Abstract
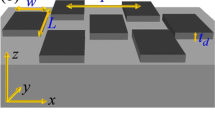
Polarization-independent plasmonic light absorbers have been widely investigated in the past decades. Nevertheless, the feasibility for artificial manipulation of the optical properties by controlling the polarization state is desirable for numerous applications including the coloring, displaying, filtering, etc. Here, we present a straightforward method to achieve tunable multiple narrowband light absorption by using the polarization-dependent plasmonic cavity resonances in a common metal-dielectric-metal structure consisting of an elliptical disk array. Multiple light absorption bands with the maximal absorption of 98 % are achieved. Moreover, by controlling the illumination polarization state, artificial spectral modulation depth of these light absorption bands can be up to 90 % based on this structure platform. In addition, since this multispectral polarization-manipulated absorber is realized in such a common sub-wavelength plasmonic structure, it will open up a simple and universal approach for multispectral nanophotonic devices including the high-compact polychromatic color filtering, imaging, and detecting.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuller JA, Barnard ES, Cai W, Jun YC, White JS, Brongersma ML (2010) Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat Mater 9:193–204
Li JF, Huang YF, Ding Y, Yang ZL, Li SB, Zhou XS, Fan FR, Zhang W, Zhou ZY, Wu DY, Ren B, Wang ZL, Tian ZQ (2010) Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464:392–395
Zhou H, Qiu C, Yu F, Yang H, Chen M, Hu L, Sun L (2011) Thickness-dependent morphologies and surface-enhanced Raman scattering of Ag deposited on n-layer graphenes. J Phys Chem C 115:11348–11354
Teperik V, De Abajo FJG, Borisov AG, Abdelsalam M, Bartlett PN, Sugawara Y, Baumerg JJ (2008) Omnidirectional absorption in nanostructured metal surfaces. Nat Photonics 2:299–301
Hedayati MK, Javaherirahim M, Mozooni B, Abdelaziz R, Tavassolizadeh A, Chakravadhanula VSK, Zaporojtchenko V, Strunkus T, Faupel F, Elbahri M (2011) Design of a perfect black absorber at visible frequencies using plasmonic metamaterials. Adv Mater 23:5410–5414
Akimov YA, Ostrikov K, Li EP (2009) Surface plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in thin-film silicon solar cells. Plasmonics 4:107–113
Liu G, Liu Z, Chen YH, Cai ZJ, Hu Y, Zhang XN, Huang K (2014) Multi-band near-unity absorption and near-zero reflection of optical field in metal-dielectric-metal hybrid crystals. Sci Adv Mater 6:1099–1105
Liu Z, Liu X, Huang S, Pan P, Chen J, Liu G, Gu G (2015) Automatically acquired broadband plasmonic-metamaterial black absorber during the metallic film-formation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4962–4968
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213
Chen X, Chen Y, Yan M, Qiu M (2012) Nanosecond photothermal effects in plasmonic nanostructures. ACS Nano 6:2550–2557
Freeston I, Meeks N, Sax M, Higgitt C (2007) The Lycurgus cup—a Roman nanotechnology. Gold Bull 40:270
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Padilla WJ (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100:207402
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10:2342–2348
Zhao Y, Hao Q, Ma Y, Lu M, Zhang B, Lapsley M, Khoo I-C, Huang TJ (2012) Light-driven tunable dual-band plasmonic absorber using liquid-crystal-coated asymmetric nanodisk array. Appl Phys Lett 100:053119
Alaee R, Menzel C, Huebner U, Pshenay-Severin E, Hasan SB, Pertsch T, Rockstuhl C, Lederer F (2013) Deep-subwavelength plasmonic nanoresonators exploiting extreme coupling. Nano Lett 13:3482–3486
Liu Z, Shao H, Liu G, Liu X, Zhou H, Hu Y, Zhang X, Cai Z, Gu G (2014) λ 3/20000 plasmonic nanocavities with multispectral ultra-narrowband absorption for high-quality sensing. Appl Phys Lett 104:081116
Chen K, Adato R, Altug H (2012) Dual-band perfect absorber for multispectral plasmon-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Nano 6:7998–8006
Aydin K, Ferry VE, Briggs RM, Atwater HA (2011) Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers. Nat Commun 2:517
Søndergaard T, Novikov SM, Holmgaard T, Eriksen RL, Beermann J, Han Z, Pedersen K, Bozhevolnyi SI (2012) Plasmonic black gold by adiabatic nanofocusing and absorption of light in ultra-sharp convex grooves. Nat Commun 3:969
Wang J, Chen Y, Chen X, Hao J, Yan M, Qiu M (2011) Photothermal reshaping of gold nanoparticles in a plasmonic absorber. Opt Express 19:14726–14734
Cheng C-W, Abbas MN, Chiu C-W, Lai K-T, Shih M-H, Chang Y-C (2012) Wide-angle polarization independent infrared broadband absorbers based on metallic multi-sized disk arrays. Opt Express 20:10376–10381
Ding F, Cui Y, Ge X, Jin Y, He S (2012) Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber. Appl Phys Lett 100:103506
Cui Y, Fung KH, Xu J, Ma H, Jin Y, He S, Fang NX (2012) Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab. Nano Lett 12:1443–1447
Bossard JA, Lin L, Yun S, Liu L, Werner DH, Mayer TS (2014) Near-ideal optical metamaterial absorbers with super-octave bandwidth. ACS Nano 8:1517–1524
Najiminaini M, Kaminska B, Lawrence KS, Carson JJL (2014) Bolus tracking with nanofilter-based multispectral videography for capturing microvasculature hemodynamics. Sci Rep 4:4737
Zhang Z, Wang J, Zhao Y, Lu D, Xiong Z (2011) Numerical investigation of a branch-shaped filter based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 6:773–778
Chen J, Xu R, Mao P, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Tang C, Liu J, Chen T (2015) Realization of Fanolike resonance due to diffraction coupling of localized surface plasmon resonances in embedded nanoantenna arrays. Plasmonics 10:341–346
Zeng B, Gao Y, Bartoli FJ (2014) Ultrathin nanostructured metals for highly transmissive plasmonic subtractive color filters. Sci Rep 3:2840
Liu Z, Liu G, Liu X, Shao H, Chen J, Huang S, Liu M, Fu G (2015) Multispectral sharp plasmon resonances for polarization-manipulated subtractive polychromatic filtering and sensing. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-014-9869-y
Knight MW, Sobhani H, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2011) Photodetection with active optical antennas. Science 332:702–704
Liu Z, Liu G, Huang S, Liu X, Pan P, Wang Y, Gu G (2015) Multispectral spatial and frequency selective sensing with ultra-compact cross-shaped antenna plasmonic crystals. Sensors Actuators B 215:480–488
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297
Zhang B, Zhao Y, Hao Q, Kiraly B, Khoo I-C, Chen S, Huang TJ (2011) Polarization-independent dual-band infrared perfect absorber based on a metal-dielectric-metal elliptical nanodisk array. Opt Express 19:15221–15228
Watts CM, Liu X, Padilla WJ (2012) Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater 24:OP98–OP120
Cui Y, He Y, Jin Y, Ding F, Yang L, Ye Y, Zhong S, Lin Y, He S (2014) Plasmonic and metamaterial structures as electromagnetic absorbers. Laser Photonics Rev 8:495–520
Liu Z, Liu G, Huang S, Liu X, Wang Y, Liu M, Gu G (2015) Enabling access to the confined optical field to achieve high-quality plasmon sensing. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27:1212–1215
Chu Y, Banaee MG, Crozier KB (2010) Double-resonance plasmon substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering with enhancement at excitation and Stokes frequencies. ACS Nano 4:2804–2810
Li T, Li Q, Xu Y, Chen XJ, Dai QF, Liu H, Lan S, Tie S, Wu LJ (2012) Three-dimensional orientation sensors by defocused imaging of gold nanorods through an ordinary wide-field microscope. ACS Nano 6:1268–1277
Chen L, Li GC, Liu GY, Dai QF, Lan S, Tie SL, Deng HD (2013) Sensing the moving direction, position, size, and material type of nanoparticles with the two-photon-induced luminescence of a single gold nanorod. J Phys Chem C 117:20146–20153
Clausen JS, Højlund-Nielsen E, Christiansen AB, Yazdi S, Grajower M, Taha H, Levy U, Kristensen A, Asger Mortensen N (2014) Plasmonic metasurfaces for coloration of plastic consumer products. Nano Lett 14:4499–4504
Liu Z, Liu G, Liu X, Fu G, Liu M (2014) Improved multispectral anti-reflection and sensing of plasmonic slits by silver mirror. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26:2111
Lin J, Zhang Y, Qian J, He S (2014) A nano-plasmonic chip for simultaneous sensing with dual-resonance surface-enhanced Raman scattering and localized surface plasmon resonance. Laser Photonics Rev 8:610–616
Qin LD, Zou SL, Xue C, Atkinson A, Schatz GC, Mirkin CA (2006) Designing, fabricating, and imaging Raman hot spots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:13300–13303
Su KH, Wei QH, Zhang X (2006) Tunable and augmented plasmon resonances of Au/SiO2/Au nanodisks. Appl Phys Lett 88:063118–063121
Joshi B, Chakrabarty A, Wei QH (2010) Numerical studies of metal–dielectric–metal nanoantennas. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 9:701–707
Minkowski F, Wang F, Chakrabarty A, Wei QH (2014) Resonant cavity modes of circular plasmonic patch nanoantennas. Appl Phys Lett 104:021111
Wang F, Chakrabarty A, Minkowski F, Sun K, Wei QH (2012) Cavity modes and their excitations in elliptical plasmonic patch nanoantennas. Opt Express 20:11615–11624
Liu G, Hu Y, Liu Z, Chen Y, Cai Z, Zhang X, Huang K (2013) Robust multispectral transparency in continuous metal film structures via multiple near-field plasmon coupling by a finite-difference time-domain method. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:4320–4328
Sönnichsen C (2001) Plasmons in metal nanostructures. PhD Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universtät München, München
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Zhang Q, Xiao JJ, Zhang XM, Han D, Gao L (2015) Core–shell structured dielectric–metal circular nanodisk antenna: gap plasmon assisted magnetic toroid-like cavity modes. ACS Photonics 2:60–65
Cai Y, Li Y, Nordlander P, Cremer PS (2012) Fabrication of elliptical nanorings with highly tunable and multiple plasmonic resonances. Nano Lett 12:4881–4888
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11464019, 11264017, and 61308096), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant 20142BAB212001), and Young Scientist development program of Jiangxi Province (Grant 20142BCB23008).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Liu, G., Wang, Y. et al. Polarization-Induced Tunability of Plasmonic Light Absorption in Arrays of Sub-Wavelength Elliptical Disks. Plasmonics 11, 79–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0024-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0024-1