Abstract
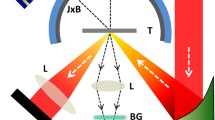
The characteristics of hot electrons produced by p-polarized femtosecond laser-solid interactions are studied. The experimental results show that the outgoing electrons are mainly emitted in three directions: along the target surface, the normal direction and the laser backward direction. The electrons flowing along the target surface are due to the confinement of the electrostatic field and the surface magnetic field, while the electrons in the normal direction due to the resonant absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L M, Zhang J, Li Y T, et al. Effects of laser polarization on jet emission of fast electrons in femtosecond-laser plasmas. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 87(22): 225001
Bastiani S, Rousse A, Geindre J P, et al. Experimental study of the interaction of subpicosecond laser pulses with solid targets of varying initial scale lengths. Phys Rev E, 1997, 56(6): 7179–7185
Chen L M, Zhang J, Dong Q L, et al. Hot electron generation via vacuum heating process in femtosecond laser-solid interactions. Physics of Plasmas, 2001, 8(6): 2925–2929
Li Y T, Zhang J, Chen L M, et al. Hot electrons in the interaction of femtosecond laser pulses with foil targets at a moderate laser intensity. Phys Rev E, 2001, 64(4): 46407
Malka G, Miquel J L. Experimental confirmation of ponderomotive-force electrons produced by an ultrarelativistic laser pulse on a solid target. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77(1): 75–78
Cowan T E, Hunt A W, Phillips T W, et al. Photonuclear fission from high energy electrons from ultraintense laser-solid interactions. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84(5): 903–906
Li Y T, Zhang J, Sheng Z M, et al. High-energy electrons produced in subpicosecond laser-plasma interactions from subrelativistic laser intensities to relativistic intensities. Phys Rev E, 2004, 69(3): 036405
Santala M I K, Zepf M, Watts I, et al. Effect of the plasma density scale length on the direction of fast electrons in relativistic laser-solid interactions. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84(7): 1459–1462
Tanaka K A, Yabuuchi T, Sato T, et al. Calibration of imaging plate for high energy electron spectrometer. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(1): 13507
Zhang J, Zhang J, Sheng Z M, Li Y T, et al. Emission direction of fast electrons in laser-solid interactions at intensities from the nonrelativistic to the relativistic. Phys Rev E, 2004, 69(4): 46408
Zhidkov A, Sasaki A, Utsumi T, et al. Prepulse effects on the interaction of intense femtosecond laser pulses with high-Z solids. Phys Rev E, 2000, 62(5): 7232–7240
Estabrook K, Kruer W L. Properties of resonantly heated electron distributions. Phys Rev Lett, 1978, 40(1): 42–45
Forslund D W, Kindel J M, Lee K. Theory of hot-electron spectra at high laser intensity. Phys Rev Lett, 1977, 39(5): 284–288
Sentoku Y, Ruhl H, Mima K, et al. Plasma jet formation and magnetic-field generation in the intense laser plasma under oblique incidence. Physics of Plasmas, 1999, 6(7): 2855–2861
Kruer W L, Estabrook K. J×B heating by very intense laser light. Phys Fluids, 1985, 28(1): 430–432
Nakamura T, Kato S, Nagatomo H, et al. Surface-magnetic-field and fast-electron current-layer formation by ultraintense laser irradiation. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 93(26): 265002
Cai D F, Gu Y Q, Zheng Z J, et al. Experimental study for angular distribution of the hot electrons generated by femtosecond laser interaction with solid targets. Physics of Plasmas, 2003, 10(8): 3265–3269
Andreev A A, Platonov K Y, Salomaa R R E. Backscattering of ultrashort high intensity laser pulses from solid targets at oblique incidence. Physics of Plasmas, 2002, 9(2): 581–588
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Li, Y., Yuan, X. et al. Generation of surface electrons in femtosecond laser-solid interactions. SCI CHINA SER G 49, 335–340 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-006-0335-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-006-0335-5