Abstract
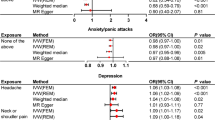
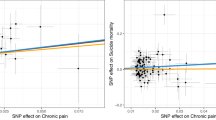
Observational studies have reported positive associations between opioid dependence and major mental disorders. However, the causal relationships and causal mechanisms between opioid dependence and mental disorders remain unknown due to potential confounding bias and reverse causality. In this study, we aim to investigate the causal associations and possible mediating mechanisms between opioid dependence and mental disorders via Mendelian randomization. Comprehensive bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) studies were conducted between opioid dependence and major mental disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, panic disorder, anorexia, obsessive–compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, and insomnia. Inverse variance weighted approach was adopted as the primary analytic method with series of sensitivity analyses. Mediation effects of chronic pain along the opioid dependence–mental disorders causal pathway were assessed by multivariate MR and two-step MR. Forward MR identified significant positive causal effects of opioid dependence on insomnia (OR = 1.03, 95% CI = (1.01, 1.05), p = 0.005), while reverse MR showed significant positive causal effects of schizophrenia on opioid dependence (OR = 1.20, 95% CI = (1.07, 1.34), p = 0.002). No significant causal associations were found between opioid dependence and other mental disorders. Neither opioid dependence on insomnia nor schizophrenia on opioid dependence causal pathway was significantly mediated by chronic pain. Higher risks of genetically predicted opioid dependence may lead to higher risks of insomnia, while higher risks of genetically predicted schizophrenia may lead to higher risks of developing opioid dependence. The majority of causal effects were acted directly rather than via chronic pain.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The GWAS summary data of opioid dependence is available at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/studies/GCST90043725. The GWAS summary data of 8 mental disorders are available at https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/an2019/14671980; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/bip2021_noUKBB/22564402; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/MDD2_MDD2018_GWAS_sumstats_w_o_UKBB/21655784; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/ocd2018/14672103; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/panic2019/16602218; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/ptsd2019/14672133; https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/scz2022/19426775; https://research.23andme.com/collaborate/#publication. The GWAS summary data of chronic pain is available at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/studies/GCST90043740. Ethics statement All relevant GWAS had obtained ethical permissions from corresponding institutional review boards. Since our study involves only publicly available GWAS summary statistics, no ethical approval was required from the institutional review board.
References
Abdel-Baki, A., Ouellet-Plamondon, C., Salvat, É., Grar, K., & Potvin, S. (2017). Symptomatic and functional outcomes of substance use disorder persistence 2 years after admission to a first-episode psychosis program. Psychiatry Research, 247, 113–119.
Amare, A. T., Vaez, A., Hsu, Y. H., Direk, N., Kamali, Z., Howard, D. M., ... & Hartman, C. A. (2020). Bivariate genome-wide association analyses of the broad depression phenotype combined with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder or schizophrenia reveal eight novel genetic loci for depression. Molecular psychiatry, 25(7), 1420–1429.
Arnold, P. D., Askland, K. D., Barlassina, C., Bellodi, L., Bienvenu, O. J., Black, D., ... & Zai, G. (2018). Revealing the complex genetic architecture of obsessive-compulsive disorder using meta-analysis. Molecular psychiatry, 23(5), 1181–1181.
Asaad, T. A., Ghanem, M. H., Samee, A. M. A., & El-Habiby, M. M. (2011). Sleep profile in patients with chronic opioid abuse: A polysomnographic evaluation in an Egyptian sample. Addictive Disorders & Their Treatment, 10(1), 21–28.
Barkus, E. (2016). High-potency cannabis increases the risk of psychosis. BMJ Ment Health, 19(2), 54–54.
Battle, D. E. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM). In Codas, 25(2), 191–192.
Burgess, S., & Thompson, S. G. (2017). Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. European Journal of Epidemiology, 32, 377–389.
Burgess, S., Davies, N. M., & Thompson, S. G. (2016). Bias due to participant overlap in two-sample Mendelian randomization. Genetic Epidemiology, 40(7), 597–608.
Cardno, A. G., & Owen, M. J. (2014). Genetic relationships between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 40(3), 504–515.
Carter, A. R., Sanderson, E., Hammerton, G., Richmond, R. C., Davey Smith, G., Heron, J., ... & Howe, L. D. (2021). Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: Current methods and challenges for implementation. European journal of epidemiology, 36(5), 465–478.
Chambers, R. A., Krystal, J. H., & Self, D. W. (2001). A neurobiological basis for substance abuse comorbidity in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 50(2), 71–83.
Chang, K. C., Lee, K. Y., Lu, T. H., Hwang, J. S., Lin, C. N., Ting, S. Y., ... & Wang, J. D. (2019). Opioid agonist treatment reduces losses in quality of life and quality-adjusted life expectancy in heroin users: Evidence from real world data. Drug and alcohol dependence, 201, 197–204.
Chiappelli, J., Chen, S., Hackman, A., & Hong, L. E. (2018). Evidence for differential opioid use disorder in schizophrenia in an addiction treatment population. Schizophrenia Research, 194, 26–31.
Choi, K. W., Chen, C. Y., Stein, M. B., Klimentidis, Y. C., Wang, M. J., Koenen, K. C., & Smoller, J. W. (2019). Assessment of bidirectional relationships between physical activity and depression among adults: A 2-sample mendelian randomization study. JAMA Psychiatry, 76(4), 399–408.
Clark, S. D., & Abi-Dargham, A. (2019). The role of dynorphin and the kappa opioid receptor in the symptomatology of schizophrenia: A review of the evidence. Biological Psychiatry, 86(7), 502–511.
Clark, S. D., Van Snellenberg, J. X., Lawson, J. M., & Abi-Dargham, A. (2020). Opioid antagonists are associated with a reduction in the symptoms of schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Neuropsychopharmacology, 45(11), 1860–1869.
Davis, M. A., Lin, L. A., Liu, H., & Sites, B. D. (2017). Prescription opioid use among adults with mental health disorders in the United States. The Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine, 30(4), 407–417.
Degenhardt, L., Grebely, J., Stone, J., Hickman, M., Vickerman, P., Marshall, B. D., ... & Larney, S. (2019). Global patterns of opioid use and dependence: Harms to populations, interventions, and future action. The Lancet, 394(10208), 1560–1579.
Dijkstra, B. A., De Jong, C. A., Krabbe, P. F., & van der Staak, C. P. (2008). Prediction of abstinence in opioid-dependent patients. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 2(4), 194–201.
Dolsen, E. A., & Harvey, A. G. (2017). Life-time history of insomnia and hypersomnia symptoms as correlates of alcohol, cocaine and heroin use and relapse among adults seeking substance use treatment in the United States from 1991 to 1994. Addiction, 112(6), 1104–1111.
Dowell, D., Arias, E., Kochanek, K., Anderson, R., Guy, G. P., Losby, J. L., & Baldwin, G. (2017). Contribution of opioid-involved poisoning to the change in life expectancy in the United States, 2000–2015. JAMA, 318(11), 1065–1067.
Dunn, K. E., Saulsgiver, K. A., Miller, M. E., Nuzzo, P. A., & Sigmon, S. C. (2015). Characterizing opioid withdrawal during double-blind buprenorphine detoxification. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 151, 47–55.
Farrell, M., Boys, A., Bebbington, P., Brugha, T., Coid, J., Jenkins, R., ... & Taylor, C. (2002). Psychosis and drug dependence: Results from a national survey of prisoners. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 181(5), 393–398.
Feingold, D., Brill, S., Goor-Aryeh, I., Delayahu, Y., & Lev-Ran, S. (2018). The association between severity of depression and prescription opioid misuse among chronic pain patients with and without anxiety: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 235, 293–302.
Forstner, A. J., Awasthi, S., Wolf, C., Maron, E., Erhardt, A., Czamara, D., ... & Schumacher, J. (2021). Genome-wide association study of panic disorder reveals genetic overlap with neuroticism and depression. Molecular psychiatry, 26(8), 4179–4190.
Gage, S. H., & Munafò, M. R. (2015). Rethinking the association between smoking and schizophrenia. The Lancet Psychiatry, 2(2), 118–119.
Gage, S. H., Bowden, J., Davey Smith, G., & Munafò, M. R. (2018). Investigating causality in associations between education and smoking: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. International Journal of Epidemiology, 47(4), 1131–1140.
Garland, E. L., Froeliger, B., Zeidan, F., Partin, K., & Howard, M. O. (2013). The downward spiral of chronic pain, prescription opioid misuse, and addiction: Cognitive, affective, and neuropsychopharmacologic pathways. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(10), 2597–2607.
Haack, M., Simpson, N., Sethna, N., Kaur, S., & Mullington, J. (2020). Sleep deficiency and chronic pain: Potential underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Neuropsychopharmacology, 45(1), 205–216.
Han, B., Compton, W. M., Jones, C. M., & Cai, R. (2015). Nonmedical prescription opioid use and use disorders among adults aged 18 through 64 years in the United States, 2003–2013. JAMA, 314(14), 1468–1478.
Han, B., Jones, C. M., Blanco, C., & Compton, W. M. (2017). National trends in and correlates of nonmedical use of prescription stimulants, nonmedical use frequency, and use disorders. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 78(9), 21718.
Hartwell, E. E., Pfeifer, J. G., McCauley, J. L., Moran-Santa Maria, M., & Back, S. E. (2014). Sleep disturbances and pain among individuals with prescription opioid dependence. Addictive Behaviors, 39(10), 1537–1542.
Hjorthøj, C., Albert, N., & Nordentoft, M. (2018). Association of substance use disorders with conversion from schizotypal disorder to schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry, 75(7), 733–739.
Huedo-Medina, T. B., Sánchez-Meca, J., Marín-Martínez, F., & Botella, J. (2006). Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychological Methods, 11(2), 193.
Jiang, L., Zheng, Z., Fang, H., & Yang, J. (2021). A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nature Genetics, 53(11), 1616–1621.
Jones, C. M. (2018). Reprint of trends and key correlates of prescription opioid injection misuse in the United States. Addictive Behaviors, 86, 24–31.
Jones, C. M., & McCance-Katz, E. F. (2019). Co-occurring substance use and mental disorders among adults with opioid use disorder. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 197, 78–82.
Kay, D. C., Pickworth, W. B., & Neider, G. L. (1981). Morphine-like insomnia from heroin in nondependent human addicts. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 11(2), 159–169.
Kendler, K. S., Lönn, S. L., Sundquist, J., & Sundquist, K. (2015). Smoking and schizophrenia in population cohorts of Swedish women and men: A prospective co-relative control study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 172(11), 1092–1100.
Khantzian, E. J. (1997). The self-medication hypothesis of substance use disorders: A reconsideration and recent applications. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 4(5), 231–244.
Ko, J. Y., Patrick, S. W., Tong, V. T., Patel, R., Lind, J. N., & Barfield, W. D. (2016). Incidence of neonatal abstinence syndrome—28 states, 1999–2013. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 65(31), 799–802.
Koob, G. F. (2020). Neurobiology of opioid addiction: Opponent process, hyperkatifeia, and negative reinforcement. Biological Psychiatry, 87(1), 44–53.
Li, K. J., Chen, A., & DeLisi, L. E. (2020). Opioid use and schizophrenia. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 33(3), 219–224.
Moore, J. T., & Kelz, M. B. (2009). Opiates, sleep, and pain: The adenosinergic link. The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, 111(6), 1175–1176.
Morgan, P. T., Pace-Schott, E., Pittman, B., Stickgold, R., & Malison, R. T. (2010). Normalizing effects of modafinil on sleep in chronic cocaine users. American Journal of Psychiatry, 167(3), 331–340.
Mueser, K. T., Yarnold, P. R., Levinson, D. F., Singh, H., Bellack, A. S., Kee, K., ... & Yadalam, K. G. (1990). Prevalence of substance abuse in schizophrenia: Demographic and clinical correlates. Schizophrenia bulletin, 16(1), 31–56.
Mullins, N., Forstner, A. J., O’Connell, K. S., Coombes, B., Coleman, J. R., Qiao, Z., ... & Potash, J. B. (2021). Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nature genetics, 53(6), 817–829.
Nievergelt, C. M., Maihofer, A. X., Klengel, T., Atkinson, E. G., Chen, C. Y., Choi, K. W., ... & Stevens, J. S. (2019). International meta-analysis of PTSD genome-wide association studies identifies sex-and ancestry-specific genetic risk loci. Nature communications, 10(1), 4558.
Nordmann, S., Lions, C., Vilotitch, A., Michel, L., Mora, M., Spire, B., ... & ANRS Methaville study group. (2016). A prospective, longitudinal study of sleep disturbance and comorbidity in opiate dependence (the ANRS Methaville study). Psychopharmacology, 233, 1203–1213.
Overdose, O. (2018). Understanding the epidemic. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta.
Pasman, J. A., Verweij, K. J., Gerring, Z., Stringer, S., Sanchez-Roige, S., Treur, J. L., ... & Vink, J. M. (2018). GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal effect of schizophrenia liability. Nature neuroscience, 21(9), 1161–1170.
Peters, P. J., Pontones, P., Hoover, K. W., Patel, M. R., Galang, R. R., Shields, J., ... & Duwve, J. M. (2016). HIV infection linked to injection use of oxymorphone in Indiana, 2014–2015. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(3), 229–239.
Pierce, B. L., & Burgess, S. (2013). Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: Subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. American Journal of Epidemiology, 178(7), 1177–1184.
Pierce, B. L., Ahsan, H., & VanderWeele, T. J. (2011). Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. International Journal of Epidemiology, 40(3), 740–752.
Regier, D. A., Farmer, M. E., Rae, D. S., Locke, B. Z., Keith, S. J., Judd, L. L., & Goodwin, F. K. (1990). Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse: Results from the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) study. JAMA, 264(19), 2511–2518.
Rosoff, D. B., Smith, G. D., & Lohoff, F. W. (2021). Prescription opioid use and risk for major depressive disorder and anxiety and stress-related disorders: A multivariable Mendelian randomization analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 78(2), 151–160.
Roth, T. (2009). Does effective management of sleep disorders reduce substance dependence? Drugs, 69, 65–75.
Sayers, S. L., Campbell, E. C., Kondrich, J., Mann, S. C., Cornish, J., O’Brien, C., & Caroff, S. N. (2005). Cocaine abuse in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine versus haloperidol. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 193(6), 379–386.
Schierenbeck, T., Riemann, D., Berger, M., & Hornyak, M. (2008). Effect of illicit recreational drugs upon sleep: Cocaine, ecstasy and marijuana. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 12(5), 381–389.
Schulte, M. T., & Hser, Y. I. (2013). Substance use and associated health conditions throughout the lifespan. Public Health Reviews, 35(2), 1–27.
SCORE, U. R. A. P. (2018). Statistical inference in two-sample summary-data mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.09652.
Serdarevic, M., Osborne, V., Striley, C. W., & Cottler, L. B. (2017). The association between insomnia and prescription opioid use: Results from a community sample in Northeast Florida. Sleep Health, 3(5), 368–372.
Shaheed, C. A., McLachlan, A. J., & Maher, C. G. (2019). Rethinking “long term” opioid therapy. Bmj, 367.
Shaw, I. R., Lavigne, G., Mayer, P., & Choinière, M. (2005). Acute intravenous administration of morphine perturbs sleep architecture in healthy pain-free young adults: A preliminary study. Sleep, 28(6), 677–682.
Shekhar, A. (2019). Role of kappa opioid receptors in symptoms of schizophrenia: What is the neurobiology? Biological Psychiatry, 86(7), 494–496.
Skrivankova, V. W., Richmond, R. C., Woolf, B. A., Yarmolinsky, J., Davies, N. M., Swanson, S. A., ... & Richards, J. B. (2021). Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: The STROBE-MR statement. Jama, 326(16), 1614–1621.
Sullivan, M. D., Edlund, M. J., Zhang, L., Unützer, J., & Wells, K. B. (2006). Association between mental health disorders, problem drug use, and regular prescription opioid use. Archives of Internal Medicine, 166(19), 2087–2093.
Tran, A., Fuller, J. M., Wong, K. K., Krass, I., Grunstein, R., & Saini, B. (2009). The development of a sleep disorder screening program in Australian community pharmacies. Pharmacy World & Science, 31, 473–480.
Trubetskoy, V., Pardiñas, A. F., Qi, T., Panagiotaropoulou, G., Awasthi, S., Bigdeli, T. B., ... & Lazzeroni, L. C. (2022). Map** genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature, 604(7906), 502–508.
Vekaria, V., Bose, B., Murphy, S. M., Avery, J., Alexopoulos, G., & Pathak, J. (2021). Association of co-occurring opioid or other substance use disorders with increased healthcare utilization in patients with depression. Translational Psychiatry, 11(1), 265.
Verbanck, M., Chen, C. Y., Neale, B., & Do, R. (2018). Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nature Genetics, 50(5), 693–698.
Wang, D., & Teichtahl, H. (2007). Opioids, sleep architecture and sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 11(1), 35–46.
Watanabe, K., Jansen, P. R., Savage, J. E., Nandakumar, P., Wang, X., Hinds, D. A., ... & Posthuma, D. (2022). Genome-wide meta-analysis of insomnia prioritizes genes associated with metabolic and psychiatric pathways. Nature genetics, 54(8), 1125–1132.
Watkins, A., John, A., Bradshaw, C., Jones, J., & Jones, M. (2019). Schizophrenia in high risk opioid users: A short communication on an autopsy study. Psychiatry Research, 276, 112–114.
Watson, H. J., Yilmaz, Z., Thornton, L. M., Hübel, C., Coleman, J. R., Gaspar, H. A., ... & Seitz, J. (2019). Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nature genetics, 51(8), 1207–1214.
Wray, N. R., Ripke, S., Mattheisen, M., Trzaskowski, M., Byrne, E. M., Abdellaoui, A., ... & Viktorin, A. (2018). Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nature genetics, 50(5), 668–681.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shanghai Science and Technology Commission for supporting this study.
Funding
This work is supported by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82304241) and the General Projects of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (Grant No. 21ZR1405000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL contributed to the conception and design of the study. YH and LQ participated in the assessments and data extraction processes. YH, RS, and HD performed the statistical analyses. XL and YH discussed the results and wrote the original draft of the manuscript. XL performed the review and editing. XL supervised the project and contributed to the funding acquisition. All authors had full access to all data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. All authors read and approved the finalized manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Qian, L., Shi, R. et al. Understanding the Causal Relationships Between Opioid Dependence and Risk of Mental Disorders: A Comprehensive Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Int J Ment Health Addiction (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-024-01315-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-024-01315-y