Abstract
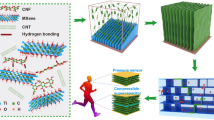
Breaking up bulk crystals of functional materials into nanoscale thinner layers can lead to interesting properties and enhanced functionalities due to the size and interface effects. However, unlike the van der Waals layered crystals, many materials cannot be exfoliated into thin layers by liquid exfoliation. BiFeO3 is a piezoelectric ceramic material, which is commonly synthesized as bulk crystals, limiting its wider applications. In this contribution, a freeze-drying assisted liquid exfoliation method was adopted to fabricate thin-layered BiFeO3 nanoplates with lateral sizes of up to 500 nm and thicknesses of 10–20 nm. The freeze-drying process showed a vital role in the preparation process by imposing stress on the dispersed BiFeO3 crystals during the liquid-to-solid-to-gas transition of the solvent. Such stress resulted in lattice strains in the freeze-dried BiFeO3 crystals, which enabled their further exfoliation under subsequent ultrasonication. Considering the intrinsic piezoelectric effect of BiFeO3, pressure sensors based on bulk and thin-layer BiFeO3 were also fabricated. The pressure sensor based on BiFeO3 nanoplates exhibited a largely enhanced sensitivity with a wider working range than the bulk counterpart, because of the stronger piezoelectric effect induced and the extra electrical charges at abundant interlayer interfaces. We suggest that the freeze-drying assisted liquid exfoliation method can be applied to other non-van der Waals crystals to bring about more functional material systems.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Tao, K. Zhang, H. Tian, Y. Liu, D. Y. Wang, Y. Q. Chen, Y. Yang, and T. L. Ren, Graphene-paper pressure sensor for detecting human motions, ACS Nano 11(9), 8790 (2017)
L. Guan, A. Nilghaz, B. Su, L. Jiang, W. Cheng, and W. Shen, Stretchable-fiber-confined wetting conductive liquids as wearable human health monitors, Adv. Funct. Mater. 26(25), 4511 (2016)
C. M. Boutry, L. Beker, Y. Kaizawa, C. Vassos, H. Tran, A. C. Hinckley, R. Pfattner, S. Niu, J. Li, J. Claverie, Z. Wang, J. Chang, P. M. Fox, and Z. Bao, Biodegradable and flexible arterial-pulse sensor for the wireless monitoring of blood flow, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3(1), 47 (2019)
L. Li, J. Zheng, J. Chen, Z. Luo, Y. Su, W. Tang, X. Gao, Y. Li, C. Cao, Q. Liu, X. Kang, L. Wang, and H. Li, Flexible pressure sensors for biomedical applications: From ex vivo to in vivo, Adv. Mater. Inter-faces 7(17), 2000743 (2020)
D. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ma, Y. S. Kim, R. H. Kim, S. Wang, J. Wu, S. M. Won, H. Tao, A. Islam, K. J. Yu, T. Kim, R. Chowdhury, M. Ying, L. Xu, M. Li, H. J. Chung, H. Keum, M. McCormick, P. Liu, Y. W. Zhang, F. G. Omenetto, Y. Huang, T. Coleman, and J. A. Rogers, Epidermal electronics, Science 333(6044), 838 (2011)
S. C. B. Mannsfeld, B. C. K. Tee, R. M. Stoltenberg, C. V. H. H. Chen, S. Barman, B. V. O. Muir, A. N. Sokolov, C. Reese, and Z. Bao, Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers, Nat. Mater. 9(10), 859 (2010)
D. J. Lipomi, M. Vosgueritchian, B. C. K. Tee, S. L. Hellstrom, J. A. Lee, C. H. Fox, and Z. Bao, Skin-like pressure and strain sensors based on transparent elastic films of carbon nanotubes, Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(12), 788 (2011)
F. Fan, L. Lin, G. Zhu, W. Wu, R. Zhang, and Z. L. Wang, Transparent triboelectric nanogenerators and self-powered pressure sensors based on micropatterned plastic films, Nano Lett. 12(6), 3109 (2012)
Y. Ding, J. Yang, C. R. Tolle, and Z. Zhu, Flexible and compressible PEDOT: PSS@melamine conductive sponge prepared via one-step dip coating as piezoresistive pressure sensor for human motion detection, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(18), 16077 (2018)
X. Shuai, P. Zhu, W. Zeng, Y. Hu, X. Liang, Y. Zhang, R. Sun, and C. Wong, Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensor based on silver nanowires-embedded poly-dimethylsiloxane electrode with microarray structure, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(31), 26314 (2017)
K. Maity, S. Garain, K. Henkel, D. Schmeißer, and D. Mandal, Self-powered human-health monitoring through aligned PVDF nanofibers interfaced skin-interactive piezoelectric sensor, ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2(2), 862 (2020)
S. Xu, Y. Qin, C. Xu, Y. Wei, R. Yang, and Z. L. Wang, Self-powered nanowire devices, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5(5), 366 (2010)
L. Lin, Y. Xie, S. Wang, W. Wu, S. Niu, X. Wen, and Z. L. Wang, Triboelectric active sensor array for self-powered static and dynamic pressure detection and tactile imaging, ACS Nano 7(9), 8266 (2013)
T. Huang, S. Yang, P. He, J. Sun, S. Zhang, D. Li, Y. Meng, J. Zhou, H. Tang, J. Liang, G. Ding, and X. Xie, Phase-separation-induced PVDF/graphene coating on fabrics toward flexible piezoelectric sensors, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10(36), 30732 (2018)
M. Ha, S. Lim, J. Park, D. S. Um, Y. Lee, and H. Ko, Bioinspired interlocked and hierarchical design of ZnO nanowire arrays for static and dynamic pressure-sensitive electronic skins, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25(19), 2841 (2015)
Y. Kim, K. Y. Lee, S. K. Hwang, C. Park, S. W. Kim, and J. Cho, Layer-by-layer controlled perovskite nanocomposite thin films for piezoelectric nanogenerators, Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(40), 6262 (2014)
Y. Qi and M. C. McAlpine, Nanotechnology-enabled flexible and biocompatible energy harvesting, Energy Environ. Sci. 3(9), 1275 (2010)
H. Liu, J. Zhong, C. Lee, S. W. Lee, and L. Lin, A comprehensive review on piezoelectric energy harvesting technology: Materials, mechanisms, and applications, Appl. Phys. Rev. 5(4), 041306 (2018)
H. G. Yeo, T. Xue, S. Roundy, X. Ma, C. Rahn, and S. Trolier-McKinstry, Strongly (001) oriented bimorph PZT film on metal foils grown by RF -sputtering for wrist-worn piezoelectric energy harvesters, Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(36), 1801327 (2018)
J. Yi, L. Liu, L. Shu, Y. Huang, and J. F. Li, Outstanding ferroelectricity in sol-gel-derived polycrystalline BiFeO3 films within a wide thickness range, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(18), 21696 (2022)
J. Wang, J. B. Neaton, H. Zheng, V. Nagarajan, S. B. Ogale, B. Liu, D. Viehland, V. Vaithyanathan, D. G. Schlom, U. V. Waghmare, N. A. Spaldin, K. M. Rabe, M. Wuttig, and R. Ramesh, Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures, Science 299(5613), 1719 (2003)
J. Silva, A. Reyes, H. Esparza, H. Camacho, and L. Fuentes, BiFeO3: A review on synthesis, doping and crystal structure, Integr. Ferroelectr. 126(1), 47 (2011)
M. Dai, Z. Wang, F. Wang, Y. Qiu, J. Zhang, C. Y. Xu, T. Zhai, W. Cao, Y. Fu, D. Jia, Y. Zhou, and P. A. Hu, Two-dimensional van der Waals materials with aligned in-plane polarization and large piezoelectric effect for self-powered piezoelectric sensors, Nano Lett. 19(8), 5410 (2019)
M. H. Lee, D. J. Kim, J. S. Park, S. W. Kim, T. K. Song, M. H. Kim, W. J. Kim, D. Do, and I. K. Jeong, High-performance lead-free piezoceramics with high Curie temperatures, Adv. Mater. 27(43), 6976 (2015)
K. Shimizu, H. Hojo, Y. Ikuhara, and M. Azuma, Enhanced piezoelectric response due to polarization rotation in cobalt-substituted BiFeO3 epitaxial thin films, Adv. Mater. 28(39), 8639 (2016)
K. Shimizu, H. Hojo, Y. Ikuhara, and M. Azuma, Piezoelectric materials: Enhanced piezoelectric response due to polarization rotation in cobalt-substituted BiFeO3 epitaxial thin films, Adv. Mater. 28(39), 8785 (2016)
P. Hu, L. Yan, C. Zhao, Y. Zhang, and J. Niu, Double-layer structured PVDF nanocomposite film designed for flexible nanogenerator exhibiting enhanced piezoelectric output and mechanical property, Compos. Sci. Technol. 168, 327 (2018)
K. N. Duerloo, M. T. Ong, and E. J. Reed, Intrinsic piezoelectricity in two-dimensional materials, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3(19), 2871 (2012)
Liu, G. D. Zhao, T. Hu, L. Bellaiche, and W. Ren, Structural and magnetic properties of two-dimensional layered BiFeO3 from first principles, Phys. Rev. B 103, 081403 (2021)
H. Yan, H. Deng, N. Ding, J. He, L. Peng, L. Sun, P. Yang, and J. Chu, Influence of transition elements doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 films fabricated by magnetron sputtering, Mater. Lett. 111, 123 (2013)
X. Zhang, J. Deng, J. Yan, Y. Song, Z. Mo, J. Qian, X. Wu, S. Yuan, H. Li, and H. Xu, Cryo-mediated liquid-phase exfoliated 2D BP coupled with 2D C3N4 to photodegradate organic pollutants and simultaneously generate hydrogen, Appl. Surf. Sci. 490, 117 (2019)
H. Wang, W. Lv, J. Shi, H. Wang, D. Wang, L. Jin, J. Chao, P. A. van Aken, R. Chen, and W. Huang, Efficient liquid nitrogen exfoliation of MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets in the pure 2H phase, ACS Sustain. Chem. & Eng. 8(1), 84 (2020)
Y. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Wu, H. Xu, X. Wen, X. Zhang, C. S. Tiwary, W. Yang, R. Vajtai, Y. Zhang, N. Chopra, I. N. Odeh, Y. Wu, and P. M. Ajayan, Cryo-mediated exfoliation and fracturing of layered materials into 2D quantum dots, Sci. Adv. 3(12), 1701500 (2017)
M. Abroodi, A. Bagheri, and B. M. Razavizadeh, Surface tension of binary and ternary systems containing monoethanolamine (MEA), water and alcohols (methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol) at 303.15 K, J. Chem. Eng. Data 65(6), 3173 (2020)
S. Cesur, M. E. Cam, F. S. Sayin, and O. Gunduz, Electrically controlled drug release of donepezil and BiFeO3 magnetic nanoparticle-loaded PVA microbubbles/nanoparticles for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 67, 102977 (2022)
H. Ding, S. T. Khan, S. Zeng, and L. Sun, Exfoliation of nanosized α-zirconium phosphate in methanol, Inorg. Chem. 60(11), 8276 (2021)
K. Jonnalagadda, S. W. Cho, I. Chasiotis, T. Friedmann, and J. Sullivan, Effect of intrinsic stress gradient on the effective mode-I fracture toughness of amorphous diamond-like carbon films for MEMS, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56(2), 388 (2008)
K. Park, J. H. Son, G. T. Hwang, C. K. Jeong, J. Ryu, M. Koo, I. Choi, S. H. Lee, M. Byun, Z. L. Wang, and K. J. Lee, Highly-efficient, flexible piezoelectric PZT thin film nanogenerator on plastic substrates, Adv. Mater. 26(16), 2514 (2014)
A. Barzegar, D. Damjanovic, and N. Setter, Analytical modeling of the apparent d33 piezoelectric coefficient determined by the direct quasistatic method for different boundary conditions, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferro-electr. Freq. Control 52(11), 1897 (2005)
J. Dong and G. Ouyang, Edge effect on the piezoelectric characteristics of rectangular-shaped monolayer MSe2 (M = Cr, Mo, W) nanosheets, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 54(23), 235502 (2021)
Z. Zhu, A. Zhang, G. Ouyang, and G. Yang, Edge effect on band gap shift in Si nanowires with polygonal cross-sections, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(26), 263112 (2011)
J. Dong and G. Ouyang, Edge effect on the piezoelectric characteristics of rectangular-shaped monolayer MSe2 (M = Cr, Mo, W) nanosheets, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54(23), 235502 (2021)
Y. Lee, J. Park, S. Cho, Y. E. Shin, H. Lee, J. Kim, J. Myoung, S. Cho, S. Kang, C. Baig, and H. Ko, Flexible ferroelectric sensors with ultrahigh pressure sensitivity and linear response over exceptionally broad pressure range, ACS Nano 12(4), 4045 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Eo. 51832001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Dong, M., Zou, X. et al. Freeze-drying assisted liquid exfoliation of BiFeO3 for pressure sensing. Front. Phys. 18, 63303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1301-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1301-7