Abstracts
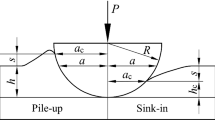
Pile-up around indenter is usually observed during instrumented indentation tests on bulk metallic glass. Neglecting the pile-up effect may lead to errors in evaluating hardness, Young’s modulus, stress-strain response, etc. Finite element analysis was employed to implement numerical simulation of spherical indentation tests on bulk metallic glass. A new model was proposed to describe the pile-up effect. By using this new model, the contact radius and hardness of Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass were obtained under several different indenter loads with pile-up, and the results agree well with the data generated by numerical simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson W L. Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys: Science and technology. MRS Bull, 1999, 24: 42–56
Inoue A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater, 2000, 48: 279–306
Wang W H, Dong C, Shek C H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mat Sci Eng R, 2004, 44: 45–89
Eckert J, Das J, Pauly S, et al. Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses and composites. J Mater Res, 2007, 22(2): 285–301
Hui X D, Chen G L. Bulk Metallic Glass (in Chinese). Beijing: Chemical Industry Publishing House, 2006
Spaepen F. A microscopic mechanism for steady state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall, 1977, 25: 407–415
Hufnagel T C, EI-Deiry P, Vinci R P. Development of shear band structure during deformation of a Zr57Ti5Cu20Ni8Al10 bulk metallic glass. Script Mater, 2000, 43(12): 1071–1075
Liu Y H, Wang G, Wang W H, et al. Super plastic bulk metallic glasses at room temperature. Science, 2007, 315: 1385–1388
Zhang Z F, Eckert J, Schultz L. Difference in compressive and tensile fracture mechanisms of Zr59Cu20Al10Ni8Ti3 bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 1167–1179
Liu L F, Dai L H, Bai Y L, et al. Characterization of rate-dependent shear behavior of Zr-based bulk metallic glass using shear-punch testing. J Mater Res, 2006, 21(1): 153–160
Liu L F, Dai L H, Bai Y L, et al. Initiation and propagation of shear bands in Zr-based bulk metallic glass under quasi-static and dynamic shear loadings. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2005, 351: 3259–3270
Zhang T, Inoue A. Thermal and mechanical properties of Ti-Ni-Cu-Sn amorphous alloys with a wide supercooled liquid region before crystallization. Mater Trans JIM, 1998, 39(10): 1001–1006
Hu X, Ng S C, Li Y, et al. Cooling-rate dependence of the density of Pd40Ni10Cu30P20 bulk metallic glass. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64(17): 172201
Dai L H, Yan M, Liu L F, et al. Adiabatic shear banding instability in bulk metallic glasses. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87(14): 141916
Yao K F, Zhang C Q. Fe-based bulk metallic glass with high plasticity. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90(6): 061901
Jiang Q K, Zhang G Q, Jiang J Z, et al. Glass formability, thermal stability and mechanical properties of La-based bulk metallic glasses. J Alloy Compd, 2006, 424(1-2): 183–186
Fu H M, Wang H, Zhang H F, et al. In situ TiB-reinforced Cu-based bulk metallic glass composites. Script Mater, 2006, 54(11): 1961–1966
Chen Q J, Shen J, Zhang D L, et al. Mechanical performance and fracture behavior of Fe41Co7Cr15Mo14Y2C15B6 bulk metallic glass. J Mater Res, 2007, 22(2): 358–363
Oliver W C, Pharr G M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res, 1992, 7(6): 1564–1583
Cheng Y T, Cheng C M. Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater Sci Eng R, 2004, 44: 91–149
Schuh C A, Nieh T G. A nanoindentation study of serrated flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 87–99
Zhang H W, Jing X N, Subhash G, et al. Investigation of shear band evolution in amorphous alloys beneath a Vickers indentation. Acta Mater, 2005, 53: 3849–3859
Wei B C, Zhang L C, Zhang T H, et al. Strain rate dependence of plastic flow in Ce-based bulk metallic glass during nanoindentation. J Mater Res, 2007, 22(2): 258–263
Li W H, Zhang T H, Wei B C, et al. Instrumented indentation study of plastic deformation in bulk metallic glasses. J Mater Res, 2006, 21(1): 75–81
Bhowmich R, Raghavan R, Chattopadhyay K, et al. Plastic flow softening in a bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater, 2006, 54: 4221–4228
Liu L, Chan K C. Plastic deformation of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses under nanoindentation. Mater Lett, 2005, 59: 3090–3094
Matthews J R. Indentation hardness and hot pressing. Acta Metall, 1980, 28: 311–318
Hill R, Storkers R, Zdunek A B. A theoretical study of the Brinell hardness test. Proc R Soc London A, 1989, 423: 301–330
Tuck J R, Korsunsky A M, Bull S J, et al. On the application of the work-of-indentation approach to depth-sensing indentation experiments in coated systems. Surf Coat Tech, 2001, 137: 217–224
Taljat B, Zacharia T. New analytical procedure to determine stress-strain curve from spherical indentation data. Int J Solids Struct, 1998, 35(33): 4411–4426
Hernot X, Bartier O, Bekouche Y, et al. Influence of penetration depth and mechanical properties on contact radius determination for spherical indentation. Int J Solids Struct, 2006, 43: 4136–4153
Tabor D. A simple theory of static and dynamic hardness. Proc R Soc London A-Math Phys, 1948, 192(1029): 247–274
Hertz H. On the Contact of Elastic Solids. London: Macmillan, 1896
Johnson K L. Contact Mechanics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1985
Johnson W L, Samwer K. A universal criterion for plastic yielding of metallic glasses with a (T = T g)2/3 temperature dependence. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 95: 195501
Yang B, Liu C T, Nieh T G. Unified equation for the strength of bulk metallic glasses. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 221911
Kameda J, Yokoyama Y, Allen T R. Strain-controlling mechanical behavior in noncrystalline materials (I): Onset of plastic deformation. Mat Sci Eng A, 2007, 448: 235–241
Liu L F, Dai L H, Bai Y L, et al. Behavior of multiple shear bands in Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Mater Chem Phys, 2005, 93: 174–177
Trichy G R, Scattergood R O, Koch C C, et al. Ball indentation tests for a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. Script Mater, 2005, 53(12): 1461–1465
Kim S H, Baik M K, Kwon D. Determination of precise indentation flow properties of metallic materials through analysis contact characteristics beneath indenter. J Eng Mater-T ASME, 2005, 127: 265–272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos 10725211, 10721202 and 10472119) and the Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant Nos KJCX2-YW-M04 and KJCX-SW-L08)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ai, K., Dai, L. Numerical study of pile-up in bulk metallic glass during spherical indentation. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. As 51, 379–386 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0043-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-008-0043-4