Abstract
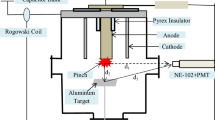
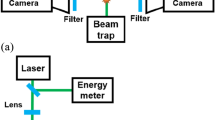
Image Plate (IP) is convenient to be used and very suitable for radiation detection because of its advantages such as wide dynamic range, high detective quantum efficiency, ultrahigh sensitivity and superior linearity. The function mechanism and characteristics of IP are introduced in this paper. IP was employed in the study of hot electrons generated from intense laser-plasma interaction. The angular distribution and energy spectrum of hot electrons were measured with IP in the experiments. The results demonstrate that IP is an effective radiation detector for the study of laser-plasma interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouseph P J. Introduction to Nuclear Radiation Detectors (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1980. 44–157
Chen C M. Development of Radiation Detectors in Physics and Biology (in Chinese). Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1978. 50–97
http://www.fujifilm.com/products/life_science/si_imgplate/img_plate.html, 2008-07
Kolodner P, Yablonovitch E. Proof of the resonant acceleration mechanism for fast electrons in gaseous laser targets. Phys Rev Lett, 1976, 37: 1754–1757
Moore C I, Ting A, McNaught S J, et al. A laser-accelerator injector based on laser ionization and ponderomotive acceleration of electrons. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82: 1688–1691
Li Y T, Zhang J, Sheng Z M, et al. Spatial distribution of high-energy electron emission from water plasmas produced by femtosecond laser pulses. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90: 165002
Miyahara J, Takahashi K. A new type of X-ray area detector utilizing laser stimulated luminescence. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A, 1986, 246: 572–578
Amemiya Y, Miyahara J. Imaging plate illuminates many fields. Nature, 1988, 336: 89–90
Rowlands J A. The physics of computed radiography. Phys Med Biol, 2002, 47: 123–166
Qi J. Digital X-ray photography: From now to future. J China Clin Med Imag (in Chinese), 1999, 10: 4–5
Yu R S, Wang B Y, Wei L, et al. Application of image plate as a sensitive detector of positrons. Nucl Tech (in Chinese), 2000, 23: 401–404
Tanaka K A, Kodama R, Fujita H, et al. Studies of ultra-intense laser plasma interactions for fast ignition. Phys Plasmas, 2000, 7: 2014–2022
Tanaka K A, Toshinori Y, Takashi S, et al. Calibration of imaging plate for high energy electron spectrometer. Rev Sci Instrum, 2005, 76: 013507
Li Y T, Yuan X H, Xu M H, et al. Observation of a fast electron beam emitted along the surface of a target irradiated by intense femtosecond laser pulses. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 165003
Izumi N, Snavely R, Gregori G, et al. Application of imaging plates to X-ray imaging and spectroscopy in laser plasma experiments. Rev Sci Instrum, 2006, 77: 10E325
Iwabuchi Y, Mori N, Takahashi K, et al. Mechanism of photostimulated luminescence process in BaFBr:Eu2+ phosphors. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1994, 33: 178–185
Gales S G, Bentley C D. Image plates as X-ray detectors in plasma physics experiments. Rev Sci Instrum, 2004, 75: 4001
Taniyama A, Shindo D, Oikawa T, et al. Detective quantum efficiency of the 25 um pixel size Imaging Plate for transmission electron microscopes. J Electron Microsc, 1997, 46: 303–310
Yuan X H, Li Y T, Xu M H, et al. Influence of laser incidence angle on hot electrons generated in the interaction of ultrashort intense laser pulses with foil target. Acta Phys Sin (in Chinese), 2006, 55: 5899–5904
Xu M H, Li Y T, Yuan X H, et al. Generation of surface electrons in femtosecond laser-solid interactions. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2006, 49(3): 335–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 10675164, 60621063, 10334110, 10575129, 10510490, and 10390161), the Funds of the Chinese Academy of Sciences for Key Topics in Innovation Engineering (Grant No. KJCX2-YW-T01) and the National High-Tech ICF Program
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, W., Li, Y., Xu, M. et al. Study of hot electrons generated from intense laser-plasma interaction employing Image Plate. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 51, 1455–1462 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0146-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0146-y