Abstract
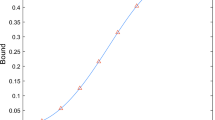
A universal entangler is a very powerful fault-tolerant entangling device for generating quantum entanglements from any joint states. Our paper aims to address the construction of universal entanglers. We prove that universal entanglers may be obtained from random unitary gates according to the Harr measure. The success probability is close to 1 for large system spaces. This result represents the typical density of entanglement subspaces in large state spaces. It also partially solves an open problem of universal bipartite entanglers and is explained by some experiment simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crépeau C, et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70: 1895–1899
Bouwmeester D, Pan J W, Mattle K, et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature, 1997, 390: 575–579
Bennett C H, DiVincenzo D P, Shor P W, et al. Remote state preparation. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 87: 077902
Ye M Y, Zhang Y S, Guo G C. Faithful remote state preparation using finite classical bits and a nonmaximally entangled state. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 022310
Luo M X, Chen X B, Ma S Y, et al. Joint remote preparation of an arbitrary three-qubit state. Opt Commun, 2010, 283: 4796–4801
Long L R, Li HW, Zhou P, et al. Multiparty-controlled teleportation of an arbitrary GHZ-class state by using a d-dimensional (N + 2)-particle nonmaximally entangled state as the quantum channel. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2011, 54(3): 484–490
Zhang X H, Yang Z Y, Xu P P. Teleporting N-qubit unknown atomic state by utilizing the V-type three-level atom. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2009, 52: 1034–1038
Luo M X, Deng Y, Chen X B, et al. The faithful remote preparation of general quantum states. Quantum Inf Process, 2013, 12: 279–294
Barenco A, Ekert A. Dense coding based on quantum entanglement. J Mod Opt, 1995, 42: 1253–1259
Mozes S, Reznik B, Oppenheim J. Deterministic dense coding with partially entangled states. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 012311
Bruß D, D’Ariano G M, Lewenstein M, et al. Distributed quantum dense coding. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 93: 210501
Liu X S, Long G L, Tong D M, et al. General scheme for superdense coding between multi-parties. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 022304
Zhang J F, Xie J Y, Wang C, et al. Implementation of a multiple round quantum dense coding using nuclear magnetic resonance. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2005, 48(6): 706–715
Dur W, Cirac J I. Classification of multiqubit mixed states: Separability and distillability properties. Phys Rev A, 2000, 61: 042314
Verstraete F, Dehaene J, Moor B D, et al. Four qubits can be entangled in nine different ways. Phys Rev A, 2002, 65: 052112
Miyake A, Verstraete F. Multipartite entanglement in 2×2×n quantum systems. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 012101
Vedral V, Plenio M B, Rippin M A, et al. Quantifying entanglement. Phys Rev Lett, 1997, 78: 2275–2278
Plenio M B, Vedral V. Bounds on relative entropy of entanglement for multi-party systems. J Phys A, 2000, 34: 6997–7002
Wang Y Z, Hou J C, Guo Y. An entanglement criterion for states in infinite-dimensional multipartite quantum systems. Chin Sci Bull, 2012, 57(1 4): 1643–1647
Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, et al. Quantum entanglement, Rev Mod Phys, 2009, 81: 865–942
Nielsen M A, Chuang I L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000
DiVincenzo D P, Terhal B M, Thapliyal A V. Optimal decomposition of barely separable states. J Mod Opt, 2000, 47: 377–385
Buzek V, Hillery M. Optimal manipulations with qubits: Universal quantum entanglers. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 022303
Kraus B, Cirac J I. Optimal creation of entanglement using a two-qubit gate. Phys Rev A, 2001, 63: 062309
Chen J, Duan R, Ji Z, et al. Existence of universal entangler. J Math Phys, 2008, 49: 012103
Chen J, Ji Z, Kribs D W, et al. Minimum entangling power is close to its maximum. arXiv:1210.1296v1
Yu N K, Duan R Y, Ying M S. Optimal simulation of a perfect entangler. Phys Rev A, 2010, 81: 032328
Chen L, Dokovic D. Equivalence classes and canonical forms for twoqutrit entangled states of rank four having positive partial transpose. J Math Phys, 2012, 53: 102205
Xie Q, Wu X X, Ding X M, et al. Testing quantum entanglement with local measurement. Chin Phys Lett, 2012, 29: 070306
Ren X Z, Cong H L, Wang X W, et al. Quantum entanglement of the binomial field interacting with a cascade three-level atom beyond the rotating wave approximation. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2011, 54: 1625–1630
Hamma A, Santra S, Zanardi P. Quantum entanglement in random physical states. Phys Rev Lett, 2012, 109: 040502
Rezakhani A T. Characterization of two-qubit perfect entanglers. Phys Rev A, 2004, 70: 052313
Clarisse L, Ghosh S, Severini S, et al. Entangling power of pemutations. Phys Rev A, 2005, 72: 012314
Hiai F, Petz D. The Semicircle Law, Free Random Variables and Entropy. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs 77, Am Math Soc, 2000
Hayden P, Leung D W, Shor P W. Randomizing quantum states: Constructions and applications. Commun Math Phys, 2004, 250: 371–391
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Luo, M., Chen, X. et al. Typical universal entanglers. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 1913–1917 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5524-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5524-z