Abstract
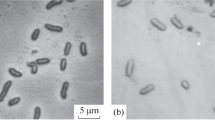
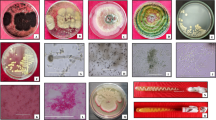
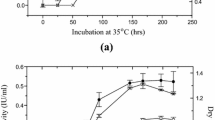
Cellulose is a kind of renewable resource that is abundant in nature. It can be degraded by microorganisms such as mildew. A mildew strain with high cellulase activity was isolated from mildewy maize cob and classified as Aspergillus glaucus XC9 by morphological and 18S rRNA gene sequence analyses. We studied the effects of nitrogen source, initial pH, temperature, incubation time, medium composition, and surfactants on cellulase production. Maximal activities of carboxymethylcellulase (6,812 U/g dry koji) and filter paperase (172 U/g dry koji) were obtained in conditions as follows: initial pH, 5.5–6.0; temperature, 30°C; cultivation period, 3–4 days; inoculum ratio, 6% (vol/vol); sugarcane bagasse/wheat bran ratio, 4:6. When bagasse was used as substrate and mixed with wet koji at a 1:1 (wt/wt) ratio, the yield of reducing sugars was 36.4%. The corresponding conversion rate of cellulose to reducing sugars went as high as 81.9%. The results suggest that A. glaucus XC9 is a preferred candidate for cellulase production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng H. Z. and Li Z. H., Microorganisms grown on cellulosic materials and utilization of biomass, Sci. Technol. Mark. Chem. Eng., 2001, 5: 17–20 (in Chinese)
Lutzen N. W., Nielsen M. H., Oxenboell K. M., Schulein M. and Olesen B. S., Cellulase and their applications in the conversion of lignocelluloses to fermentable sugars, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., 1983, 300: 283–291
Sanjeev K. S., Krishan L. K. and Harmeet S. G. Enzymatic saccharification of pretreated sunflower stalks, Biomass Bioenergy, 2002, 23: 237–243
Gao P. J., Qu Y. B., Wang T. H. and Yan B. X., Advances of molecular biology in microbial degradation of cellulose, Sci. Technol. Cellul., 1995, 3(2): 1–19 (in Chinese)
Xu Y. T., Shi J. L. and Zhang M., Microbial Engineering for Pollution Control, Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2001, 201–202 (in Chinese)
Ye J. Y., A new method for quick determination of cellulolytic microbes, Biol. Aviso., 1997, 32(12): 34 (in Chinese)
Ronald M. T. and Peter J. W., Use of congo red-polysaccharide interaction in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1982, 38: 148–158
Wei J. C., Fungi Identification Handbook, Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1979, 495–499 (in Chinese)
Zhang W. Z., Han T. C., Tang Y. Q., Wan Z. M. and Zhang S. D., Studies on rapid diagnosis of fungi secondary infection of acute necrosis pancreatitis by PCR, Chi. Lab. Diagn., 2000, 4(3): 109–111 (in Chinese)
Qi Y. P., Cellulase and Its Application, Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1990 (in Chinese)
Mandels M. and Anereotti R. E., Enzymatic hydrolysis of waste cellulose, Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp., 1976, 6: 17–21
Zhang S. Z., Enzyme Preparation Industry, 2nd vol, Beijing: Science Press, 1984, 619–623 (in Chinese)
Yan J. F., Wang Y. L., Wu L. Y. and Xiong Y. Z., Quick determination of whole-fiber, J. Wuhan Food Ind. Coll., 1994, 2: 29–32 (in Chinese)
Wang Y. L. and Yan J. F., Effect of surfactants on cellulase production by Trichoderma, Biotechnology, 2002, 12(3): 23–24 (in Chinese)
Yan Y. Q. and Zhang S. Q., Studies on the cellulase producer Trichoderma viride T-99, Appl. Environ. Biol., 1999, 5(Suppl): 200–203 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from the Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2005, 44(1) (in Chinese)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Long, M., Wu, X. et al. Screening and Characterization of the High-Cellulase-Producing Strain Aspergillus glaucus XC9. Front. Biol. China 1, 35–40 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-005-0010-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-005-0010-7