Abstract
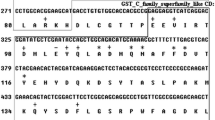
The glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) play important roles in detoxification of microcystins (MCs), but the responses of GSTs to MC-LR have not been well characterized in freshwater gastropod, Cipangopaludina cahayensis. In the present study, we cloned full-length cDNAs of mu- and pi-class GSTs (GSTM and GSTP) and partial cDNA of omega-class GST (GSTO), and determined the transcriptional responses of the three GST genes to different concentrations of MC-LR (0, 1, 10 and 100 μg/L) in C. cahayensis. The full-length cDNAs of GSTM and GSTP of C. cahayensis were 813 and 820 bp, containing an open reading frame (ORF) of 648 bp (encoding 215 amino acids) and 624 bp (encoding 207 amino acids), respectively. The mRNA expression of GSTM and GSTO significantly decreased after exposure to 10 μg/L MC-LR, and the mRNA expression of GSTP significantly decreased after 100 μg/L MC-LR exposure. This might contribute to the detoxication of MCs in C. cahayensis, which is consistent with its sedentary life and filter-feeder status. The mRNA expression of the three GST isoforms in C. cahayensis could be used as biomarkers for water contamination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen J, Xie P, Li L et al (2009) First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicol Sci 108:81–89
Carmichael WW (1997) The cyanotoxins. Adv Bot Res 27:211–256
Codd GA, Ward CJ, Bell SG (1997) Cyanobacterial toxins: occurrence, modes of action, health effects and exposure routes. In: Seiler JP, Vilanova E (eds) Applied toxicology: approaches through basic science. Springer, Berlin p 399–410
Dietrich D, Hoeger S (2005) Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue-green algal supplements): a reasonable or misguided approach. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:273–289
Fastner J, Codd GA, Metcalf JS et al (2002) An international intercomparison exercise for the determination of purified microcystin-LR and microcystins in cyanobacterial field material. Anal Bioanal Chem 374:437–444
Fischer WJ, Dietrich DR (2000) Pathological and biochemical characterization of microcystin-induced hepatopancreas and kidney damage in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 164:73–81
Kotak BG, Semalulu S, Fritz DL et al (1996) Hepatic and renal pathology of intraperitoneally administered microcystin-LR in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicon 34:517–525
Tencalla F, Dietrich D (1997) Biochemical characterization of microcystin toxicity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicon 35:583–595
Ibelings BW, Chorus I (2007) Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: a review. Environ Pollut 150:177–192
Martins JC, Vasconcelos VM (2009) Microcystin dynamics in aquatic organisms. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 12:65–82
Zurawell RW, Chen H, Burke JM et al (2005) Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J Toxicol Environ Health Sci 68:1–37
Amorim A, Vasconcelos V (1999) Dynamics of microcystins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 37:1041–1052
Pires LM, Karlsson KM, Meriluoto JAO et al (2004) Assimilation and depuration of microcystin-LR by the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha Aquat Toxicol 69:385–396
Watanabe MF, Park HD, Kondo F et al (1997) Identification and estimation of microcystins in freshwater mussels. Nat Toxins 5:31–35
Williams DE, Dawe SC, Kent ML et al (1997) Bioaccumulation and clearance of microcystins from salt water mussels, Mytilus edulis, and in vivo evidence for covalently bound microcystins in mussel tissues. Toxicon 35:1617–1625
Chen J, Xie P, Guo L et al (2005) Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in a freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Environ Pollut 134:423–430
Magalhães VF, Marinho MM, Domingos P et al (2003) Microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) bioaccumulation in fish and crustaceans from Sepetiba Bay (Brasil, RJ). Toxicon 42:289–295
Vasconcelos V, Oliveira S, Teles FO (2001) Impact of a toxic and a non-toxic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa on the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Toxicon 39:1461–1470
Gkelis S, Lanaras T, Sivonen K (2006) The presence of microcystins and other cyanobacterial bioactive peptides in aquatic fauna collected from Greek freshwaters. Aquat Toxicol 78:32–41
Ernst B, Dietz L, Hoeger SJ et al (2005) Recovery of MC-LR in fish liver tissue. Environ Toxicol 20:449–458
Magalhães VF, Soares RM, Azevedo SM (2001) Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepagua Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): ecological implication and human health risk. Toxicon 39:1077–1085
Mohamed ZA, Carmichael WW, Hussein AA (2003) Estimation of microcystins in the freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus in an Egyptian fish farm containing a Microcystis bloom. Environ Toxicol 18:137–141
Xie L, Yokoyama A, Nakamura K et al (2007) Accumulation of microcystins in various organs of the freshwater snail Sinotaia histrica and three fishes in a temperate lake, the eutrophic Lake Suwa. Japan. Toxicon 49:646–652
Gérard C, Brient L, Bertrand LR (2005) Variation in the response of juvenile and adult gastropods (Lymnaea stagnalis) to cyanobacterial toxin (microcystin-LR). Environ Toxicol 20:592–596
Lance E, Brient L, Bormans M et al (2006) Interactions between cyanobacteria and gastropods I. Ingestion of toxic Planktothrix agardhii by Lymnaea stagnalis and the kinetics of microcystin bioaccumulation and detoxification. Aquat Toxicol 79:140–148
Zhang D, Xie P, Liu Y et al (2007) Bioaccumulation of the hepatotoxic microcystins in various organs of a freshwater snail from a subtropical Chinese lake, Taihu Lake, with dense toxic Microcystis blooms. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:171–176
Habdija I, Latjner J, Belinić I (1995) The contribution of gastropod biomass in macrobenthic communities of a karstic river. Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 80:103–110
Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Oberemm A et al (1998) Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: the first step of detoxication. Biochim Biophys Acta 1425:527–533
Dai M, Xie P, Liang G et al (2008) Simultaneous determination of microcystin-LR and its glutathione conjugate in fish tissues by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry J Chromatogr B 862:43–50
Mannervik B, Alin P, Guthenberg C et al (1985) Identification of three classes of cytosolic glutathione transferase common to several mammalian species: correlation between structural data and enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7202–7206
Meyer DJ, Coles B, Pemble SE et al (1991) Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J 274:409–414
Pemble SE, Wardle AF, Taylor JB (1996) Glutathione S-transferase class Kappa: characterization by the cloning of rat mitochondrial GST and identification of a human homologue. Biochem J 319:749–754
Sheehan D, Meade G, Foley VM et al (2001) Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem J 360:1–16
Buet A, Banas D, Vollaire Y et al (2006) Biomarker responses in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) exposed to persistent organic pollutants. A field study in the Vaccares lagoon (Camargue, France). Chemosphere 65:1846–1858
Dellali M, Gnassia Barelli M, Romeo M et al (2001) The use of acetylcholinesterase activity in Ruditapes decussatus and Mytilus galloprovincialis in the biomonitoring of Bizerta lagoon. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 130:227–235
Lee YM, Park TJ, Jung SO et al (2006) Cloning and characterization of glutathione S-transferase gene in the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus and its expression after exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Mar Environ Res 62:219–223
Park H, Ahn IY, Kim H et al (2009) Glutathione S-transferase as a biomarker in the Antarctic bivalve Laternula elliptica after exposure to the polychlorinated biphenyl mixture Aroclor 1254. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 150:528–536
Monserrat JM, Martínez PE, Geracitano LA et al (2007) Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: critical review and new perspectives. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 146:221–234
Moreno I, Pereira P, Franca S, Camean A (2004) Toxic cyanobacteria strains isolated from blooms in the Guadiana river (Southwest of Spain). Biol Res 37:405–417
Lance E, Josso C, Dietrich D et al (2010) Histopathology and microcystin distribution in Lymnaea stagnalis (Gastropoda) following toxic cyanobacterial or dissolved microcystin-LR exposure. Aquat Toxicol 98:211–220
He S, Liang X-F, Sun J et al (2013) Induction of liver GST transcriptions by tert-butylhydroquinone reduced microcystin-LR accumulation in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Ecotox Environ Safe 90:128–135
Liang XF, Li GG, He S et al (2007) Transcriptional responses of alpha- and rho-class glutathione S-transferase genes in the liver of three freshwater fishes intraperitoneally injected with microcystin-LR: relationship of inducible expression and tolerance. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 5:289–298
Wang L, Liang X-F, Liao W-Q et al (2006) Structural and functional characterization of microcystin detoxification-related liver genes in a phytoplanktivorous fish, Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Phys C 144:216–227
Ji X, Zhang P, Armstrong RN et al (1992) The three-dimensional structure of a glutathione S-transferase from the mu gene class. Structural analysis of the binary complex of isoenzyme 3-3 and glutathione at 2.2-A resolution. Biochemistry 31:10169–10184
Rosa de Lima MF, Sanchez Ferreira CA, Joaquim de Freitas DR et al (2002) Cloning and partial characterization of a Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) glutathione S-transferase. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:747–754
Hong SJ, Lee JY, Lee DH et al (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a mu-class glutathione S-transferase from Clonorchis sinensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 115:69–75
Eaton DL, Bammler TK (1999) Concise review of the glutathione S-transferases and their significance to toxicology. Toxicol Sci 49:156–164
Reinemer P, Dirr HW, Ladenstein R et al (1992) Three-dimensional structure of class pi glutathione S-transferase from human placenta in complex with S-hexylglutathione at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol 227:214–226
Liu S, Zhang P, Ji X et al (1992) Contribution of tyrosine 6 to the catalytic mechanism of isoenzyme 3-3 of glutathione S-transferase. J Biol Chem 267:4296–4299
Ji X, Tordova M, O’Donnell R et al (1997) Structure and function of the xenobiotic substrate-binding site and location of a potential non-substrate-binding site in a class pi glutathione S-transferase. Biochemistry 36:9690–9702
Dirr H, Reinemer P, Huber R (1994) X-ray crystal structures of cytosolic glutathione S-transferases. Implications for protein architecture, substrate recognition and catalytic function. Eur J Biochem 220:645–661
Lo Bello M, Oakley AJ, Battistoni A et al (1997) Multifunctional role of Tyr 108 in the catalytic mechanism of human glutathione transferase P1-1. Crystallographic and kinetic studies on the Y108F mutant enzyme. Biochemistry 36:6207–6217
Doyen P, Vasseur P, Rodius F (2005) cDNA cloning and expression pattern of pi-class glutathione S-transferase in the freshwater bivalves Unio tumidus and Corbicula fluminea. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 140:300–308
Lo Bello M, Parker M W, Desideri A, et al. Peculiar spectroscopic and kinetic properties of Cys-47 in human placenta glutathione transferase, evidence for an atypical thiolate ion pair near the active site. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268: 19033-19038
Stenberg G, Abdalla AM, Mannervik B (2000) Tyrosine 50 at the subunit interface of dimeric human glutathione transferase P1-1 is a structural key residue for modulating protein stability and catalytic function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271:59–63
Hariharakrishnan J, Anand T, Satpute RM et al (2009) Activity and gene expression profile of certain antioxidant enzymes in different organs of rats after subacute cyanide exposure: effect of alpha-ketoglutarate. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:268–276
Hao L, Xie P, Fu J et al (2008) The effect of cyanobacterial crude extract on the transcription of GST mu, GST kappa and GST rho in different organs of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Aquat Toxicol 90:1–7
Li GY, Xi P, Fu J et al (2008) Microcystin-induced variations in transcription of GSTs in an omnivorous freshwater fish, goldfish. Aquat Toxicol 88:75–80
Lance E, Paty C, Bormans M et al (2007) Interactions between cyanobacteria and gastropods II. Impact of toxic Planktothrix agardhii on the life-history traits of Lymnaea stagnalis. Aquat Toxicol 81:389–396
Fu J, Xie P (2006) The acute effects of microcystin LR on the transcription of nine glutathione S-transferase genes in common carp Cyprinus carpio. L Aquat Toxicol 80:261–266
Bulera SJ, Eddy SM, Ferguson E et al (2001) RNA expression in the early characterization of hepatotoxicants in Wistar rats by high-density DNA microarrays. Hepatology 33:1239–1258
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2012BAD25B04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272641, 31172420), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013SC13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liang, XF., He, S. et al. Transcriptional responses of mu-, pi- and omega-class glutathione S-transferase genes in the hepatopancreas of Cipangopaludina cahayensis exposed to microcystin-LR. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 3153–3161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0305-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0305-7