Abstract
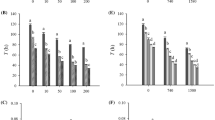
To avoid unfavorable environmental conditions, Scrippsiella trochoidea is capable of forming a resting cyst in the process of growth. In the present study, we investigated the effects of nitrate and ammonium on the growth and encystment of S. trochoidea. We incubated S. trochoidea in modified f/2 media without nitrogen and silicate in flasks. The flasks were divided into two groups. Nitrate was added as a nitrogen source in the first group, and ammonium was added in the second group. The concentrations of the nitrogen compounds were 0, 10, 30, 60, and 90 μmol/L. The results indicate that NO3 −-N favors cell growth, and the cultures with a higher concentration of NO3 −-N were ineffective at forming cysts. In contrast, NH4 +-N promoted cell growth and cyst formation. At similar concentrations as NO3 −-N, NH4 +-N had a toxic effect on cell growth and increased the cyst formation ratio. Thus, the NH4 +-N concentration is an important factor for controlling encystment. We believe that the impact of NH4 +-N in inducing cyst formation may be a useful feedback mechanism in ecological systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Blackburn SI, Parker N (2005) Microalgal life cycles: encystment and excystment. In: Andersen RA (ed) Algal culturing techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 399–417
Figueroa RI, Rengefors K, Bravo I et al (2010) From homothally to heterothally: mating preferences and genetic variation within clones of the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Deep Sea Res Part II 57:190–198
Tang YZ, Gobler CJ (2012) The toxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium Polykrikoides (Dinophyceae) produces resting cysts. Harm Algae 20:71–80
Wang ZH, Qi YZ, Yang YF (2007) Cyst formation: an important mechanism for the termination of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) bloom. J Plankton Res 29:209–218
Deng G, Li YG, Hu HJ et al (2004) Effects of temperature, light and pH on photosynthesis, and of light-dark cycle on growth rate and biomass of Scrippsiella trochoidea and Alexandrium tamarense. J Wuhan Bot Res 22:129–135 (in Chinese)
Cho HJ, Matsuoka K (2001) Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar Micropaleontol 42:103–123
Ishikawa A, Taniguchi A (1996) Contribution of benthic cysts to the population dynamics of Scrippsiella spp. (Dinophyceae) in Onagawa Bay, northeast Japan. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 140:169–178
Qi YZ, Hong Y, Zheng L et al (1996) Dinoflagellate cysts from resent marine sediments of the South and East China Seas. Asian Mar Biol 13:87–103
Wang ZH, Matsuoka K, Qi Y et al (2004) Dinoflagellate cyst records in recent sediments from Daya Bay, South China Sea. Phycol Res 52:396–407
Jensen MØ, Moestrup Ø (1997) Autoecology of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii: life history and growth at different temperatures and salinities. Eur J Phycol 32:9–18
Anderson DM, Wall D (1978) Potential importance of benthic cysts of Gonyaulax tamarensis and G. excavate in initiating toxic dinoflagellate blooms. J Phycol 20:224–234
Rintala JM, Spilling K, Blomster J (2007) Temporary cyst enables long-term dark survival of Scrippsiella hangoei. Mar Biol 152:57–62
Grzebyk D, Berland B (1996) Influences of temperature, salinity and irradiance on growth of Prorocentrum minimum (Dinophyceae) from the Mediterranean Sea. J Plankton Res 18:1837–1849
Granéli L (2011) Influence of altered light conditions and grazers on Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) cyst formation. Aquat Microb Ecol 63:231–243
Doucette GJ, Cembella AD, Boyer GL (1989) Cyst formation in the red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae): effects of iron stress. J Phycol 25:721–731
Chapman AD, Pfiester LA (1995) The effect of temperature, irradiance, and nitrogen on encystment and growth of the freshwater dinoflagelates Peridinium cinclum and P. willei in culture (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 31:355–359
Von Stosch HA (1973) Observations on vegetative reproduction and sexual life cycles of two freshwater dinoflagellates, Gymnodinium pseudopalustre Schiller and Woloszynskia apiculata sp. nov. Br Phycol J 8:105–134
Pfiester L (1976) Sexual reproduction of Peridinium willei (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 12:234–238
Subba Rao DV, Stewart JE (2011) A preliminary study of the formation of a third category of cysts dinoflagellate, Alexandrium fundyense in response to elevated concentrations of ammonium chloride. Harmful Algae 10:512–552
Shikata T, Nagasoe S, Yamasaki Y et al (2008) Encystment and excystment of Gyrodinium instriatum fredudenthal et Lee. J Oceanogr 64:355–365
Guillard RR, Kilham P, Jackson TA (1973) Kinetics of silicon-limited growth in marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana Hasle and Heimdal (= Cyclotella nana Hustedt). J Phycol 9:233–237
Grigorszky I, Kiss KT, Béres V et al (2006) The effect of temperature, nitrogen, and phosphorus on the encystment of Peridinium cinctum, Stein (Dinophyta). Hydrobiologia 563:527–535
Qi YZ, Zheng L, Wang R (1997) The life cycle of Scrippsiella Trochoidea and its physiol-ecological control. Oceanol Limnol Sin 20:588–592 (in Chinese)
Stéphane LH, Christian M, Pierre LC (1996) Nitrogen uptake in permanently well-mixed temperate coastal waters. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 42:803–818
Sergio OL (2002) Effects of different nitrogen sources on the growth and biochemical profile of 10 marine microalgae in batch culture: An evaluation for aquaculture. Phycologia 42:158–168
Jiang HM, Gao KS (2004) Effects of nitrogen sources and concentrations on the growth and fatiy acid composition of Phaeoda-ctylum tricornutum. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 28:545–550 (in Chinese)
Kremp A (2000) Distribution, dynamics and in situ seeding potential of Scrippsieela hangoei (dinophyceae) cyst population from the Baltic Sea. J Plankton Res 22:2155–2169
Shumway SE, Allen SM, Dee Boersma P (2003) Marine birds and harmful algal blooms: sporadic victims or under reported events? Harmful Algae 2:1–17
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge valuable suggestions of Professor Subbo Rao D. V. This work was supported by the Fund for Creative Research Groups by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41121064), “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA11020302), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41276115) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB428706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yu, Z., Song, X. et al. Effects of ammonium and nitrate on encystment and growth of Scrippsiella trochoidea . Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 4491–4497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0486-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0486-0