Abstract
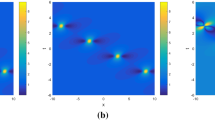
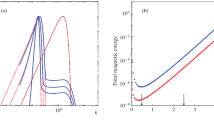
Dynamo theory describes the magnetic field induced by the rotating, convecting and electrically conducting fluid in a celestial body. The classical ABC-flow model represents fast dynamo action, required to sustain such a magnetic field. In this letter, Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs) in the ABC-flow are detected through Finite-time Lyapunov exponents (FTLE). The flow skeleton is identified by extracting intersections between repelling and attracting LCSs. For the case A = B = C = 1, the skeleton structures are made up from lines connecting two different types of stagnation points in the ABC-flow. The corresponding kinematic ABC-dynamo problem is solved using a spectral method, and the distribution of cigar-like magnetic structures visualized. Inherent links are found to exist between LCSs in the ABC-flow and induced magnetic structures, which provides insight into the mechanism behind the ABC-dynamo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. I. Arnold, Vladimir I. Arnold-Collected Works (Springer, Heidelberg, 1965) pp. 15–18.
V. I. Arnold, Y. B. Zel’dovich, A. A. Ruzmalkin, and D. D. Sokolov, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 81, 2052 (1981).
T. Dombre, U. Frisch, J. M. Greene, M. Hénon, A. Mehr, and A. M. Soward, J. Fluid Mech. 167, 353 (1986).
D. Galloway, and U. Frisch, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 36, 53 (1986).
V. Archontis, S. B. F. Dorch, and A. Nordlund, Astron. Astrophys. 397, 393 (2003).
V. Archontis, S. B. F. Dorch, and A. Nordlund, Astron. Astrophys. 410, 759 (2003).
I. Bouya, and E. Dormy, Phys. Fluids 25, 037103 (2013), arXiv: 1206.5186.
M. T. Xu, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 044702 (2015).
A. Alexakis, Phys. Rev. E 84, 026321 (2011), arXiv: 1105.3692.
E. Zienicke, H. Politano, and A. Pouquet, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4640 (1998).
G. Haller, and G. Yuan, Phys. D-Nonlin. Phenom. 147, 352 (2000).
G. Haller, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 47, 137 (2015).
G. Haller, Phys. D-Nonlin. Phenom. 149, 248 (2001).
H. Teramoto, G. Haller, and T. Komatsuzaki, Chaos 23, 043107 (2013).
Q. Wu, G. Y. Wang, B. Huang, and Z. Y. Bai, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 1169 (2014).
E. L. Rempel, A. C. L. Chian, A. Brandenburg, P. R. Muñoz, and S. C. Shadden, J. Fluid Mech. 729, 309 (2013), arXiv: 1210.6637.
D. Galloway, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 106, 450 (2012).
B. Galanti, P. L. Sulem, and A. Pouquet, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 66, 183 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51979162).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Lin, Z., Huang, C. et al. Flow and magnetic structures in a kinematic ABC-dynamo. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 284712 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-019-1568-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-019-1568-x