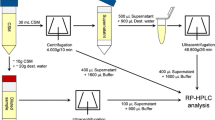
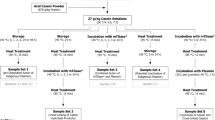
Abstract
The objective of present study is to investigate and compare the effects of different commercially utilized thermal treatments of 65 ℃ for 30 min, 80 ℃ for 15 s, 95 ℃ for 5 min and 137 ℃ for 5 s on the interactions between casein and β-lactoglobulin (β-LG) and the consequent digestion profile in simulating gastrointestinal (GI) environments. It was demonstrated, by the measurements of turbidity, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and molecular affinity between β-LG and casein, that high temperature (95 ℃ and 137 ℃) or long heating time (30 min) significantly increased the turbidity of β-LG and casein mixture, promoted the self-aggregates of β-LG, and enhanced the complexation of β-LG and κ-casein, as a result of the intermolecular thiol and disulfide interchange, as well as the strong affinity between β-LG and casein. Comparatively, the pasteurization of about 80 ℃ for 15 s decreased the turbidity of the model mixture of β-LG and casein, and did not lead to β-LG and κ-casein aggregates cross-linked with disulfide. In addition, the affinity of the heated casein and β-LG with the thermal treatment of 80 ℃ for 15 s was the lowest compared with the ones shown in the other three treatments. In the simulated gastric condition, the model mixture of β-LG and casein heated at 80 ℃ for 15 s appeared to be digested faster compared with the one treated at 137 ℃ for 5 s. However, this phenomenon could not be observed obviously in the simulated intestinal condition. Therefore, the formation of disulfide between the reactive thiols in denatured β-LG and κ-casein accounts mainly for the β-LG self-aggregates and the β-LG-casein complexes in the commercially utilized thermal treatments. In terms of interactions between β-LG and casein, pasteurization may be considered as an ideal thermal treatment of milk for heating processing, without significant impact on product properties.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Doiron, P. Yu, J.J. McKinnon, D.A. Christensen, J. Dairy. Sci. 92, 3319–3330 (2009)
R.N. Pereira, J.A. Teixeira, A.A. Vicente, L.P. Cappato, M. V. Da Silva Ferreira, R. Da Silva Rocha, A. G. Da Cruz, Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 22, SI 95–101 (2018)
R.W. Han, R.J. Shi, Z.N. Yu, H. Ho, Q.J. Du, X.H. Sun, J. Wang, H.N. Jiang, R.B. Fan, Y.X. Yang, Food Chem. 365, 130640 (2021)
S.G. Anema, Int. Dairy. J. 122, 105–136 (2021)
G.C. Liu, C. Carøe, Z.H. Qin, D.M.E. Munk, M. Crafack, M.A. Petersena, L.L. Ahrné, LWT - Food Sci. Techn. 127, 109370 (2020)
M. Corredig, D.G. Dalgleish, Int. Dairy. J. 9, 233–236 (1999)
L. Condict, V.D. Paramita, S. Kasapis, Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 27, 8–17 (2019)
M. Corredig, D.G. Dalgleish, J. Dairy. Res. 63, 441–449 (1996)
Y. Wada, B. Lönnerdal, J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 4175–4185 (2014)
L.L. Zhao, X.L. Wang, Q. Tian, X.Y. Mao, J. Dairy. Sci. 99, 7768–7775 (2016)
D.G. Dalgleish, L. van Mourik, M. Corredig, J. Agric. Food Chem. 45, 4806–4813 (1997)
Z. Pan, A.Q. Ye, A. Dave, K. Fraser, H. Singh, J. Dairy. Sci. 105, 3871–3882 (2022)
M. Carbonaro, M. Cappelloni, S. Sabbadini, E. Carnovale, J. Agric. Food Chem. 45, 95–100 (1997)
Y.D. Livney, D.G. Dalgleish, J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 5527–5532 (2004)
M.S. Pinto, J. Léonil, G. Henry, C. Cauty, A.F. Carvalho, S. Bouhallab, Food Res. Int. 55, 70–76 (2014)
S.F. Hansen, S.D. Nielsen, J.T. Rasmusen, L.B. Larsen, L. Wiking, J. Dairy. Sci. 103, 5874–5881 (2020)
P. Smits, J.H.V. van Brouwershawen, J. Dairy. Res. 47, 313–325 (1980)
P.J. Wang, H.N. Liu, P.C. Wen, H. Zhang, H.Y. Guo, F.Z. Ren, Int. Dairy. J. 31, 107–110 (2013)
Y.H. Ye, K. Engholm-Keller, Y.J. Fang, C.F. Nielsen, A. Jordà, M.N. Lund, D.E.W. Chatterton, Food Funct. 13, 344–355 (2022)
N.H.A. Nguyen, M. Wong, S.G. Anema, P. Havea, F. Guyomarc’h, J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 2337–2342 (2012)
Z. Yuksel, Y.K. Erdem, J. Food Eng. 67, 301–308 (2005)
N. Parris, J.M. Purcell, S.M. Ptashkin, J. Agric. Food Chem. 39, 2167–2170 (1991)
T.T. Wang, Z.W. Guo, Z.P. Liu, Q.Y. Feng, X.L. Wang, Q. Tian, F.Z. Ren, X.Y. Mao, J. Dairy. Sci. 99, 6137–6143 (2016)
Z. Haque, J.E. Kinsella, J. Dairy. Res. 55, 67–80 (1988)
X.P. Hu, F.W. Yin, D.Y. Zhou, H.K. Xie, B.W. Zhu,, X.G. Tian, C. Wang, F. Shahidi, X. Ch. Ma. Food Chem. 276, 675–679 (2019)
Y. Hu, C.X. He, M.W. Woo, H. Xiong, J.W. Hu, Q. Zhao, Food Funct. 10, 8106 (2019)
G.A. Manderson, M.J. Hardman, L.K. Creamer, J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 5052–5061 (1998)
G.D. Moro, P.A. Báez, G.A. Busti, N.J. Ballerini, Delorenzi, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1009–1015 (2011)
Y. Cho, H. Singh, L.K. Creamer, J. Dairy. Res. 70, 61–71 (2003)
P.F. Fox, T. Uniacke-Lowe, P.L.H. Mcsweeney, J.A. O’Mahony, Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2nd edn. (Springer International Publishing, New York, NY, 2015)
Y.H. Hong, K. Guthy, H. Klostermeyer, Milchwissenschaft. 39, 28–30 (1984)
M.A. Nabhan, J.M. Girardet, S. Campagna, J.L. Gaillard, Y. Le Roux, J. Dairy. Sci. 87, 3614–3622 (2004)
A. Kroke, A.M. Schmidt, N. Amini, A. Kalotai, J. Lehmann, J.M. Haardt, H.A. Bauer, H. Bischoff-Ferrari, S. Boeing, S. Egert, T. Ellinger, S. Kuhn, S. Louis, K. Lorkowski, T. Nimptsch, M.B. Remer, R. Schulze, G.I. Siener, D. Stangl, A. Volkert, A.E. Zittermann, B. Buyken, L. Watzl, Schwingshackl, Eur. J. Nutr. 61, 2091–2101 (2022)
C. Mackie, Opin. Food Sci. 31, 96–101 (2020)
M. Holwerda, K.J.M. Paulussen, M. Overkamp, J.P.B. Goessens, I.F. Kramer, W.K.W.H. Wodziget, L.B. Verdijk, L. C. P. G. M. de Groot, L. J. C. van Loon, Am. J. Physiol-Endocrinol. Metab. 317, E473–E482 (2019)
M. Jarzaguet, S. Polakof, J. David, C. Migné, G. Joubrel, T. Efstathiou, D. Remond, L. Mosoni, D. Dardevet, Food Funct. 9, 6527–6535 (2018)
P.F. dos Santos, L. Ozorio, T.L. Azevedo, L.M.C. Cabral, C. Mellinger-Silva, Carpathian J. Food Sci. Tech. 14, 190–196 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province—Outstanding Youth Foundation (BK20200022), Jiangsu Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Fund (CX(21)3040), Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project (NZ2021034), National Natural Science Foundation of China—Youth Foundation (No. 31901760), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province—Youth Foundation (BK20190530).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.N. and B.H. wrote the main manuscript text and Y.L. prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3 and 5 and C.R. prepared Fig. 4. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Y., Ruan, C., Hu, B. et al. Effect of Commercially Utilized Thermal Treatments on Interactions Between Casein and β-lactoglobulin and Their Digestion in Simulated Gastrointestinal Environment. Food Biophysics 18, 353–361 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09776-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09776-9