Abstract
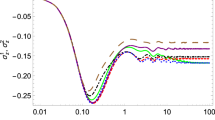
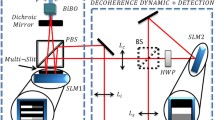
The study of open quantum systems is important for fundamental issues of quantum physics as well as for technological applications such as quantum information processing. The interaction of a quantum system with its environment is usually detrimental for the quantum properties of the system and leads to decoherence. However, sometimes a quantum control can lead to a coherent partial exchange of information between the system and the dynamics of the open system might become non-Markovian. In this article, we study experimentally discrete non-Markovian open quantum system dynamics. We implement a local control protocol using linear optics for controlling the information flow between the open system and the environment. We show how the transition from Markovian to non-Markovian dynamics can be controlled using only local operations for the open system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breuer HP, Petruccione F (2007) Theory of open quantum systems. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Alicki R, Lendi K (1987) Lecture notes in physics. In: Quantum dynamical semigroups and applications. Springer, Berlin
Gorini V, Kossakowski A, Sudarshan ECG (1976) Completely positive dynamical semigroups of \(N\)-level systems. J Math Phys 17:821–825
Lindblad G (1976) On the generators of quantum dynamical semigroups. Comm Math Phys 48:119–130
Gardiner CW, Zoller P (1999) Quantum noise. Springer series in synergetics. Springer, Berlin
Breuer HP, Laine EM, Piilo J et al (2015) Non-Markovian dynamics in open quantum systems. arXiv:1505.01385
Wolf MM, Cirac JI (2008) Dividing quantum channels. Comm Math Phys 279:147–168
Wolf MM, Eisert J, Cubitt TS et al (2008) Assessing non-Markovian quantum dynamics. Phys Rev Lett 101:150402
Breuer HP, Laine EM, Piilo J (2009) Measure for the degree of non-Markovian behavior of quantum processes in open systems. Phys Rev Lett 103:210401
Rivas Á, Huelga SF, Plenio MB (2010) Entanglement and non-Markovianity of quantum evolutions. Phys Rev Lett 105:050403
Luo S, Fu S, Song H (2012) Quantifying non-Markovianity via correlations. Phys Rev A 86:044101
Lorenzo S, Plastina F, Paternostro M (2013) Geometrical characterization of non-Markovianity. Phys Rev A 88:020102
Chruściński D, Maniscalco S (2014) Degree of non-Markovianity of quantum evolution. Phys Rev Lett 112:120404
Bylicka B, Chruściński D, Maniscalco S (2014) Non-Markovianity and reservoir memory of quantum channels: a quantum information theory perspective. Sci Rep 4:5720
Pollock FA, Rodríguez-Rosario C, Frauenheim T et al (2015) Complete framework for efficient characterisation of non-Markovian processes. arXiv:1512.00589
Liu BH, Li L, Huang YF et al (2011) Experimental control of the transition from Markovian to non-Markovian dynamics of open quantum systems. Nat Phys 7:931–934
Smirne A, Brivio D, Cialdi S et al (2011) Experimental investigation of initial system-environment correlations via trace-distance evolution. Phys Rev A 84:032112
Chiuri A, Greganti C, Mazzola L et al (2012) Linear optics simulation of quantum non-Markovian dynamics. Sci Rep 2:968
Bernardes NK, Cuevas A, Orieux A et al (2015) Experimental observation of weak non-Markovianity. Sci Rep 5:17520
Jirari H, Pötz W (2006) Quantum optimal control theory and dynamic coupling in the spin-boson model. Phys Rev A 74:022306
Rebentrost P, Serban I, Schulte-Herbrüggen T et al (2009) Optimal control of a qubit coupled to a non-Markovian environment. Phys Rev Lett 102:090401
Lapert M, Zhang Y, Braun M et al (2010) Singular extremals for the time-optimal control of dissipative spin \(\frac{1}{2}\) particles. Phys Rev Lett 104:83001
Schmidt R, Negretti A, Ankerhold J et al (2011) Optimal control of open quantum systems: cooperative effects of driving and dissipation. Phys Rev Lett 107:130404
Hwang B, Goan HS (2012) Optimal control for non-Markovian open quantum systems. Phys Rev A 85:032321
Tai JS, Lin KT, Goan HS (2014) Optimal control of quantum gates in an exactly solvable non-Markovian open quantum bit system. Phys Rev A 89:062310
D’Arrigo A, Franco RL, Beneti G et al (2014) Recovering entantlement by local operations. Ann Phys 350:211–224
Orieux A, D’Arrigo A, Ferranti G et al (2015) Experimental on-demand recovery of entanglement by local operations within non-Markovian dynamics. Sci Rep 5:8575
Dong WB, Wu RB, Yuan XH et al (2015) The modelling of quantum control systems. Sci Bull 60:1493–1508
Jing J, Wu LA (2015) Overview of quantum memory protection and adiabaticity induction by fast signal control. Sci Bull 60:328–335
Jin J, Giovannetti V, Fazio R et al (2015) All-optical non-Markovian stroboscopic quantum simulator. Phys Rev A 91:012122
Viola L, Knill E, Lloyd S (1999) Dynamical decoupling of open quantum systems. Phys Rev Lett 82:2417
Uhrig GS (2007) Keeping a quantum bit alive by optimized \(\pi \)-pulse sequences. Phys Rev Lett 98:100504
Lidar DA (2014) Quantum information and computation for chemistry. Wiley, New York
Lo Franco R, D’Arrigo A, Falci G et al (2014) Preserving entanglement and nonlocality in solid-state qubits by dynamical decoupling. Phys Rev B 90:054304
Nielsen M, Chuang I (2000) Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Luoma K, Piilo J (2015) Discrete dynamics and non-Markovianity. J Phys B. arXiv:1509.04231
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation and Academy of Finland (287750), National Natural Science Foundation of China (61327901, 11274289 and 11325419), the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB01030300). C.F.L. and J.P. acknowledge financial support from the EU Collaborative project QuProCS (Grant Agreement 641277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Sun, YN., Li, CF. et al. Non-Markovian discrete qubit dynamics. Sci. Bull. 61, 1031–1036 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1089-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1089-8