Abstract
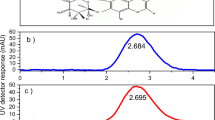
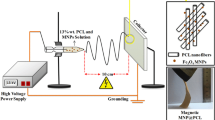
A PEGylated-PLGA random nanofibrous membrane loaded with gold and iron oxide nanoparticles and with silibinin was prepared by electrospinning deposition. The nanofibrous membrane can be remotely controlled and activated by a laser light or magnetic field to release biological agents on demand. The nanosystems were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analyses. The drug loading efficiency and drug content percentages were determined by UV-vis optical absorption spectroscopy. The nanofibrous membrane irradiated by a relatively low-intensity laser or stimulated by a magnetic field showed sustained silibinin release for at least 60 h, without the burst effect. The proposed low-cost electrospinning procedure is capable of assembling, via a one-step procedure, a stimuli-responsive drug-loaded nanosystem with metallic nanoparticles to be externally activated for controlled drug delivery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Raghavan, D. H. Lim, J. H. Ahn, C. Nah, D. C. Sherrington, H. S. Ryu, and H. J. Ahn, Electrospun polymer nanofibers: The booming cutting edge technology, React. Funct. Polym. 72(12), 915 (2012)
A. Krupa, A. Jaworek, A. T. Sobczyk, M. Lackowski, T. Czech, S. Ramakrishna, S. Sundarrajan, and D. Pliszka, Electrosprayed nanoparticles for nanofiber coating, ILASS 2008, 8-10.IX. 2008, Como Lake, Italy (Proc., Paper ID P-13)
K. C. Gupta, A. Haider, Y. Choi, and I. Kang, Nanofibrous scaffolds in biomedical applications, Biomaterials Research 18(1), 5 (2014)
S. Y. Chew, J. Wen, E. K. F. Yim, and K. W. Leong, Sustained release of proteins from electrospun biodegradable fibers, Biomacromolecules 6(4), 2017 (2005)
F. Zheng, S. Wang, M. Shen, M. Zhu, and X. Shi, Antitumor efficacy of doxorubicin-loaded electrospun nanohydroxyapatite–poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite nanofibers, Polym. Chem. 4(4), 933 (2013)
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, and S. Ramakrishna, A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites, Compos. Sci. Technol. 63(15), 2223 (2003)
T. T. Marquez-Lago, D. M. Allen, and J. Thewalt, A novel approach to modelling water transport and drug diffusion through the stratum corneum, Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 7(1), 33 (2010)
E. Fazio, A. Scala, S. Grimato, A. Ridolfo, G. Grassi, and F. Neri, Laser light triggered smart release of silibinin from a PEGylated–PLGA gold nanocomposite, J. Mater. Chem. B Mater. Biol. Med. 3(46), 9023 (2015)
F. Neri, A. Scala, S. Grimato, M. Santoro, S. Spadaro, F. Barreca, F. Cimino, A. Speciale, A. Saija, G. Grassi, and E. Fazio, Biocompatible silver nanoparticles embedded in a PEG–PLA polymeric matrix for stimulated laser light drug release, J. Nanopart. Res. 18(6), 153 (2016)
A. Hervault and N. T. K. Thanh, Magnetic nanoparticle-based therapeutic agents for thermochemotherapy treatment of cancer, Nanoscale 6(20), 11553 (2014)
E. Fazio, M. Santoro, G. Lentini, D. Franco, S. P. P. Guglielmino, and F. Neri, Iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation: Synthesis, structural properties and antimicrobial activity, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 490, 98 (2016)
S. H. Shim and T. S. Duffy, Raman spectroscopy of Fe2O3 to 62 GPa, Am. Mineral. 87(2–3), 318 (2002)
V. Rebuttini, E. Fazio, S. Santangelo, F. Neri, G. Caputo, C. Martin, T. Brousse, F. Favier, and N. Pinna, Chemical modification of graphene oxide through diazonium chemistry and its influence on the structureproperty relationships of graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposites, Chemistry 21(35), 1 (2015)
C. S. S. R. Kumar and F. Mohammad, Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63(9), 789 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spadaro, S., Santoro, M., Barreca, F. et al. PEG-PLGA electrospun nanofibrous membranes loaded with Au@Fe2O3 nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Front. Phys. 13, 136201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-017-0703-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-017-0703-9