Abstract
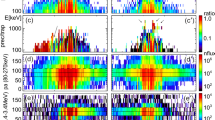
Electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EMIC) emission is an efficient mechanism for scattering loss of energetic protons. Here, we report an event that provides both in-situ observation of energetic proton differential fluxes in the inner magnetosphere and precipitation of protons at ionospheric altitudes. During the 7–8 September 2015 geomagnetic storm the Van Allen Probes observed strong EMIC waves around L = 5 and a distinct decrement in fluxes of tens of keV protons around pitch angles 0°–45°. Meanwhile, precipitating protons at ionospheric altitudes were found to significantly enhanced (by several orders of magnitude), measured by NOAA 18 and 19 when they magnetically linked to the Van Allen Probe-A. By solving the Fokker-Planck diffusion equation, we show that EMIC waves can efficiently produce loss of energetic protons within about 2 h in the pitch angle range of ∼ 0°–45°, comparable to the satellite observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y F, Zong Q G, Zhou X Z. Test particle simulation on the ion and electron zebra stripes and their time evolution in inner radiation belt. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 623–632
Lv X, Liu W L. Measurements of convection electric field in the inner magnetosphere. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 1866–1871
Liu B J, Zhang X X, He F. Tilt of the ring current during the main phases of intense geomagnetic storms. Sci China Tech Sci, 2019, 62: 820–828
Su Z, Wang G, Liu N, et al. Direct observation of generation and propagation of magnetosonic waves following substorm injection. Geophys Res Lett, 2017, 44: 7587–7597
Guo M Y, Zhou Q H, Xiao F L, et al. Upward propagation of lightning-generated whistler waves into the radiation belts. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 243–248
He J B, Jin Y Y, Xiao F L, et al. The influence of various frequency chorus waves on electron dynamics in radiation belts. Sci China Tech Sci, 2021, 64: 890–897
Mauk B H, McPherron R L. An experimental test of the electromagnetic ion cyclotron instability within the earth’s magnetosphere. Phys Fluids, 1980, 23: 2111–2127
Horne R B, Thorne R M. Convective instabilities of electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves in the outer magnetosphere. J Geophys Res, 1994, 99: 17259–17274
Min K, Lee J, Keika K, et al. Global distribution of EMIC waves derived from THEMIS observations. J Geophys Res, 2012, 117: A05219
Meredith N P, Horne R B, Kersten T, et al. Global morphology and spectral properties of EMIC waves derived from CRRES observations. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2014, 119: 5328–5342
Zhang X J, Li W, Thorne R M, et al. Statistical distribution of EMIC wave spectra: Observations from Van Allen Probes. Geophys Res Lett, 2016, 43: 12, 348
Guan C Y, Shang X J, Xie Y Q, et al. Generation of simultaneous H+ and He+ band EMIC waves in the nightside radiation belt. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 2369–2374
Teng S, Li W, Tao X, et al. Generation and characteristics of unusual high frequency EMIC waves. Geophys Res Lett, 2019, 46: 14230–14238
Wang D, Yuan Z, Yu X, et al. Statistical characteristics of EMIC waves: Van Allen Probe observations. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2015, 120: 4400–4408
Wang Z, Yuan Z, Li M, et al. Statistical characteristics of EMIC wave-driven relativistic electron precipitation with observations of POES satellites: Revisit. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2014, 119: 5509–5519
Erlandson R E, Ukhorskiy A J. Observations of electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves during geomagnetic storms: Wave occurrence and pitch angle scattering. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 3883–3895
Wang D, Yuan Z, Yu X, et al. Geomagnetic storms and EMIC waves: Van Allen Probe observations. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2016, 121: 6444–6457
Jordanova V K, Farrugia C J, Thorne R M, et al. Modeling ring current proton precipitation by electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves during the May 14–16, 1997, storm. J Geophys Res, 2001, 106: 7–22
Xiao F, Chen L, He Y, et al. Modeling for precipitation loss of ring current protons by electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves. J Atmos Sol-Terrestrial Phys, 2011, 73: 106–111
Xiao F, Yang C, Zhou Q, et al. Nonstorm time scattering of ring current protons by electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves. J Geophys Res, 2012, 117: A08204
Summers D. Quasi-linear diffusion coefficients for field-aligned electromagnetic waves with applications to the magnetosphere. J Geophys Res, 2005, 110: A08213
Li W, Shprits Y Y, Thorne R M. Dynamic evolution of energetic outer zone electrons due to wave-particle interactions during storms. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112: A10220
He H Y, Chen L X, Li J F. Geophysics, astronomy, and astrophysics: Characteristics of wave particle interaction in a hydrogen plasma. Chin Phys Lett, 2008, 25: 3511–3514
Zhu H, Su Z, Xiao F, et al. Nonlinear interaction between ring current protons and electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves. J Geophys Res, 2012, 117: A12217
Su Z, Zhu H, Xiao F, et al. Latitudinal dependence of nonlinear interaction between electromagnetic ion cyclotron wave and terrestrial ring current ions. Phys Plasmas, 2014, 21: 052310
Yahnin A G, Yahnina T A. Energetic proton precipitation related to ion cyclotron waves. J Atmos Sol-Terrestrial Phys, 2007, 69: 1690–1706
Usanova M E, Mann I R, Kale Z C, et al. Conjugate ground and multisatellite observations of compression-related EMIC Pc1 waves and associated proton precipitation. J Geophys Res, 2010, 115: A07208
Engebretson M J, Posch J L, Wygant J R, et al. Van Allen probes, NOAA, GOES, and ground observations of an intense EMIC wave event extending over 12 h in magnetic local time. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2015, 120: 5465–5488
Ni B, Cao X, Zou Z, et al. Resonant scattering of outer zone relativistic electrons by multiband EMIC waves and resultant electron loss time scales. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2015, 120: 7357–7373
He F, Cao X, Ni B, et al. Combined scattering loss of radiation belt relativistic electrons by simultaneous three-band EMIC waves: A case study. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2016, 121: 4446–4451
Wang B, Su Z, Zhang Y, et al. Nonlinear Landau resonant scattering of near equatorially mirroring radiation belt electrons by oblique EMIC waves. Geophys Res Lett, 2016, 43: 3628–3636
Sandanger M, Søraas F, Aarsnes K, et al. Loss of relativistic electrons: Evidence for pitch angle scattering by electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves excited by unstable ring current protons. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112: A12213
Yuan Z, Liu K, Yu X, et al. Precipitation of radiation belt electrons by EMIC waves with conjugated observations of NOAA and Van Allen Satellites. Geophys Res Lett, 2018, 45: 12,694
Wang D D, Yuan Z G, Deng X H, et al. Compression-related EMIC waves drive relativistic electron precipitation. Sci China Tech Sci, 2014, 57: 2418–2425
Mauk B H, Fox N J, Kanekal S G, et al. Science objectives and rationale for the radiation belt storm probes mission. Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 3–27
Stratton J M, Harvey R J, Heyler G A. Mission overview for the radiation belt storm probes mission. Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 29–57
Evans D S, Greer M S. Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellite Space Environment Monitor-2: Instrument Descriptions and Archive Data Documentation. NOAA Technical Memorandum OAR SEC-93. Boulder, 2004
Mitchell D G, Lanzerotti L J, Kim C K, et al. Radiation belt storm probes ion composition experiment (RBSPICE). Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 263–308
Funsten H O, Skoug R M, Guthrie A A, et al. Helium, oxygen, proton, and electron (HOPE) mass spectrometer for the radiation belt storm probes mission. Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 423–484
Spence H E, Reeves G D, Baker D N, et al. Science goals and overview of the radiation belt storm probes (RBSP) energetic particle, composition, and thermal plasma (ECT) suite on NASA’s Van Allen Probes mission. Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 311–336
Kletzing C A, Kurth W S, Acuna M, et al. The electric and magnetic field instrument suite and integrated science (EMFISIS) on RBSP. Space Sci Rev, 2013, 179: 127–181
Davidson R C, Ogden J M. Electromagnetic ion cyclotron instability driven by ion energy anisotropy in high-beta plasmas. Phys Fluids, 1975, 18: 1045–1050
Chen L, Thorne R M, Horne R B. Simulation of EMIC wave excitation in a model magnetosphere including structured high-density plumes. J Geophys Res, 2009, 114: A07221
Summers D. Relativistic electron pitch-angle scattering by electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves during geomagnetic storms. J Geophys Res, 2003, 108: 1143
He H Y, Chen L X, Tian T, et al. Astrophysics and space plasma: Gyroresonance between electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves and particles in a multi-ion plasma. Plasma Sci Technol, 2009, 11: 539–543
Lyons L R, Thorne R M. Parasitic pitch angle diffusion of radiation belt particles by ion cyclotron waves. J Geophys Res, 1972, 77: 5608–5616
Horne R B, Thorne R M, Glauert S A, et al. Electron acceleration in the Van Allen radiation belts by fast magnetosonic waves. Geophys Res Lett, 2007, 34: L17107
Su Z, Gao Z, Zhu H, et al. Nonstorm time dropout of radiation belt electron fluxes on 24 September 2013. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2016, 121: 6400–6416
Gao Z, Su Z, Zhu H, et al. Intense low-frequency chorus waves observed by Van Allen Probes: Fine structures and potential effect on radiation belt electrons. Geophys Res Lett, 2016, 43: 967–977
Yang C, Su Z, Xiao F, et al. Rapid flattening of butterfly pitch angle distributions of radiation belt electrons by whistler-mode chorus. Geophys Res Lett, 2016, 43: 8339–8347
Yang C, Xiao F, He Y, et al. Storm time evolution of outer radiation belt relativistic electrons by a nearly continuous distribution of chorus. Geophys Res Lett, 2018, 45: 2159–2167
Kurth W S, De Pascuale S, Faden J B, et al. Electron densities inferred from plasma wave spectra obtained by the Waves instrument on Van Allen Probes. J Geophys Res Space Phys, 2015, 120: 904–914
Shprits Y Y, Chen L, Thorne R M. Simulations of pitch angle scattering of relativistic electrons with MLT-dependent diffusion coefficients. J Geophys Res, 2009, 114: A03219
Su Z, Zheng H, Wang S. Evolution of electron pitch angle distribution due to interactions with whistler mode chorus following substorm injections. J Geophys Res, 2009, 114: A08202
Su Z P, Zheng H N. Resonant scattering of relativistic outer zone electrons by plasmaspheric plume electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves. Chin Phys Lett, 2009, 26: 129401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41774194, 41974212 and 42074198) and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories. The authors acknowledge the University of Iowa as the source for the EMFISIS data. We acknowledge Herb Funsten, Ruth Skoug, Brian Larsen and Geoff Reeves for the use of HOPE data. We thank NOAA for the access to the POES data. Data can be found at the following websites: http://emfisis.physics.uiowa.edu/Flight/ (EMFISIS), http://www.RBSP-ect.lanl.gov/ (ECT) and https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/satellite/poes/ (NOAA).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Wang, Z., Xiao, F. et al. Correlated observations linking loss of energetic protons to EMIC waves. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 65, 131–138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-021-1882-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-021-1882-x