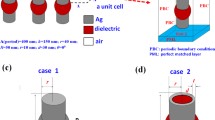
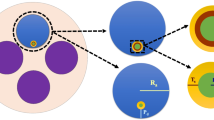
Abstract
A universal method for improving sensing performance has been computationally studied based on a common triple-layer metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) plasmonic perfect absorber (PA). Calculation results show that the originally idled resonant optical field in the middle dielectric spacer can be exploited to enhance the sensing capability via etching the dielectric spacer to open a channel for analyte. By comparing with the sensitivity (S) of the common PA-based sensor, an enhancement factor up to 5.0 can be achieved for an etched PA-based sensor. Moreover, in order to maintain the mechanical stability of the structure, a modified PA-based sensor platform with a solid support for the suspended plasmonic disks array was further employed to study the sensing properties. In comparison with the referenced sensor without suspension technique, all the three sensing factors of the S, the figure of merit (FOM), and the spectral intensity difference related figure of merit (FOM*) are noticeably improved with the enhancement factors up to 2.5, 3, and 57, respectively. In addition, since there is no special dealing with the structure except the need of hollowing the dielectric spacer to open the sensing channel for the analysis, the predicted method profiles itself as a simple and universal strategy to improve the sensing performance of a wide variety of nanoplasmonic sensors.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LSPR:
-
Localized surface plasmon resonance
- MDM:
-
Metal-dielectric-metal
- PA:
-
Perfect absorber
- FOM:
-
Figure of merit
- FWHM:
-
Full-width at half-maximum
References
Schuller JA, Barnard ES, Cai W, Jun YC, White JS, Brongersma ML (2010) Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat Mater 9:193–204
Halas NJ, Lal S, Chang WS, Link S, Nordlander P (2011) Plasmons in strongly coupled metallic nanostructures. Chem Rev 111:3913–3961
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Ann Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297
Zhu J, Deng XC (2011) Improve the refractive index sensitivity of gold nanotube by reducing the restoring force of localized surface plasmon resonance. Sens Actuator B 155:843–847
Sagle LB, Ruvuna LK, Ruemmele JA, Van Duyne RP (2011) Advances in localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy biosensing. Nanomedicine 6:1447–1462
Chen L, Li GC, Liu GY, Dai QF, Lan S, Tie SL, Deng HD (2013) Sensing the moving direction, position, size, and material type of nanoparticles with the two-photon-induced luminescence of a single gold nanorod. J Phys Chem C 117:20146–20153
Li T, Li Q, Xu Y, Chen XJ, Dai QF, Liu H, Lan S, Tie S, Wu LJ (2012) Three-dimensional orientation sensors by defocused imaging of gold nanorods through an ordinary wide-field microscope. ACS Nano 6:1268–1277
Khorasaninejad M, Raeis-Zadeh SM, Amarloo H, Abedzadeh N, Safavi-Naeini S, Saini SS (2013) Colorimetric sensors using nano-patch surface plasmon resonators. Nanotechnology 24:355501
Liu J, Xu B, Zhang J, Song G (2013) Double plasmon-induced transparency in hybrid waveguide-plasmon system and its application for localized plasmon resonance sensing with high figure of merit. Plasmonics 8:995–1001
Lodewijks K, Ryken J, Van Roy W, Borghs G, Lagae L, Dorpe PV (2013) Tuning the Fano resonance between localized and propagating surface plasmon resonances for refractive index sensing applications. Plasmonics 8:1379–1385
Liu Z, Liu G, Liu X, Shao H, Chen J, Huang S, Liu M, Fu G (2015) Multispectral sharp plasmon resonances for polarization-manipulated subtractive polychromatic filtering and sensing. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-014-9869-y
Nien L, Chao B, Li J, Hsueh C (2015) Optimized sensitivity and electric field enhancement by controlling localized surface plasmon resonances for bowtie nanoring nanoantenna arrays. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-014-9840-y
Zhou H, Qiu C, Yu F, Yang H, Chen M, Hu L, Sun L (2011) Thickness-dependent morphologies and surface-enhanced Raman scattering of Ag deposited on n-layer graphenes. J Phys Chem C 115:11348–11354
Otte MA, Estevez M-C, Carrascosa LG, Gonzalez-Guerrero AB, Lechuga LM, Sepulveda B (2011) Improved biosensing capability with novel suspended nanodisks. J Phys Chem C 115:5344–5351
Keathley PD, Hastings JT (2012) Nano-gap-enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensors. Plasmonics 7:59–69
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 17:442–453
Willett DR, Chumanov G (2014) LSPR sensor combining sharp resonance and differential optical measurements. Plasmonics 9:1391–1396
Liu Z, Liu G, Liu X, Fu G, Liu M (2014) Improved multispectral anti-reflection and sensing of plasmonic slits by silver mirror. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 26:2111
Chanda D, Shigeta K, Truong T, Lui E, Mihi A, Schulmerich M, Braun PV, Bhargava R, Rogers JA (2011) Coupling of plasmonic and optical cavity modes in quasi-three dimensional plasmonic crystals. Nat Commun 2:479
Katyal J, Soni RK (2014) Localized surface plasmon resonance and refractive index sensitivity of metal–dielectric–metal multilayered nanostructures. Plasmonics 9:1171–1181
Shen H, Lu G, Zhang T, Liu J, Gu Y, Perriat P, Martini M, Tillement O, Gong Q (2013) Shape effect on a single-nanoparticle based plasmonic nanosensor. Nanotechnology 24:285502
Liu Z, Yu M, Huang S, Liu X, Wang Y, Liu M, Pan P, Liu G (2015) Enhancing refractive index sensing capability with hybrid plasmonic–photonic absorbers. J Mater Chem C 3:4222
Shen Y, Zhou J, Liu T, Tao Y, Jiang R, Liu M, Xiao G, Zhu J, Zhou Z, Wang X, Jin C, Wang J (2013) Plasmonic gold mushroom arrays with refractive index sensing figures of merit approaching the theoretical limit. Nat Commun 4:2381
Ameling R, Langguth L, Hentschel M, Mesch M, Braun PV, Giessen H (2010) Cavity-enhanced localized plasmon resonance sensing. Appl Phys Lett 97:253116
Liu Z, Shao H, Liu G, Liu X, Zhou H, Hu Y, Zhang X, Cai Z, Gu G (2014) λ 3/20000 plasmonic nanocavities with multispectral ultra-narrowband absorption for high-quality sensing. Appl Phys Lett 104:081116
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10:2342–2348
Becker J, Truegler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Soennichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5:161–167
Chen K, Adato R, Altug H (2012) Dual-band perfect absorber for multispectral plasmon-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Nano 6:7998–8006
Cheng F, Yang X, Gao J (2014) Enhancing intensity and refractive index sensing capability with infrared plasmonic perfect absorbers. Opt Lett 39:3185–3188
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock JJ, Smith DR, Padilla WJ (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100:207402
Taflove A, Hagness SC (2000) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method. Artech House, USA
Liu G, Hu Y, Liu Z, Chen Y, Cai Z, Zhang X, Huang K (2013) Robust multispectral transparency in continuous metal film structures via multiple near-field plasmon coupling by a finite-difference time-domain method. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:4320–4328
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kästel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8:758–762
Joshi B, Chakrabarty A, Wei QH (2010) Numerical studies of metal–dielectric–metal nanoantennas. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 9:701–707
Minkowski F, Wang F, Chakrabarty A, Wei QH (2014) Resonant cavity modes of circular plasmonic patch nanoantennas. Appl Phys Lett 104:021111
Liu Z, Hang J, Chen J, Yan Z, Tang C, Chen Z, Zhan P (2012) Optical transmission of corrugated metal films on a two-dimensional hetero-colloidal crystal. Opt Express 20:9215–9225
Liu Z, Liu G, Shao H, Liu X, Liu M, Huang S, Fu G, Xu H, Gao H (2015) Refractometric sensing of silicon layer coupled plasmonic–colloidal crystals. Mater Lett 140:9–11
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11464019 and 11264017), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant 20142BAB212001), Young Scientist development program of Jiangxi Province (Grant 20142BCB23008).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Liu, G., Liu, X. et al. Improving Plasmon Sensing Performance by Exploiting the Spatially Confined Field. Plasmonics 11, 29–36 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0017-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0017-0