Abstract
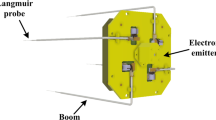
The China Seismo-Electromagnetic satellite (CSES) was designed to study the ionospheric disturbances associated with earthquakes. Satellite payload includes nine instruments. Among them, we recall instruments for plasma analysis, electric, magnetic fields and high energy particle detectors. Langmuir probe (LP) and plasma analyzer package (PAP) are the in-situ payloads to measure space plasma. Its scientific objective is to research space plasma physics phenomena and the ionosphere changes caused by seismic. It is the first application of in-situ measurement technology in the field of space exploration in China. The Langmuir probe and Plasma Analyzer Package have been tested and calibrated to verify the performance in INAF-IAPS. Currently, on-orbit testing is being performed with satellites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bleier T, Freund F. Impending earthquake have been sending us warning signals and people are starting to listen. IEEE Spectrum International, 2005, 12: 17–21
Parrot M, Berthelier J J, Lebreton J P, et al. Examples of unusual ionospheric observations made by the DEMETER satellite over seismic regions. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C, 2006, 31: 486–495
Hasbi A M, Mohd Ali M A, Misran N. Ionospheric variations before some large earthquakes over Sumatra. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci, 2011, 11: 597–611
Heki K. Ionospheric electron enhancement preceding the 2011 Tohoku- Oki earthquake. Geophys Res Lett, 2011, 38: L17312
Hsiao C C, Liu J Y, Oyama K I, et al. Ionospheric electron density anomaly prior to the December 26, 2006 M7.0 Pingtung earthquake doublet observed by FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C, 2009, 34: 474–478
Pulinets S A, Ouzounov D, Ciraolo L, et al. Thermal, atmospheric and ionospheric anomalies around the time of the Colima M7.8 earthquake of 21 January 2003. Ann Geophys, 2006, 24: 835–849
Kamogawa M. Preseismic lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling. Eos Trans AGU, 2006, 87: 417–424
Hayakawa M. Electromagnetic phenomena associated with earthquakes: Review. IEEJ Trans FM, 2001, 121: 893–898
Liu J, Huang J, Zhang X. Ionospheric perturbations in plasma parameters before global strong earthquakes. Adv Space Res, 2014, 53: 776–787
Hobara Y, Nakamura R, Suzuki M, et al. Ionospheric perturbations observed by the low altitude satellite DEMETER and possible relation with seismicity. J Atmos Electricity, 2013, 33: 21–29
Karia S, Sarkar S, Pathak K. Analysis of GPS-based TEC and electron density by the DEMETER satellite before the Sumatra earthquake on 30 September 2009. Int J Remote Sens, 2012, 33: 5119–5134
Yang F, Shen X H, Wu Y. Electromagnetic satellite and its application in the field of seismo-precursor detection. Space Eng, 2008, 17: 68–73
Zhang X, Shen X, Zhao S, et al. The characteristics of quasistatic electric field perturbations observed by DEMETER satellite before large earthquakes. J Asian Earth Sci, 2014, 79: 42–52
Shen X H, Wu Y, Shan X J. Remote sensing application in earthquake science and general proposal for earthquake satellite project in China. Recent Develop World Seismol, 2007, 344: 38–45
Shen X H, Zhang X M, Yuan S G, et al. The state-of-the-art of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite mission. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 634–642
Cao J B, Zeng L, Zhan F, et al. The electromagnetic wave experiment for CSES mission: Search coil magnetometer. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 653–658
Cheng B J, Zhou B, Magnes W, et al. High precision magnetometer for geomagnetic exploration onboard of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 659–668
Ambrosi G, Bartocci S, Basara L, et al. The HEPD particle detector of the CSES satellite mission for investigating seismo-associated perturbations of the Van Allen belts. Sci China Tech Sci, 2018, 61: 643–652
Mott-Smith H M, Langmuir I. the theory of collectors in gaseous discharges. Phys Rev, 1926, 28: 727–763
Guan Y, Wang S, Liu C. Design and simulation for the sensor of the space based Langmuir probe. Chin J Space Sci, 2012, 32: 750–756
Liu C, Guan Y B, Zhang A B. The ionosphere measurement technology of Langmuir probe on China seismo-electromagnetic satellite. Acta Phys Sin, 2016, 65: 189401
Wahlström M K, Johansson E, Veszelei E, et al. Improved Langmuir probe surface coatings for the Cassini satellite. Thin Solid Films, 1992, 220: 315–320
Eriksson A I, Boström R, Gill R, et al. RPC-LAP: The Rosetta Langmuir probe instrument. Space Sci Rev, 2007, 128: 729–744
Jiao W X. Space Exploration. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2002. 217–218
Rich F J. Users Guide for the Topside Ionospheric Plasma Monitor (SSIES, SSIES-2 and SSIES-3) on Spacecraft of the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program. Environ Res Paper, 1994, No.1151
Heelis R A, Hanson W B. Measurement techniques in space plasmas. Geophys Monogr Ser, 1998, 61: 102
Zheng X Z, Zhang A B, Guan Y B. Research on retarding potential analyzer abroad CSES. Acta Phys Sin, 2017, 66: 079401
Marrese C M, Majumdar N, Haas J M. Development of a Singleorifice Retarding Potential Analyzer for Hall Thruster Plume Characterization. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Electric Propulsion conference. Cleveland, 1997, 24: 397–404
Dahl D A. 2000SIMION 3D version 7.0 user’s manual, INEEL-95/0403. Idaho: Idaho National Engineering and Environment Laboratory
Maha S. QUASSIM. Inter-Calibration Between Plasma Instruments Onboard DEMETER. Plasma Science and Technology, 2008, 10: 539–545
Vannaroni G, Bruno R, Giammaria F, et al. “The INAF-IFSI Plasma Chamber. Technical Description”. INAF-IFSI-2009-18, 2009
Vannaroni G, Bruno R, Giammaria F, et al. “The INAF-IFSI Plasma Chamber. Ground-based ionospheric plasma simulation: Plasma parameter maps vs. magnetic field”. INAF-IFSI-2010-6, 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Guan, Y., Zheng, X. et al. The technology of space plasma in-situ measurement on the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62, 829–838 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-018-9345-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-018-9345-8