smolik S M (1998). Protein kinase A directly regulates the activity and proteolysis of cubitus interruptus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95(5): 2349–2354
Chen Y, Struhl G (1996). Dual roles for patched in sequestering and transducing Hedgehog. Cell, 87(3): 553–563
Cheng S Y, Bishop J M (2002). Suppressor of Fused represses Glimediated transcription by recruiting the SAP18-mSin3 corepressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99(8): 5442–5447
Cheung H O, Zhang X, Ribeiro A, Mo R, Makino S, Puviindran V, Law K K, Briscoe J, Hui C C (2009). The kinesin protein Kif7 is a critical regulator of Gli transcription factors in mammalian hedgehog signaling. Sci Signal, 2(76): ra29
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Harris M P, Simandl B K, Li Y, Beachy P A, Fallon J F (2001). Manifestation of the limb prepattern: limb development in the absence of sonic hedgehog function. Dev Biol, 236(2): 421–435
Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young K E, Corden J L, Westphal H, Beachy P A (1996). Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature, 383(6599): 407–413
Chuang P T, Kawcak T, McMahon A P (2003). Feedback control of mammalian Hedgehog signaling by the Hedgehog-binding protein, Hip1, modulates Fgf signaling during branching morphogenesis of the lung. Genes Dev, 17(3): 342–347
Chuang P T, McMahon A P (1999). Vertebrate Hedgehog signaling modulated by induction of a Hedgehog-binding protein. Nature, 397(6720): 617–621
Cooper A F, Yu K P, Brueckner M, Brailey L L, Johnson L, McGrath J M, Bale A E (2005). Cardiac and CNS defects in a mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development, 132(19): 4407–4417
Corbit K C, Aanstad P, Singla V, Norman A R, Stainier D Y, Reiter J F (2005). Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature, 437(7061): 1018–1021
Cox B, Briscoe J, Ulloa F (2010). SUMOylation by Pias1 regulates the activity of the Hedgehog dependent Gli transcription factors. PLoS ONE, 5(8): e11996
Dawber R J, Hebbes S, Herpers B, Docquier F, van den Heuvel M (2005). Differential range and activity of various forms of the Hedgehog protein. BMC Dev Biol, 5(1): 21
Denef N, Neubüser D, Perez L, Cohen S M (2000). Hedgehog induces opposite changes in turnover and subcellular localization of patched and smoothened. Cell, 102(4): 521–531
Desbordes S C, Sanson B (2003). The glypican Dally-like is required for Hedgehog signalling in the embryonic epidermis of Drosophila. Development, 130(25): 6245–6255
Ding Q, Fukami S, Meng X, Nishizaki Y, Zhang X, Sasaki H, Dlugosz A, Nakafuku M, Hui C (1999). Mouse suppressor of fused is a negative regulator of sonic hedgehog signaling and alters the subcellular distribution of Gli1. Curr Biol, 9(19): 1119–1122
Ding Q, Motoyama J, Gasca S, Mo R, Sasaki H, Rossant J, Hui C C (1998). Diminished Sonic hedgehog signaling and lack of floor plate differentiation in Gli2 mutant mice. Development, 125(14): 2533–2543
Dyer M A, Farrington S M, Mohn D, Munday J R, Baron M H (2001). Indian hedgehog activates hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis and can respecify prospective neurectodermal cell fate in the mouse embryo. Development, 128(10): 1717–1730
Endoh-Yamagami S, Evangelista M, Wilson D, Wen X, Theunissen JW, Phamluong K, Davis M, Scales S J, Solloway M J, de Sauvage F J, Peterson A S (2009). The mammalian Cos2 homolog Kif7 plays an essential role in modulating Hh signal transduction during development. Curr Biol, 19(15): 1320–1326
Frank-Kamenetsky M, Zhang XM, Bottega S, Guicherit O, Wichterle H, Dudek H, Bumcrot D, Wang F Y, Jones S, Shulok J, Rubin L L, Porter J A (2002). Small-molecule modulators of Hedgehog signaling: identification and characterization of Smoothened agonists and antagonists. J Biol, 1(2): 10
Gerdes J M, Davis E E, Katsanis N (2009). The vertebrate primary cilium in development, homeostasis, and disease. Cell, 137(1): 32–45
Goodrich L V, Milenković L, Higgins K M, Scott M P (1997). Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science, 277(5329): 1109–1113
Han C, Belenkaya T Y, Wang B, Lin X (2004). Drosophila glypicans control the cell-to-cell movement of Hedgehog by a dynaminindependent process. Development, 131(3): 601–611
Han Y G, Kwok B H, Kernan M J (2003). Intraflagellar transport is required in Drosophila to differentiate sensory cilia but not sperm. Curr Biol, 13(19): 1679–1686
Haycraft C J, Banizs B, Aydin-Son Y, Zhang Q, Michaud E J, Yoder B K (2005). Gli2 and Gli3 localize to cilia and require the intraflagellar transport protein polaris for processing and function. PLoS Genet, 1(4): e53
Heberlein U, Wolff T, Rubin G M (1993). The TGF beta homolog dpp and the segment polarity gene hedgehog are required for propagation of a morphogenetic wave in the Drosophila retina. Cell, 75(5): 913–926
Heydeck W, Zeng H, Liu A (2009). Planar cell polarity effector gene Fuzzy regulates cilia formation and Hedgehog signal transduction in mouse. Dev Dyn, 238(12): 3035–3042
Hirokawa N, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Takeda S (2006). Nodal flow and the generation of left-right asymmetry. Cell, 125(1): 33–45
Hooper J E, Scott M P (1989). The Drosophila patched gene encodes a putative membrane protein required for segmental patterning. Cell, 59(4): 751–765
Hoover A N, Wynkoop A, Zeng H, Jia J, Niswander L A, Liu A (2008). C2cd3 is required for cilia formation and Hedgehog signaling in mouse. Development, 135(24): 4049–4058
Houde C, Dickinson R J, Houtzager V M, Cullum R, Montpetit R, Metzler M, Simpson E M, Roy S, Hayden M R, Hoodless P A, Nicholson DW (2006). Hippi is essential for node cilia assembly and Sonic hedgehog signaling. Dev Biol, 300(2): 523–533
Hu Q, Milenkovic L, Jin H, Scott M P, Nachury M V, Spiliotis E T, Nelson W J (2010). A septin diffusion barrier at the base of the primary cilium maintains ciliary membrane protein distribution. Science, 329(5990): 436–439
Huangfu D, Anderson K V (2005). Cilia and Hedgehog responsiveness in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(32): 11325–11330
Huangfu D, Liu A, Rakeman A S, Murcia N S, Niswander L, Anderson K V (2003). Hedgehog signalling in the mouse requires intraflagellar transport proteins. Nature, 426(6962): 83–87
Hui C C, Joyner A L (1993). A mouse model of greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome: the extra-toesJ mutation contains an intragenic deletion of the Gli3 gene. Nat Genet, 3: 241–246
Humke E W, Dorn K V, Milenkovic L, Scott M P, Rohatgi R (2010). The output of Hedgehog signaling is controlled by the dynamic association between suppressor of Fused and the Gli proteins. Genes Dev, 24(7): 670–682
Jia H, Liu Y, Yan W, Jia J (2009a). PP4 and PP2A regulate Hedgehog signaling by controlling Smo and Ci phosphorylation. Development, 136(2): 307–316
Jia J, Kolterud A, Zeng H, Hoover A, Teglund S, Toftgård R, Liu A (2009b). Suppressor of Fused inhibits mammalian Hedgehog signaling in the absence of cilia. Dev Biol, 330(2): 452–460
Jia J, Tong C, Jiang J (2003). Smoothened transduces Hedgehog signal by physically interacting with Costal2/Fused complex through its Cterminal tail. Genes Dev, 17(21): 2709–2720
Jia J, Tong C, Wang B, Luo L, Jiang J (2004). Hedgehog signalling activity of Smoothened requires phosphorylation by protein kinase A and casein kinase I. Nature, 432(7020): 1045–1050
Jiang J, Struhl G (1998). Regulation of the Hedgehog and Wingless signalling pathways by the F-box/WD40-repeat protein Slimb. Nature, 391(6666): 493–496
Jin H, White S R, Shida T, Schulz S, Aguiar M, Gygi S P, Bazan J F, Nachury M V (2010). The conserved Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins assemble a coat that traffics membrane proteins to cilia. Cell, 141(7): 1208–1219
Kawakami T, Kawcak T, Li Y J, Zhang W, Hu Y, Chuang P T (2002). Mouse dispatched mutants fail to distribute hedgehog proteins and are defective in hedgehog signaling. Development, 129(24): 5753–5765
Khaliullina H, Panáková D, Eugster C, Riedel F, Carvalho M, Eaton S (2009). Patched regulates Smoothened trafficking using lipoproteinderived lipids. Development, 136(24): 4111–4121
Kovacs J J, Whalen E J, Liu R, Xiao K, Kim J, Chen M, Wang J, Chen W, Lefkowitz R J (2008). Beta-arrestin-mediated localization of smoothened to the primary cilium. Science, 320(5884): 1777–1781
Koziel L, Kunath M, Kelly O G, Vortkamp A (2004). Ext1-dependent heparan sulfate regulates the range of Ihh signaling during endochondral ossification. Dev Cell, 6(6): 801–813
Kraus P, Fraidenraich D, Loomis C A (2001). Some distal limb structures develop in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog signaling. Mech Dev, 100(1): 45–58
Krauss S, Concordet J P, Ingham P W (1993). A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell, 75(7): 1431–1444
Lee J D, Treisman J E (2001). Sightless has homology to transmembrane acyltransferases and is required to generate active Hedgehog protein. Curr Biol, 11(14): 1147–1152
Lee J J, Ekker S C, von Kessler D P, Porter J A, Sun B I, Beachy P A (1994). Autoproteolysis in hedgehog protein biogenesis. Science, 266(5190): 1528–1537
Lee Y, Miller H L, Russell H R, Boyd K, Curran T, McKinnon P J (2006). Patched2 modulates tumorigenesis in patched1 heterozygous mice. Cancer Res, 66(14): 6964–6971
Lei Q, Zelman A K, Kuang E, Li S, Matise M P (2004). Transduction of graded Hedgehog signaling by a combination of Gli2 and Gli3 activator functions in the developing spinal cord. Development, 131(15): 3593–3604
Lewis P M, Dunn M P, McMahon J A, Logan M, Martin J F, St-Jacques B, McMahon A P (2001). Cholesterol modification of sonic hedgehog is required for long-range signaling activity and effective modulation of signaling by Ptc1. Cell, 105(5): 599–612
Li Y, Zhang H, Litingtung Y, Chiang C (2006). Cholesterol modification restricts the spread of Shh gradient in the limb bud. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(17): 6548–6553
Liem K F Jr, He M, Ocbina P J, Anderson K V (2009). Mouse Kif7/Costal2 is a cilia-associated protein that regulates Sonic hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 106(32): 13377–13382
Litingtung Y, Chiang C (2000). Specification of ventral neuron types is mediated by an antagonistic interaction between Shh and Gli3. Nat Neurosci, 3(10): 979–985
Litingtung Y, Dahn R D, Li Y, Fallon J F, Chiang C (2002). Shh and Gli3 are dispensable for limb skeleton formation but regulate digit number and identity. Nature, 418(6901): 979–983
Liu A, Wang B, Niswander L A (2005). Mouse intraflagellar transport proteins regulate both the activator and repressor functions of Gli transcription factors. Development, 132(13): 3103–3111
Lum L, Yao S, Mozer B, Rovescalli A, Von Kessler D, Nirenberg M, Beachy P A (2003a). Identification of Hedgehog pathway components by RNAi in Drosophila cultured cells. Science, 299(5615): 2039–2045
Lum L, Zhang C, Oh S, Mann R K, von Kessler D P, Taipale J, Weis-Garcia F, Gong R, Wang B, Beachy P A (2003b). Hedgehog signal transduction via Smoothened association with a cytoplasmic complex scaffolded by the atypical kinesin, Costal-2. Mol Cell, 12(5): 1261–1274
Ma C, Zhou Y, Beachy P A, Moses K (1993). The segment polarity gene hedgehog is required for progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell, 75(5): 927–938
Ma Y, Erkner A, Gong R, Yao S, Taipale J, Basler K, Beachy P A (2002). Hedgehog-mediated patterning of the mammalian embryo requires transporter-like function of dispatched. Cell, 111(1): 63–75
Marigo V, Davey R A, Zuo Y, Cunningham J M, Tabin C J (1996). Biochemical evidence that patched is the Hedgehog receptor. Nature, 384(6605): 176–179
Martinelli D C, Fan C M (2007). Gas1 extends the range of Hedgehog action by facilitating its signaling. Genes Dev, 21(10): 1231–1243
Matise MP, Epstein D J, Park H L, Platt K A, Joyner A L (1998). Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons in the mouse central nervous system. Development, 125: 2759–2770
Matise M P, Joyner A L (1999). Gli genes in development and cancer. Oncogene, 18(55): 7852–7859
May S R, Ashique A M, Karlen M, Wang B, Shen Y, Zarbalis K, Reiter J, Ericson J, Peterson A S (2005). Loss of the retrograde motor for IFT disrupts localization of Smo to cilia and prevents the expression of both activator and repressor functions of Gli. Dev Biol, 287(2): 378–389
McCarthy R A, Barth J L, Chintalapudi M R, Knaak C, Argraves W S (2002). Megalin functions as an endocytic sonic hedgehog receptor. J Biol Chem, 277(28): 25660–25667
McLellan J S, Zheng X, Hauk G, Ghirlando R, Beachy P A, Leahy D J (2008). The mode of Hedgehog binding to Ihog homologues is not conserved across different phyla. Nature, 455(7215): 979–983
Merchant M, Evangelista M, Luoh S M, Frantz G D, Chalasani S, Carano R A, van Hoy M, Ramirez J, Ogasawara A K, McFarland L M, Filvaroff E H, French D M, de Sauvage F J (2005). Loss of the serine/threonine kinase fused results in postnatal growth defects and lethality due to progressive hydrocephalus. Mol Cell Biol, 25(16): 7054–7068
Methot N, Basler K (2000). Suppressor of fused opposes hedgehog signal transduction by impeding nuclear accumulation of the activator form of Cubitus interruptus. Development, 127(18): 4001–4010
Methot N, Basler K (2001). An absolute requirement for Cubitus interruptus in Hedgehog signaling. Development, 128(5): 733–742
Micchelli C A, The I, Selva E, Mogila V, Perrimon N (2002). Rasp, a putative transmembrane acyltransferase, is required for Hedgehog signaling. Development, 129(4): 843–851
Milenkovic L, Scott M P, Rohatgi R (2009). Lateral transport of Smoothened from the plasma membrane to the membrane of the cilium. J Cell Biol, 187(3): 365–374
Mukhopadhyay S, Wen X, Chih B, Nelson C D, Lane W S, Scales S J, Jackson P K (2010). TULP3 bridges the IFT-A complex and membrane phosphoinositides to promote trafficking of G proteincoupled receptors into primary cilia. Genes Dev, 24(19): 2180–2193
Nachury M V, Loktev A V, Zhang Q, Westlake C J, Peränen J, Merdes A, Slusarski D C, Scheller R H, Bazan J F, Sheffield V C, Jackson P K (2007). A core complex of BBS proteins cooperates with the GTPase Rab8 to promote ciliary membrane biogenesis. Cell, 129(6): 1201–1213
Nakano Y, Guerrero I, Hidalgo A, Taylor A, Whittle J R, Ingham P W (1989). A protein with several possible membrane-spanning domains encoded by the Drosophila segment polarity gene patched. Nature, 341(6242): 508–513
Norman R X, Ko H W, Huang V, Eun C M, Abler L L, Zhang Z, Sun X, Eggenschwiler J T (2009). Tubby-like protein 3 (TULP3) regulates patterning in the mouse embryo through inhibition of Hedgehog signaling. Hum Mol Genet, 18(10): 1740–1754
Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980). Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature, 287(5785): 795–801
Nybakken K, Vokes S A, Lin T Y, McMahon A P, Perrimon N (2005). A genome-wide RNA interference screen in Drosophila melanogaster cells for new components of the Hh signaling pathway. Nat Genet, 37(12): 1323–1332
Ocbina P J, Anderson K V (2008). Intraflagellar transport, cilia, and mammalian Hedgehog signaling: analysis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Dev Dyn, 237(8): 2030–2038
Ogden S K, Ascano M Jr, Stegman M A, Suber L M, Hooper J E, Robbins D J (2003). Identification of a functional interaction between the transmembrane protein Smoothened and the kinesin-related protein Costal2. Curr Biol, 13(22): 1998–2003
Ogden S K, Fei D L, Schilling N S, Ahmed Y F, Hwa J, Robbins D J (2008). G protein Galphai functions immediately downstream of Smoothened in Hedgehog signalling. Nature, 456(7224): 967–970
Okada A, Charron F, Morin S, Shin D S, Wong K, Fabre P J, Tessier-Lavigne M, McConnell S K (2006). Boc is a receptor for sonic hedgehog in the guidance of commissural axons. Nature, 444(7117): 369–373
Orenic T V, Slusarski D C, Kroll K L, Holmgren R A (1990). Cloning and characterization of the segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus Dominant of Drosophila. Genes Dev, 4(6): 1053–1067
Paces-Fessy M, Boucher D, Petit E, Paute-Briand S, Blanchet-Tournier M F (2004). The negative regulator of Gli, suppressor of fused (Sufu), interacts with SAP18, Galectin3 and other nuclear proteins. Biochem J, 378(Pt 2): 353–362
Pan Y, Bai C B, Joyner A L, Wang B (2006). Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by suppressing its processing and degradation. Mol Cell Biol, 26(9): 3365–3377
Panakova D, Sprong H, Marois E, Thiele C, Eaton S (2005). Lipoprotein particles are required for Hedgehog and Wingless signalling. Nature, 435(7038): 58–65
Park H L, Bai C, Platt K A, Matise MP, Beeghly A, Hui C C, Nakashima M, Joyner A L (2000). Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2 mutation. Development, 127: 1593–1605
Park T J, Haigo S L, Wallingford J B (2006). Ciliogenesis defects in embryos lacking inturned or fuzzy function are associated with failure of planar cell polarity and Hedgehog signaling. Nat Genet, 38(3): 303–311
Patterson V L, Damrau C, Paudyal A, Reeve B, Grimes D T, Stewart M E, Williams D J, Siggers P, Greenfield A, Murdoch J N (2009). Mouse hitchhiker mutants have spina bifida, dorso-ventral patterning defects and polydactyly: identification of Tulp3 as a novel negative regulator of the Sonic hedgehog pathway. Hum Mol Genet, 18(10): 1719–1739
Pearse R V 2nd, Collier L S, Scott M P, Tabin C J (1999). Vertebrate homologs of Drosophila suppressor of fused interact with the gli family of transcriptional regulators. Dev Biol, 212(2): 323–336
Pepinsky R B, Zeng C, Wen D, Rayhorn P, Baker D P, Williams K P, Bixler S A, Ambrose C M, Garber E A, Miatkowski K, Taylor F R, Wang E A, Galdes A (1998). Identification of a palmitic acidmodified form of human Sonic hedgehog. J Biol Chem, 273(22): 14037–14045
Porter J A, Ekker S C, Park WJ, von Kessler D P, Young K E, Chen C H, Ma Y, Woods A S, Cotter R J, Koonin E V, Beachy P A (1996a). Hedgehog patterning activity: role of a lipophilic modification mediated by the carboxy-terminal autoprocessing domain. Cell, 86(1): 21–34
Porter J A, von Kessler D P, Ekker S C, Young K E, Lee J J, Moses K, Beachy P A (1995). The product of hedgehog autoproteolytic cleavage active in local and long-range signalling. Nature, 374(6520): 363–366
Porter J A, Young K E, Beachy P A (1996b). Cholesterol modification of hedgehog signaling proteins in animal development. Science, 274(5285): 255–259
Preat T (1992). Characterization of Suppressor of fused, a complete suppressor of the fused segment polarity gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics, 132(3): 725–736
Price M A, Kalderon D (1999). Proteolysis of cubitus interruptus in Drosophila requires phosphorylation by protein kinase A. Development, 126(19): 4331–4339
Price M A, Kalderon D (2002). Proteolysis of the Hedgehog signaling effector Cubitus interruptus requires phosphorylation by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 and Casein Kinase 1. Cell, 108(6): 823–835
Qin J, Lin Y, Norman R X, Ko H W, Eggenschwiler J T (2011). Intraflagellar transport protein 122 antagonizes Sonic Hedgehog signaling and controls ciliary localization of pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108(4): 1456–1461
Rink J C, Gurley K A, Elliott S A, Sánchez Alvarado A (2009). Planarian Hh signaling regulates regeneration polarity and links Hh pathway evolution to cilia. Science, 326(5958): 1406–1410
Robbins D J, Nybakken K E, Kobayashi R, Sisson J C, Bishop J M, Thérond P P (1997). Hedgehog elicits signal transduction by means of a large complex containing the kinesin-related protein costal2. Cell, 90(2): 225–234
Roelink H, Porter J A, Chiang C, Tanabe Y, Chang D T, Beachy P A, Jessell T M (1995). Floor plate and motor neuron induction by different concentrations of the amino-terminal cleavage product of sonic hedgehog autoproteolysis. Cell, 81(3): 445–455
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Corcoran R B, Scott M P (2009). Hedgehog signal transduction by Smoothened: pharmacologic evidence for a 2-step activation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(9): 3196–3201
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L, Scott M P (2007). Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science, 317(5836): 372–376
Rohatgi R, Snell WJ (2010). The ciliary membrane. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 22(4): 541–546
Rosenbaum J L, Witman G B (2002). Intraflagellar transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 3(11): 813–825
Ruel L, Rodriguez R, Gallet A, Lavenant-Staccini L, Thérond P P (2003). Stability and association of Smoothened, Costal2 and Fused with Cubitus interruptus are regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol, 5(10): 907–913
Sarpal R, Todi S V, Sivan-Loukianova E, Shirolikar S, Subramanian N, Raff E C, Erickson J W, Ray K, Eberl D F (2003). Drosophila KAP interacts with the kinesin II motor subunit KLP64D to assemble chordotonal sensory cilia, but not sperm tails. Curr Biol, 13(19): 1687–1696
Sisson B E, Ziegenhorn S L, Holmgren R A (2006). Regulation of Ci and Su(fu) nuclear import in Drosophila. Dev Biol, 294(1): 258–270
Sisson J C, Ho K S, Suyama K, Scott M P (1997). Costal2, a novel kinesin-related protein in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell, 90(2): 235–245
St-Jacques B, Hammerschmidt M, McMahon A P (1999). Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev, 13(16): 2072–2086
Stone D M, Hynes M, Armanini M, Swanson T A, Gu Q, Johnson R L, Scott MP, Pennica D, Goddard A, Phillips H, Noll M, Hooper J E, de Sauvage F, Rosenthal A (1996). The tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for Sonic hedgehog. Nature, 384(6605): 129–134
Stone D M, Murone M, Luoh S, Ye W, Armanini M P, Gurney A, Phillips H, Brush J, Goddard A, de Sauvage F J, Rosenthal A (1999). Characterization of the human suppressor of fused, a negative regulator of the zinc-finger transcription factor Gli. J Cell Sci, 112(Pt 23): 4437–4448
Svard J, Heby-Henricson K, Persson-Lek M, Rozell B, Lauth M, Bergström A, Ericson J, Toftgård R, Teglund S (2006). Genetic elimination of Suppressor of fused reveals an essential repressor function in the mammalian Hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev Cell, 10(2): 187–197
Tabata T, Kornberg T B (1994). Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell, 76(1): 89–102
Taipale J, Cooper M K, Maiti T, Beachy P A (2002). Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of Smoothened. Nature, 418(6900): 892–897
Tay S Y, Ingham P W, Roy S (2005). A homologue of the Drosophila kinesin-like protein Costal2 regulates Hedgehog signal transduction in the vertebrate embryo. Development, 132(4): 625–634
Tenzen T, Allen B L, Cole F, Kang J S, Krauss R S, McMahon A P (2006). The cell surface membrane proteins Cdo and Boc are components and targets of the Hedgehog signaling pathway and feedback network in mice. Dev Cell, 10(5): 647–656
The I, Bellaiche Y, Perrimon N (1999). Hedgehog movement is regulated through tout velu-dependent synthesis of a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. Mol Cell, 4(4): 633–639
Tian H, Jeong J, Harfe B D, Tabin C J, McMahon A P (2005). Mouse Disp1 is required in sonic hedgehog-expressing cells for paracrine activity of the cholesterol-modified ligand. Development, 132(1): 133–142
Tran P V, Haycraft C J, Besschetnova T Y, Turbe-Doan A, Stottmann R W, Herron B J, Chesebro A L, Qiu H, Scherz P J, Shah J V, Yoder B K, Beier D R (2008). THM1 negatively modulates mouse sonic hedgehog signal transduction and affects retrograde intraflagellar transport in cilia. Nat Genet, 40(4): 403–410
Tukachinsky H, Lopez L V, Salic A (2010). A mechanism for vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: recruitment to cilia and dissociation of SuFu-Gli protein complexes. J Cell Biol, 191(2): 415–428
Varjosalo M, Li S P, Taipale J (2006). Divergence of hedgehog signal transduction mechanism between Drosophila and mammals. Dev Cell, 10(2): 177–186
Von Hoff D D, LoRusso P M, Rudin C M, Reddy J C, Yauch R L, Tibes R, Weiss G J, Borad MJ, Hann C L, Brahmer J R, Mackey HM, Lum B L, Darbonne WC, Marsters J C Jr, de Sauvage F J, Low J A (2009). Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 361(12): 1164–1172
Wang B, Fallon J F, Beachy P A (2000a). Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell, 100(4): 423–434
Wang C, Pan Y, Wang B (2010). Suppressor of fused and Spop regulate the stability, processing and function of Gli2 and Gli3 full-length activators but not their repressors. Development, 137(12): 2001–2009
Wang G, Amanai K, Wang B, Jiang J (2000b). Interactions with Costal2 and suppressor of fused regulate nuclear translocation and activity of cubitus interruptus. Genes Dev, 14(22): 2893–2905
Wang Y, Zhou Z, Walsh C T, McMahon A P (2009). Selective translocation of intracellular Smoothened to the primary cilium in response to Hedgehog pathway modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(8): 2623–2628
Wen X, Lai C K, Evangelista M, Hongo J A, de Sauvage F J, Scales S J (2010). Kinetics of hedgehog-dependent full-length Gli3 accumulation in primary cilia and subsequent degradation. Mol Cell Biol, 30(8): 1910–1922
Wijgerde M, McMahon J A, Rule M, McMahon A P (2002). A direct requirement for Hedgehog signaling for normal specification of all ventral progenitor domains in the presumptive mammalian spinal cord. Genes Dev, 16(22): 2849–2864
Williams E H, Pappano W N, Saunders A M, Kim M S, Leahy D J, Beachy P A (2010). Dally-like core protein and its mammalian homologues mediate stimulatory and inhibitory effects on Hedgehog signal response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107(13): 5869–5874
Wilson C W, Chen M H, Chuang P T (2009a). Smoothened adopts multiple active and inactive conformations capable of trafficking to the primary cilium. PLoS ONE, 4(4): e5182
Wilson C W, Nguyen C T, Chen M H, Yang J H, Gacayan R, Huang J, Chen J N, Chuang P T (2009b). Fused has evolved divergent roles in vertebrate Hedgehog signalling and motile ciliogenesis. Nature, 459(7243): 98–102
Yam P T, Langlois S D, Morin S, Charron F (2009). Sonic hedgehog guides axons through a noncanonical, Src-family-kinase-dependent signaling pathway. Neuron, 62(3): 349–362
Yan D, Wu Y, Yang Y, Belenkaya T Y, Tang X, Lin X (2010). The cellsurface proteins Dally-like and Ihog differentially regulate Hedgehog signaling strength and range during development. Development, 137(12): 2033–2044
Yao S, Lum L, Beachy P (2006). The ihog cell-surface proteins bind Hedgehog and mediate pathway activation. Cell, 125(2): 343–357
Yauch R L, Dijkgraaf G J, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn C P, Holcomb T, Pujara K, Stinson J, Callahan C A, Tang T, Bazan J F, Kan Z, Seshagiri S, Hann C L, Gould S E, Low J A, Rudin C M, de Sauvage F J (2009). Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science, 326(5952): 572–574
Yavari A, Nagaraj R, Owusu-Ansah E, Folick A, Ngo K, Hillman T, Call G, Rohatgi R, Scott M P, Banerjee U (2010). Role of lipid metabolism in smoothened derepression in hedgehog signaling. Dev Cell, 19(1): 54–65
Yin Y, Bangs F, Paton I R, Prescott A, James J, Davey M G, Whitley P, Genikhovich G, Technau U, Burt DW, Tickle C (2009). The Talpid3 gene (KIAA0586) encodes a centrosomal protein that is essential for primary cilia formation. Development, 136(4): 655–664
Zeng H, Hoover A N, Liu A (2010a). PCP effector gene Inturned is an important regulator of cilia formation and embryonic development in mammals. Dev Biol, 339(2): 418–428
Zeng H, Jia J, Liu A (2010b). Coordinated translocation of mammalian Gli proteins and suppressor of fused to the primary cilium. PLoS ONE, 5(12): e15900
Zeng X, Goetz J A, Suber LM, Scott WJ Jr, Schreiner CM, Robbins D J (2001). A freely diffusible form of Sonic hedgehog mediates longrange signalling. Nature, 411(6838): 716–720
Zhang C, Williams E H, Guo Y, Lum L, Beachy P A (2004). Extensive phosphorylation of Smoothened in Hedgehog pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101(52): 17900–17907
Zhang Q, Shi Q, Chen Y, Yue T, Li S, Wang B, Jiang J (2009). Multiple Ser/Thr-rich degrons mediate the degradation of Ci/Gli by the Cul3-HIB/SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106(50): 21191–21196
Zhang W, Zhao Y, Tong C, Wang G, Wang B, Jia J, Jiang J (2005). Hedgehog-regulated Costal2-kinase complexes control phosphorylation and proteolytic processing of Cubitus interruptus. Dev Cell, 8(2): 267–278
Zhang X M, Ramalho-Santos M, McMahon A P (2001). Smoothened mutants reveal redundant roles for Shh and Ihh signaling including regulation of L/R symmetry by the mouse node. Cell, 106(2): 781–792
Zhao Y, Tong C, Jiang J (2007). Hedgehog regulates smoothened activity by inducing a conformational switch. Nature, 450(7167): 252–258
Zheng X, Mann R K, Sever N, Beachy P A (2010). Genetic and biochemical definition of the Hedgehog receptor. Genes Dev, 24(1): 57–71
Zhu A J, Zheng L, Suyama K, Scott M P (2003). Altered localization of Drosophila Smoothened protein activates Hedgehog signal transduction. Genes Dev, 17(10): 1240–1252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, X., Liu, A. Hedgehog signaling: mechanisms and evolution. Front. Biol. 6, 504–521 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1146-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1146-2