Abstract
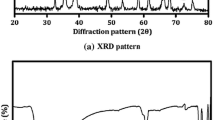
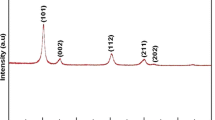
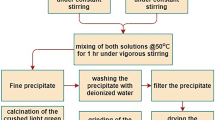
Monodisperse spherical Gd2O2S:Tb nanoparticles have been prepared using an improved homogeneous precipitation method combined with solid-gas sulfuration technology. The effects of Tb3+-doped concentration on luminescent intensity and color purity of samples were investigated, and the optimal Tb3+-doped concentration was determined. Under the excitation of X-ray, the obtained sample shows excellent luminescent properties, and its luminescent intensity is increased by about 50% under lower sulfuration temperature compared with that of the Gd2O2S:Tb nanoparticles prepared by complex precipitation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiong Z Y, Tang Q, Zhang C X. Investigation of thermoluminescence in Li2B4O7 phosphors doped with Cu, Ag and Mg. Sci China Ser G, 2007, 50: 311–320
Hu X Y, Fan J, Li T, et al. Novel trichromatic phosphor Co-doped with Eu, Tb in SiO2 gel matrix. Chinese Sci Bull, 2007, 52: 444–449
Hu X Y, Fan J, Zhang D K, et al. Tricolor white emitting phosphor co-doped with Eu, Dy in SiO2 matrix. Chinese Sci Bull, 2008, 53: 3491–3496
Li P L, Yang Z P, Wang Z J, et al. Preparation and luminescence characteristics of Sr3SiO5:Eu2+ phosphor for white LED. Chinese Sci Bull, 2008, 53: 974–977
Luo X X, Cao W H, Sun F. The development of silicate matrix phosphors with broad excitation band for phosphor-converted white LED. Chinese Sci Bull, 2008, 53: 2923–2930
Brixner L H. New X-ray phosphor. Mater Chem Phys, 1987, 16: 253–281
Cavouras D, Kandarakis I, Nomicos C D, et al. Measurement of the (Gd,La)2O2S:Tb phosphor efficiency for X-ray imaging applications. Radiation Measurements, 2000, 32: 5–13
Issler S L, Torardi C C. Solid state chemistry and luminescence of X-ray phosphors. J Alloy Compd, 1995, 229: 54–65
Wang P C, Cargill G S. Optimization of phosphor screens for charge coupled device based detectors and 7-34 keV X-rays. J Appl Phys, 1997, 81: 1031–1041
Kang Y C, Park S B. Zn2SiO4:Mn phosphor particles prepared by spray pyrolysis using a filter expansion aerosol generator. Mater Res Bull, 2000, 35: 1143–1151
Tian Y, Cao W H, Luo X X, et al. Preparation and luminescence property of Gd2O2S:Tb X-ray nano-phosphors using the complex precipitation method. J Alloy Compd, 2007, 433: 313–317
Yu S H, Han Z H, Yang J, et al. Synthesis and formation mechanism of La2O2S via a novel solvothermal pressure-relief process. Chem Mater, 1999, 11: 192–194
Dhanaraj J, Geethalakshmi M, Jagannatan R, et al. Eu3+ doped yttrium oxysulfide nanocrystals.crystallite size and luminescence transition(s). Chem Phys Lett, 2004, 387: 23–28
Vila L D, Stucchi E B, Davolos M R. Preparation and characterization of uniform, spherical particles of Y2O2S and Y2O2S:Eu. J Mater Chem, 1997, 7: 2113–2116
Matijević E, Hsu W P. Preparation and properties of monodispersed colloidal particles of lanthanide compounds. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1987, 118: 506–253
Martinez-Rubio M I, Ireland T G, Fern G R, et al. A new application for microgels: Novel method for the synthesis of spherical particles of the Y2O3:Eu phosphor using a copolymer microgel of NIPAM and acrylic acid. Langmuir, 2001, 17: 7145–7149
Tian Y, Cao W H, Luo X X, et al. Preparation of oxysulfide X-ray phosphor fine particles using emulsion liquid membrane system. J Chin Rare earth Soc, 2005, 23: 271–276
Hirai T, Orikoshi T. Preparation of yttrium oxysulfide phosphor nanoparticles with infrared-to-green and -blue upconversion emission using an emulsion liquid membrane system. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2004, 273: 470–477
Liu G X, Hong G Y, Wang J X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of spherical and hollow Gd2O3:Eu3+ phosphors. J Alloy Compd, 2007, 432: 200–204
Holsa J, Leskela M, Niinisto L. Concentration quenching of Tb3+ luminescence in LaOBr and Gd2O2S phosphors. Mat Res Bull, 1979, 14: 1403–1409
Silva A A, Cebim M A, Davolos M R. Excitation mechanisms and effects of dopant concentration in Gd2O2S:Tb3+ phosphor. J Lumin, 2008, 128: 1165–1168
Silver J, Ireland T G, Withnall R. Fine control of the dopant level in cubic Y2O3:Eu3+ phosphors. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151: H66–H68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10374011)
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, M., Cao, W., Pang, T. et al. Preparation and characterization of monodisperse spherical particles of X-ray nano-phosphors based on Gd2O2S:Tb. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 2982–2986 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0492-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0492-9