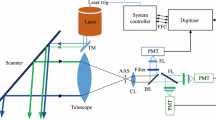
Abstract
Based on the dual-wavelength lidar we have developed, the 24 h continuous observation has been realized in its sodium channel by using Faraday atomic filter technology and other relevant technologies. This will facilitate the continuous observation of the sodium layer and the relevant upper atmosphere over Wuhan. A result of about 50 h observation indicates that the daytime column density of sodium layer over Wuhan is slightly increased compared to that during the nighttime, and the characteristics of the sporadic sodium layer occurring during the daytime are compared with that during the nighttime.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardner C S, Volez D G, et al. Lidar studies of the nighttime sodium layer over Urbana, Illinois. 1. Seasonal and nocturnal variations. J Geophys Res, 1986, 91(A12): 13659–13673
Kurzawa H, Von Zahn U. Sodium density and atmospheric temperature in the mesopause region in polar summer. J Atmos Terr Phys, 1990, 52(10): 891–993
Argall P S, Vassiliev O N, et al. Lidar measurements taken with a large-aperture liquid mirror. 2. Sodium resonance-fluorescence system. Appl Opt, 2000, 39(15): 2393–2400
Gong S S, Zeng X Z, et al. First time observation of sodium layer over Wuhan, China by sodium florescence lidar. Sci China Ser A-Math Phys Astron, 1997, 40(11): 1228–1235
Li H J, Zheng W G, et al. The observation and theoretical modeling of sodium distribution over Wuhan, China. Chin J Space Sci(in Chinese), 1999, 19(1): 54–60
Gong S S, Yang G T, Liu B M, et al. Some properties of sodium layer over Wuhan China observed by Na lidar, advances in laser remote sensing. 20th International Laser Radar Conference (ILRC). Vichy: Ecole Polytechnique, 2001. 421–424
Yang G T, Wang J M, Liu B M, et al. Contribution of the atmospheric dynamics to the sporadic sodium layer(SSL) formation. Chin Phys Lett, 2002, 19(4): 602–604
Gong S S, Yang G T, Wang J M, et al. A double sodium layer event observed over Wuhan, China by lidar. Geophys Res Lett, 2003, 30(5): 1209–1912
Chen H, She C Y, et al. Daytime mesopause temperature measurements with a sodium-vapor dispersive Faraday filter in a lidar receiver. Optics Lett, 1996, 21(5): 1093–1095
Gong S S, Jia H C, Wang J M, et al. Dual wavelength high altitude lidar. China Patent, No. ZL 00115964.X, 2000-8-18
Cheng X W, Song J, Li F Q, et al. Dual-wavelength high altitude detecting lidar technology. Chin J Lasers(in Chinese), 2006, 33(5): 601–606
Cheng X W, Li F Q, et al. Properties and applications of Faraday anomalous dispersion optical filter. Optics & Optoelectr Tech (in Chinese), 2003, 1(1): 41–43
Cheng X W, Li F Q, Song J, et al. Atomic and molecular frequency stabilization of pulse dye laser and its method. China Patent, No. 200510019816.X
Gibson A J, Sandford M C W. Daytime laser radar measurements of the atmospheric sodium layer. Nature, 1972, 239: 509–511
Granier C, Megie G. Daytime lidar measurements of the mesospheric sodium layer. Planet Space Sci, 1982, 30(2): 169–177
Gong S S, Yang G T, Wang J M, et al. Occurrence and characteristics of sporadic sodium layer observed by lidar at a mid-latitude location. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys, 2002, 64(18): 1957–1966
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. G2000078400)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Gong, S., Li, F. et al. 24 h continuous observation of sodium layer over Wuhan by lidar. SCI CHINA SER G 50, 287–293 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0032-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0032-z