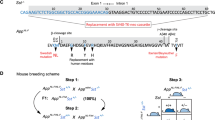
Abstract
Nitric oxide has been implicated in the regulation of enzyme activity, particularly the activity of metalloproteinases. Since the inducible form of the nitric oxide synthase (NOS2), is upregulated in Alzheimer’s disease, we investigated the activity of two amyloid β degrading enzymes, IDE and neprilysin. In vitro we demonstrated that the activity of IDE was inhibited by *NO donor Sin-1, whereas activity of neprilysin remained unaffected. In vivo the activity of insulin-degrading enzyme was lowered in APP/PS1 mice, but not in APP/PS1/NOS2(−/−) mice. These data suggest that NOS2 upregulation impairs amyloid β degradation through negative regulation of IDE activity and thus loss of NOS2 activity will positively influence amyloid β clearance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEBSF:
-
4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride
- PN:
-
Peroxynitrate
- Sin-1:
-
3-morpholino-sydnonimine
- DetaNONOate:
-
(Z)-1-[N-(2-aminoethyl)-N-(2-ammonioethyl)amino]diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate
- GSNO:
-
S-Nitrosoglutathione
References
Bulloj A, Leal MC, Xu H, Castaño EM, Morelli L (2010) Insulin-degrading enzyme sorting in exosomes: a secretory pathway for a key brain amyloid-beta degrading protease. J Alzheim Dis 19:79–95
Butterfield DA, Reed TT, Perluigi M, De Marco C, Coccia R, Keller JN, Markesbery WR, Sultana R (2007) Elevated levels of 3-nitrotyrosine in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: implications for the role of nitration in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1148:243–248
Castegna A, Thongboonkerd V, Klein JB, Lynn B, Markesbery WR, Butterfield DA (2003) Proteomic identification of nitrated proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain. J Neurochem 85:1394–1401
Cordes CM, Bennett RG, Siford GL, Hamel FG (2009) Nitric oxide inhibits insulin-degrading enzyme activity and function through S-nitrosylation. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1064–1073
Crow JP, Ischiropoulos H (1996) [17] Detection and quantitation of nitrotyrosine residues in proteins: In vivo marker of peroxynitrite. In: Nitric oxide part B: physiological and pathological processes. Academic Press, pp 185–194
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ, Guenette S (2003) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4162–4167
Fernández-Vizarra P, Fernández AP, Castro-Blanco S, Encinas JM, Serrano J, Bentura ML, Muñoz P, Martínez-Murillo R, Rodrigo J (2004) Expression of nitric oxide system in clinically evaluated cases of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:287–305
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140:918–934
Gow AJ, Farkouh CR, Munson DA, Posencheg MA, Ischiropoulos H (2004) Biological significance of nitric oxide-mediated protein modifications. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L262–L268
Heneka MT, Wiesinger H, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Riederer P, Feinstein DL, Klockgether T (2001) Neuronal and glial coexpression of argininosuccinate synthetase and inducible nitric oxide synthase in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:906–916
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK, Terwel D, Kummer MP (2010) Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 117:919–947
Hensley K, Maidt ML, Yu Z, Sang H, Markesbery WR, Floyd RA (1998) Electrochemical analysis of protein nitrotyrosine and dityrosine in the Alzheimer brain indicates region-specific accumulation. J Neurosci 18:8126–8132
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Watanabe K, Sekiguchi M, Hosoki E, Kawashima-Morishima M, Lee HJ, Hama E, Sekine-Aizawa Y et al (2000) Identification of the major Abeta1-42-degrading catabolic pathway in brain parenchyma: suppression leads to biochemical and pathological deposition. Nat Med 6:143–150
Jankowsky JL, Slunt HH, Ratovitski T, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Borchelt DR (2001) Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: a comparison of strategies. Biomol Eng 17:157–165
Kummer MP, Hermes M, Delekarte A, Hammerschmidt T, Kumar S, Terwel D, Walter J, Pape H-C, König S, Roeber S et al (2011) Nitration of tyrosine 10 critically enhances amyloid β aggregation and plaque formation. Neuron 71:833–844
Laubach VE, Shesely EG, Smithies O, Sherman PA (1995) Mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase are not resistant to lipopolysaccharide-induced death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:10688–10692
Lee SC, Zhao ML, Hirano A, Dickson DW (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the Alzheimer disease hippocampus: association with Hirano bodies, neurofibrillary tangles, and senile plaques. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:1163–1169
Lüth HJ, Holzer M, Gärtner U, Staufenbiel M, Arendt T (2001) Expression of endothelial and inducible NOS-isoforms is increased in Alzheimer’s disease, in APP23 transgenic mice and after experimental brain lesion in rat: evidence for an induction by amyloid pathology. Brain Res 913:57–67
Lüth H-J, Münch G, Arendt T (2002) Aberrant expression of NOS isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease is structurally related to nitrotyrosine formation. Brain Res 953:135–143
Malito E, Hulse RE, Tang W-J (2008) Amyloid β-degrading cryptidases: insulin degrading enzyme, neprilysin, and presequence peptidase. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2574–2585
Martin-Romero FJ, Gutiérrez-Martin Y, Henao F, Gutiérrez-Merino C (2004) Fluorescence measurements of steady state peroxynitrite production upon SIN-1 decomposition: NADH versus dihydrodichlorofluorescein and dihydrorhodamine 123. J Fluoresc 14:17–23
Nakamura T, Lipton SA (2009) Cell death: protein misfolding and neurodegenerative diseases. Apoptosis 14:455–468
Nikitovic D, Holmgren A (1996) S-nitrosoglutathione is cleaved by the thioredoxin system with liberation of glutathione and redox regulating nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 271:19180–19185
Pervin S, Singh R, Chaudhuri G (2001) Nitric oxide-induced cytostasis and cell cycle arrest of a human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231): potential role of cyclin D1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:3583–3588
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 362:329–344
Radi R (2004) Nitric oxide, oxidants, and protein tyrosine nitration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4003–4008
Ralat LA, Ren M, Schilling AB, Tang W-J (2009) Protective role of Cys-178 against the inactivation and oligomerization of human insulin-degrading enzyme by oxidation and nitrosylation. J Biol Chem 284:34005–34018
Rodrigo J, Fernández-Vizarra P, Castro-Blanco S, Bentura ML, Nieto M, Gómez-Isla T, Martínez-Murillo R, MartInez A, Serrano J, Fernández AP (2004) Nitric oxide in the cerebral cortex of amyloid-precursor protein (SW) Tg2576 transgenic mice. Neuroscience 128:73–89
Smith MA, Richey Harris PL, Sayre LM, Beckman JS, Perry G (1997) Widespread peroxynitrite-mediated damage in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 17:2653–2657
Song E-S, Juliano MA, Juliano L, Hersh LB (2003) Substrate activation of insulin-degrading enzyme (insulysin). A potential target for drug development. J Biol Chem 278:49789–49794
Souza JM, Peluffo G, Radi R (2008) Protein tyrosine nitration—functional alteration or just a biomarker? Free Radic Biol Med 45:357–366
Stamler JS, Toone EJ, Lipton SA, Sucher NJ (1997) (S)NO signals: translocation, regulation, and a consensus motif. Neuron 18:691–696
Tamboli IY, Barth E, Christian L, Siepmann M, Kumar S, Singh S, Tolksdorf K, Heneka MT, Lütjohann D, Wunderlich P et al (2010) Statins promote the degradation of extracellular amyloid {beta}-peptide by microglia via stimulation of exosome-associated insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) secretion. J Biol Chem 285:37405–37414
Tohgi H, Abe T, Yamazaki K, Murata T, Ishizaki E, Isobe C (1999) Alterations of 3-nitrotyrosine concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid during aging and in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 269:52–54
Vodovotz Y, Lucia MS, Flanders KC, Chesler L, Xie QW, Smith TW, Weidner J, Mumford R, Webber R, Nathan C et al (1996) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in tangle-bearing neurons of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Exp Med 184:1425–1433
Wilcock DM, Lewis MR, Van Nostrand WE, Davis J, Previti ML, Gharkholonarehe N, Vitek MP, Colton CA (2008) Progression of amyloid pathology to Alzheimer’s disease pathology in an amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse model by removal of nitric oxide synthase 2. J Neurosci 28:1537–1545
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (HE 3350/4-1,4-2) to MTH.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kummer, M.P., Hülsmann, C., Hermes, M. et al. Nitric Oxide Decreases the Enzymatic Activity of Insulin Degrading Enzyme in APP/PS1 Mice. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7, 165–172 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9339-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9339-7