Abstract
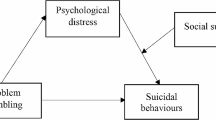
Psychoactive substance users and those having irrational beliefs tend to report more suicide ideation; however, there is paucity of research on substance use and distorted cognitions in relation to suicidality among gamblers. The possibility of a moderated mediation model has not been examined. This study examines substance use as a mechanism explaining the association between distorted cognition and suicide ideation, and it seeks to determine whether this process differed for men and women. Participants were 251 persons (mean age = 23.63 years, SD = 4.72 years, 82.1% men), drawn from sports betting centres in Southeast Nigeria. They completed the Psychoactive Substance Use Questionnaire and perceived inability to stop gambling scale of Gambling-Related Cognitions Inventory and Suicidal Ideation Attributes Scale. Moderated mediation analysis showed that substance use mediated the association between distorted cognitions and suicide ideation and this indirect effect was moderated by gender. Specifically, inability to stop gambling was linked to higher suicide ideation through substance use for men but not for women. Suicide prevention and intervention programmes should consider targeting substance use reduction in order to protect individuals from suicide ideation. Such potential interventions for alleviating drug use may be especially important for men.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abasiubong, F., Udobang, J. A., Idung, A. U., Udoh, S. B., & Jombo, H. E. (2014). Pattern of psychoactive substance use in the northern region of Nigeria. African Journal of Drug and Alcohol Studies, 13(2), 107–115.
Adamson, T. A., Ogunlesi, A. O., Morakinyo, O. I., Akinhanmi, A. O., Onifade, P. O., Erinosho, O., et al. (2015). Descriptive national survey of substance use in Nigeria. Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy, 6(3), 234–243. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6105.1000234.
Abdollahnejad, R., Delfabbro, P., & Denson, L. (2014). Understanding the relationship between pathological gambling and gambling-related cognition scores: The role of alcohol use disorder and delusion proneness. International Gambling Studies, 14(2), 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/14459795.2014.886711.
Aguocha, C. M., Duru, C. B., Nwefoh, E. C., Amadi, K. U., Olose, E. O., Igwe, M. N., & Ndukuba, A. C. (2019). Determinants of gambling among male students in secondary schools in Imo State, Nigeria. Journal of Substance Use, 24(2), 199–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2018.1535006.
Albery, I. P., Moss, A. C., Davidson, N., Mba, S., Blaszko, U., & Marchant, A. P. (2018). Selective attentional bias for novel psychoactive substance (NPS) and expectancy-related stimuli among nonproblematic NPS users and never NPS users. Journal of Substance Use, 23(4), 422–428. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2018.1436606.
Amazue, L. O., Ozor, O. T., Chukwuorji, J. C., Ifeagwazi, C. M., Onu, D. U., & Obi, N. G. (2019). Mental pain and suicide ideation in nursing students: The moderating role of emotion regulation. Cognition, Brain, Behavior. An Interdisciplinary Journal, XXIII(3), 171–191. https://doi.org/10.24193/cbb.2019.23.10.
Arenliu, A., Kelmendi, K., Haskuka, M., Halimi, T., & Canhasi, E. (2014). Drug use and reported suicide ideation and attempt among Kosovar adolescents. Journal of Substance Use, 19(5), 358–363. https://doi.org/10.3109/14659891.2013.820803.
Battersby, M., Tolchard, B., Scurrah, M., & Thomas, L. (2006). Suicide ideation and behaviour in people with pathological gambling attending a treatment service. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 4, 233–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-006-9022-z.
Beck, A. T., Wright, F. D., Newman, C. F., & Liese, B. S. (1993). Cognitive therapy of substance abuse. New York: Guilford Press.
Breet, E., Goldstone, D., & Bantjes, J. (2018). Substance use and suicidal ideation and behaviour in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. BMC Public Health, 18, 549. Doi. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5425-6.
Chen, L. Y., Martins, S. S., Strain, E. C., Mojtabai, R., & Storr, C. L. (2018). Sex and age differences in risk factors of marijuana involvement during adolescence. Addictive Disorders & Their Treatment, 17(1), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADT.0000000000000120.
Dalton, R. F. (2005). Cognitive distortions identified with type and frequency of self-reported substance abuse usage. PhD thesis. The Ohio State University.
Doksat, N. G., Zahmacioglu, O., Demirci, A. C., Kocaman, G. M., & Erdogan, A. (2017). Association of suicide attempts and non-suicidal self-injury behaviors with substance use and family characteristics among children and adolescents seeking treatment for substance use disorder. Substance Use and Misuse, 52(5), 604–613. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2016.1245745.
Eze, J. E. (2006). Cult membership as a determinant of psychoactive substance use among male undergraduates in Nigerian universities. Nigerian Journal of Psychological Research, 5, 28–36.
Ellis, T. E., & Rutherford, B. (2008). Cognition and suicide: Two decades of progress. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 1(1), 47–68.
Griffiths, M., Parke, J., & Wood, R. (2003). Excessive gambling and substance abuse: Is there a relationship? Journal of Substance Use, 7(4), 187–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659890215688.
Guillou-Landreat, M., Guilleux, A., Sauvaget, A., Brisson, L., Leboucher, J., Remaud, M., Challet-Bouju, G., & Grall-Bronnec, M. (2016). Factors associated with suicidal risk among a French cohort of problem gamblers seeking treatment. Psychiatry Research, 240, 11–18.
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: Guilford.
Iorfa, S. K., Ugwu, C., Ifeagwazi, C. M., & Chukwuorji, J. C. (2018). Substance use among youths: Roles of psychoticism, social alienation, thriving and religious commitment. African Journal of Drug & Alcohol Studies, 17(2), 133–146.
Jacobsen, L. H., Knudsen, A. K., Krogh, E., Pallesen, S., & Molde, H. (2007). An overview of cognitive mechanisms in pathological gambling. Nordic Psychology, 59(4), 347–361. https://doi.org/10.1027/1901-2276.59.4.347.
Kim, H. S., Salmon, M., Wohl, M. J. A., & Young, M. (2016). A dangerous cocktail: Alcohol consumption increases suicidal ideations among problem gamblers in the general population. Addictive Behaviors Reports, 55, 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.12.017.
Komoto, Y. (2014). Factors associated with suicide and bankruptcy in Japanese pathological gamblers. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 12, 600–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-014-9492-3.
Lamis, D. A., Ballard, E. D., May, A. M., & Dvorak, R. D. (2016). Depressive symptoms and suicidal ideation in college students: The mediating and moderating roles of hopelessness, alcohol problems, and social support. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 72(9), 919–932. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.22295.
Lloyd, J., Hawton, K., Dutton, W. H., Geddes, J. R., Goodwin, G. M., & Rogers, R. (2016). Thoughts and acts of self-harm, and suicidal ideation, in online gamblers. International Gambling Studies, 16(3), 408–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/14459795.2016.1214166.
Lorains, F. K., Cowlishaw, S., & Thomas, S. A. (2011). Prevalence of comorbid disorders in problem and pathological gambling: Systematic review and meta-analysis of population surveys. Addiction, 106(3), 490–498.
McInnes, A., Hodgins, D. C., & Holub, A. (2014). The gambling cognitions inventory: Scale development and psychometric validation with problem and pathological gamblers. International Gambling Studies, 14(3), 410–431. https://doi.org/10.1080/14459795.2014.923483.
Miller, A. B., Williams, C., Day, C., & Esposito-Smythers, C. (2017). Effects of cognitive distortions on the link between dating violence exposure and substance problems in clinically hospitalized youth. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 73(6), 733–744. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.22373.
Moghaddam, J. F., Yoon, G., Dickerson, D. L., Kim, S. W., & Westermeyer, J. (2015). Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts in five groups with different severities of gambling: Findings from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. American Journal of Addiction, 24(4), 292–298.
Modak, T., Bhad, R., & Rao, R. (2019). Utility of aripiprazole in co-occurring problem gambling and toluene dependence: A case report. Journal of Substance Use, 24(2), 117–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2018.1523964.
Nelson, E. E., Obot, I. S., & Umoh, O. O. (2017). Prioritizing public health responses in Nigerian drug control policy. African Journal of Drug & Alcohol Studies, 16(1), 49–57.
Nelson, E. E., & Pates, R. (2018). Supply control, demand reduction or harm reduction? Developments and directions for drug policy in Nigeria. Addiction Research & Theory, 26(6), 465–469. https://doi.org/10.1080/16066359.2017.1406480.
Petry, N. M., & Kiluk, B. D. (2002). Suicidal ideation and suicide attempts in treatment-seeking pathological gamblers. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 190(7), 462–469.
Petry, N. M., Stinson, F. S., & Grant, B. F. (2005). Comorbidity of DSM-IV pathological gambling and other psychiatric disorders: Results from the National Epidemiological Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 66(5), 564–574.
Poorolajal, J., Haghtalab, T., Farhadi, M., & Darvishi, N. (2015). Substance use disorder and risk of suicidal ideation, suicide attempt and suicide death: A meta-analysis. Journal of Public Health, 38(3), e 82–e 91. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdv148.
Pompili, M., Lester, D., Girardi, P., & Tatarelli, R. (2007). High suicide risk after the development of cognitive and working memory deficits caused by cannabis, cocaine and ecstasy use. Substance Abuse, 28(1), 25–30. https://doi.org/10.1300/J465v28n01_04.
Rash, C. J., Weinstock, J., & van Patten, R. (2016). A review of gambling disorder and substance use disorders. Substance Abuse and Rehabilitation, 7, 3–13.
Rontziokos, H., & Deane, F. (2019). Systematic review of suicidal behaviour in individuals who have attended substance abuse treatment. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 17(6), 1580–1598.
Raylu, N., & Oei, T. P. S. (2004). The gambling related cognitions scale (GRCS): Development, confirmatory factor validation and psychometric properties. Addiction, 99, 757–769. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00753.x.
Rush, B. R., Bassani, D. G., Urbanoski, K. A., & Castel, S. (2008). Influence of co-occurring mental and substance use disorders on the prevalence of problem gambling in Canada. Addiction, 103(11), 1847–1856.
Salvatore, T. (2017). Problem gambling and suicidal behavior: A primer for law enforcement. Washington, D.C: Federal Bureau of Investigation.
Sarkar, S., Balhara, Y. P. S., Parmar, A., & Rajhans, P. (2018). A study of pathological gambling and its correlates among patients seeking treatment for substance use disorders in North India. Journal of Substance Use, 23(2), 193–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2017.1378742.
Shalit, N., Shoval, G., Shlosberg, D., Feingold, D., & Lev-Ran, S. (2016). The association between cannabis use and suicidality among men and women: A population-based longitudinal study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 205, 216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.07.010.
Spirito, A., Esposito-Smythers, C., Weismoore, J., & Miller, A. (2012). Child and adolescent therapy: Cognitive behavioral procedures (4th ed.). New York, NY US: Guilford Press.
Spunt, B. (2002). Pathological gambling and substance misuse. Substance Use and Misuse, 37(8-10), 1299–1304. https://doi.org/10.1081/JA-120004186.
Tabore, T. O. (2019). On the neurobiological role of oxidative stress in alcohol-induced impulsive, aggressive and suicidal behavior. Substance Use & Misuse, 54(14), 2290–2303. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2019.1645179.
Unaogu, N. N., Onu, J. U., Iteke, O., Tukur, K., & Oka, I. Q. (2017). Pattern of substance abuse at the drug de-addiction unit of a Nigerian psychiatric hospital. African Journal of Drug and Alcohol Studies, 16(1), 23–31.
United Natons Office on Drug and Crime. (2012). West Africa – 2012 ATS situation report. Vienna: UNODC.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, UNODC (2018). World Drug Report 2018. Pre-briefing to the member states. Vienna: Author. Retrieved from https://www.unodc.org/wdr2018/prelaunch/Pre-briefingAM-fixed.pdf
Van Spijker, B. A. J., Batterham, P. J., Calear, A. L., Farrer, L., Christensen, H., Reynolds, J., & Kerkhof, A. J. F. M. (2014). The suicidal ideation attributes scale (SIDAS): Community-based validation study of a new scale for the measurement of suicidal ideation. Suicide and Life-threatening Behavior, 44(4), 408–419.
Wong, P. W. C., Cheung, D. Y. T., Conner, K. R., Conwell, Y., & Yip, P. S. F. (2010). Gambling and completed suicide in Hong Kong: A review of coroner court files. The Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 12(6), e1–e7. https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.09m00932blu.
Xu, X., Zhang, J., Zhou, Q., & Sun, L. (2019). Gender characteristics in methods of Chinese rural young suicides. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. Online First, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-019-00078-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chukwuorji, J.C., Nweke, A., Iorfa, S.K. et al. Distorted Cognitions, Substance Use and Suicide Ideation Among Gamblers: A Moderated Mediation Approach. Int J Ment Health Addiction 19, 1398–1409 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00232-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00232-0