Abstract
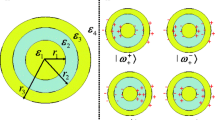
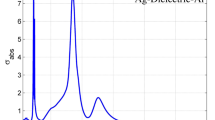
Localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) of Ag-dielectric-Ag multi-layered nanoshell are studied by quasi-static approximation and plasmon hybridization theory. Absorption properties of multi-layered nanoshell with the silver core and nanoshell separated by a dielectric layer exhibit strong coupling between the core and nanoshell. The result shows absorption spectrum of LSPRS is influenced by the refractive index of surrounding medium, the dielectric constant of middle dielectric layer, the thickness of inner core radius and outer shell layer. LSPR shift of the longest wavelength \(\left |\omega _{-}^{-}\right >\) is red-shifted with increasing the inner core radius. It is interesting to find that longer wavelength \(\left |\omega _{-}^{+}\right >\) mode is mainly effected by the ratio constant of the surrounding medium refractive index ε 4 to the middle layer dielectric constant ε 2. \(\left |\omega _{-}^{+}\right >\) mode takes place a blue-shift with increasing inner core radius when ε 2 > ε 4, a red-shift when ε 2 < ε 4, and no-shifting when ε 2 = ε 4. However, the influence of dielectric layer radius to \(\left |\omega _{-}^{+}\right >\) mode shows the different property as that of increasing the inner core radius. The underlying mechanisms are analyzed with the plasmon hybridization theory and the distribution of induced charge interaction between the inner core and outer shell. In addition, the influence of core radius, middle dielectric layer radius and outer shell radius to sensitivity of Ag-dielectric-Ag multi-layered nanoshell are also reported, a higher sensitivity could be gotten by adjusting geometrical parameters. Our theoretical study could give an easy way to analyze properties of the core-shell nanosphere based on plasmon hybridization theory and the induced charge interaction, and usefully broaden the applications in nano-optics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier S (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and application. Springer, Berlin
Novotny L, Hecht B (2006) Principle of nano-ptics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Weng GJ, Li JJ, Zhao JW (2012) Phys E 44:2072
Zhu J, Zhao SM (2016) Plasmonics 117:659
Daneshfar N (2015) J Appl Phys 117:123105
Sharma R, Roopak S, Pathak NK, Ji A, Sharma RP (2016) Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-016-0349-4
Sobhani A, Manjavacas A, Cao Y, Mclain MJ, Garcładeabajo FJ, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2015) Nano Lett 15:6946
Wu DJ, Liu XJ (2010) Appl Phys Lett 97:061904
Liu C, Lv JW, Liu ZT, Zheng SJ, Liu Q, Sun T, Mu HW, Chu PK (2016) Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-016-0214-5
Chaudhuri RG, Paria S (2011) Chem.Rev 112:2373
Xia XH, Liu Y, Backman V, Ameer GA (2006) Nanotechnology 17:5435
Khosravi H, Daneshfar N, Bahari A (2010) Phys Plasmas 17:053302
Shirzaditabar F, Saliminasab M (2013) Phys Plsmas 20:052109
Ho JF, Yanchuk BL, Zhang JB (2012) Appl Phys A 117:133
Averitt RD, Westcott SL, Halas NJ (1999) J Opt Soc Am B 16:1284
Daneshfar N, Bazyari K (2014) Appl Phys A 116:611
Haus JW, Zhou HS, Takami S, Hirasawa M, Honma I, Komiyama H (1993) J Appl Phys 739:1043
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (2000) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New York
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Phys Rev B 12:4370
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer Series in Materials Science, vol 25. Springer, Berlin
Prodan E, Radbloff C, Halas NJ, Nordander P (2003) Science 302:419
Prodan E, Nordander P (2004) J Chem Phys 120:5444
Zhang Y, Fei GT, Zhang LD (2011) J Appl Phys 109:054315
Qian J, Li YD, Chen J, Xu JJ, Sun Q (2014) Phys Chem C 118:8581
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Key Program for Excellent Young Talents in University of Anhui Province (gxyq2017027,gxyqZD2016206), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1708085MA10), and the key Scientific ResearchFoundation of Anhui Provincial Education Department under grant nos. (KJ2015A223, KJ2015ZD28, and AQKJ2015B017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, YW., Wu, ZW., Zhang, LH. et al. Theoretical Study of Sensitivity and Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of Ag-Dielectric Core-Shell Multi-layered Nanosphere. Plasmonics 13, 1255–1263 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0627-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0627-9