Abstract
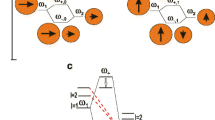
We present the first comprehensive study of a hemispherical nano-dimer interacting with an optical field. We characterize the optical response of the hemispherical dimer numerically using the finite-element method. The qualitative insight gained through the numerical analysis is enhanced with a derivation of an analytical approximation for the polarizability of a symmetric hemispherical dimer by invoking the dipole-dipole approximation. The results explain the effects of inter-particle spacing and the polarization of external excitation on the extinction spectra. Considering three configurations of hemispherical dimers, we show that both the frequency and the strength of plasmon resonances in each configuration are highly dependent on the inter-particle distance and the state of polarization of the incident light. We also show that, in the case of longitudinal polarization and an edge-to-edge orientation, the hemispherical dimer provides much better near-field confinement and produces much more enhancement of the electric field than a spherical dimer of the same volume. This result should prove useful for sensing and SERS applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer
Mayer KM, Hafner JH (2011) Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem Rev 111(6):3828–3857
Sikdar D, Rukhlenko ID, Cheng W, Premaratne M (2013) Effect of number density on optimal design of gold nanoshells for plasmonic photothermal therapy. Biomed Opt express 4(1):15–31
Lal S, Link S, Halas NJ (2007) Nano-optics from sensing to waveguiding. Nat Photonics 1(11):641–648
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2007) Review of some interesting surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of noble metal nanoparticles and their applications to biosystems. Plasmonics 2(3):107–118
Sikdar D, Rukhlenko ID, Cheng W, Premaratne M (2013) Unveiling ultrasharp scattering–switching signatures of layered gold–dielectric–gold nanospheres. J Opt Soc Am B 30(8):2066–2074
Kumarasinghe C, Premaratne M, Agrawal GP (2014) Dielectric function of spherical dome shells with quantum size effects. Opt Express 22(10):11966–11984
Nordlander P, Oubre C, Prodan E, Li K, Stockman M (2004) Plasmon hybridization in nanoparticle dimers. Nano Lett 4(5):899–903
Bao K, Mirin NA, Nordlander P (2010) Fano resonances in planar silver nanosphere clusters. Appl Phys A 100(2):333–339
Averitt RD, Westcott SL, Halas NJ (1999) Linear optical properties of gold nanoshells. J Opt Soc Am B 16(10):1824–1832
Sikdar D, Rukhlenko ID, Cheng W, Premaratne M (2014) Tunable broadband optical responses of substrate-supported metal/dielectric/metal nanospheres. Plasmonics 9(3):659–672
Ljungbert A, Lundqvist S (1985) Non-local effects in the optical absorption of small metallic particles. Surf Sci 156:839–844
Chang R, Leung P (2006) Nonlocal effects on optical and molecular interactions with metallic nanoshells. Phys Rev B 73(12):125438–125444
David C, Garcia de Abajo FJ (2011) Spatial nonlocality in the optical response of metal nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115(40):19470–19475
Prodan E, Radloff C, Halas N, Nordlander P (2003) A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302(5644):419–422
Jain PK, Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Plasmon coupling in nanorod assemblies: optical absorption, discrete dipole approximation simulation, and exciton-coupling model. J Phys Chem B 110(37):18243–18253
Fischer J, Vogel N, Mohammadi R, Butt HJ, Landfester K, Weiss CK, Kreiter M (2011) Plasmon hybridization and strong near-field enhancements in opposing nanocrescent dimers with tunable resonances. Nanoscale 3(11):4788–4797
Guerrero-Martínez A, Alonso-Gómez JL, Auguié B, Cid MM, Liz-Marzán LM (2011) From individual to collective chirality in metal nanoparticles. Nano Today 6(4):381–400
Zhao J, Pinchuk AO, McMahon JM, Li S, Ausman LK, Atkinson AL, Schatz GC (2008) Methods for describing the electromagnetic properties of silver and gold nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1710–1720
Oubre C, Nordlander P (2005) Finite-difference time-domain studies of the optical properties of nanoshell dimers. J Phys Chem B 109(20):10042–10051
Zhu S, Zhou W, Park GH, Li E (2010) Numerical design methods of nanostructure array for nanobiosensing. Plasmonics 5(3):267–271
Amendola V, Bakr OM, Stellacci F (2010) A study of the surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles by the discrete dipole approximation method: effect of shape, size, structure, and assembly. Plasmonics 5(1):85–97
Aizpurua J, Rivacoba A, Apell S (1996) Electron-energy losses in hemispherical targets. Phys Rev B 54 (4):2901–2909
Kettunen H, Wallén H, Sihvola A (2007) Polarizability of a dielectric hemisphere. J Appl Phys 102(4):044105–044112
Morse PM, Feshbach H (1953) Methods of theoretical physics
Kettunen H, Wallén H, Sihvola A (2008) Electrostatic resonances of a negative-permittivity hemisphere. J Appl Phys 103(9):094112–094120
Mayergoyz ID, Fredkin DR, Zhang Z (2005) Electrostatic (plasmon) resonances in nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 72(15):155412
Jain PK, El-Sayed MA (2010) Plasmonic coupling in noble metal nanostructures. Chem Phys Lett 487(4):153–164
Sheikholeslami S, Jun Yw, Jain PK, Alivisatos AP (2010) Coupling of optical resonances in a compositionally asymmetric plasmonic nanoparticle dimer. Nano Lett 10(7):2655–2660
Gomez D, Vernon K, Davis T (2010) Symmetry effects on the optical coupling between plasmonic nanoparticles with applications to hierarchical structures. Phys Rev B 81(7):075414
Sosa IO, Noguez C, Barrera RG (2003) Optical properties of metal nanoparticles with arbitrary shapes. J Phys Chem B 107(26):6269–6275
Weiland T, Timm M, Munteanu I (2008) A practical guide to 3-d simulation. IEEE Microw Mag 9(6):62–75
Palik ED (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids, vol 3. Academic
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (2008) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley
Esteban R, Borisov AG, Nordlander P, Aizpurua J (2012) Bridging quantum and classical plasmonics with a quantum-corrected model. Nat Commun 3:825
Hatab NA, Hsueh CH, Gaddis AL, Retterer ST, Li JH, Eres G, Zhang Z, Gu B (2010) Free-standing optical gold bowtie nanoantenna with variable gap size for enhanced raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett 10(12):4952–4955
Encina ER, Coronado EA (2010) Plasmon coupling in silver nanosphere pairs. J Phys Chem C 114(9):3918–3923
Brandl DW, Oubre C, Nordlander P (2005) Plasmon hybridization in nanoshell dimers. J Chem Phys 123(2):024,701
Rechberger W, Hohenau A, Leitner A, Krenn J, Lamprecht B, Aussenegg F (2003) Optical properties of two interacting gold nanoparticles. Opt Commun 220(1):137–141
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277(5329):1078–1081
Haes AJ, Hall WP, Chang L, Klein WL, Van Duyne RP (2004) A localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor: first steps toward an assay for Alzheimer’S disease. Nano Lett 4(6):1029– 1034
Unger A, Kreiter M (2009) Analyzing the performance of plasmonic resonators for dielectric sensing. J Phys Chem C 113(28):12,243–12,251
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Duyne RPV (2005) Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 77(17):338
Talley CE, Jackson JB, Oubre C, Grady NK, Hollars CW, Lane SM, Huser TR, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2005) Surface-enhanced raman scattering from individual au nanoparticles and nanoparticle dimer substrates. Nano Lett 5(8):1569–1574
Lu Y, Liu GL, Kim J, Mejia YX, Lee LP (2005) Nanophotonic crescent moon structures with sharp edge for ultrasensitive biomolecular detection by local electromagnetic field enhancement effect. Nano Lett 5(1):119–124
Sarid D, Challener W (2010) Modern introduction to surface plasmons: theory, Mathematica modeling, and applications. Cambridge University Press
Hao E, Schatz GC (2004) Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J Chem Phys 120(1):357–366
Raziman T, Martin OJ (2013) Polarisation charges and scattering behaviour of realistically rounded plasmonic nanostructures. Opt Express 21(18):21,500–21,507
Acknowledgments
The work of M. Premaratne and G. P. Agrawal is supported by the Australian Research Council through its Discovery Grants DP110100713 and DP140100883. T. Attanayake gratefully acknowledges financial support from Australian government and the Faculty of Engineering, Monash University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attanayake, T., Premaratne, M. & Agrawal, G.P. Characterizing the Optical Response of Symmetric Hemispherical Nano-dimers. Plasmonics 10, 1453–1466 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9946-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9946-x