Abstract
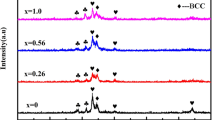
The effects of C element on the microstructure and properties of CoCrFeNiC x high entropy alloys ( x denoted the atomic fraction of C element at 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5) were investigated. The equal molar CoCrFeNi alloy with FCC structure exhibits high ductility but weak strength. With the addition of C element, both the hardness and strength of the CoCrFeNiC x high entropy alloys increase as well as the wear resistance. The solution strengthening and the formation of hard carbide phase are the main factor for the improved strength, hardness and wear resistance of CoCrFeNiC x high entropy alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh J W, Chen S K, Lin S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater, 2004, 6: 299–303
Cantor B, Chang I T H, Knight P, et al. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2004, 375–377: 213–218
Lu Z P, Wang H, Chen M W, et al. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics, 2015, 66: 67–76
Gao M C, Yeh J W, Liaw P K, et al. High-Entropy Alloys-Fundamentals and Applications. Berlin: Springer, 2016
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D, et al. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science, 2014, 345: 1153–1158
Li Z, Pradeep K G, Deng Y, et al. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature, 2016, 10: 227–230
Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1–93
Lu Y, Dong Y, Guo S, et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci Rep, 2015, 4: 6200
Liu W H, Lu Z P, He J Y, et al. Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater, 2016, 116: 332–342
Zhang Y, Zhou Y J, Hui X D, et al. Minor alloying behavior in bulk metallic glasses and high-entropy alloys. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2008, 51: 427–437
Guo S, Liu C T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog Nat Sci-Mater Int, 2011, 21: 433–446
Qiao J W, Wang Z, Ren L W, et al. Enhancement of mechanical and electrochemical properties of Al0.25CrCoFe1.25Ni1.25 high-entropy alloys by coating Ni-P amorphous films. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2016, 657: 353–358
Ding Z Y, He Q F, Yang Y. Exploring the design of eutectic or neareutectic multicomponent alloys: From binary to high entropy alloys. Sci China Technol Sci, 2017, 32
Senkov O N, Senkova S V, Dimiduk D M, et al. Oxidation behavior of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy. J Mater Sci, 2012, 47: 6522–6534
Chuang M H, Tsai M H, Wang W R, et al. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2011, 59: 6308–6317
Butler T, Weaver M. Influence of annealing on the microstructures and oxidation behaviors of A18(CoCrFeNi)92, Al15(CoCrFeNi)85, and Al30(CoCrFeNi)70 high-entropy alloys. Metals, 2016, 6: 222
Vrtnik S, Koželj P, Meden A, et al. Superconductivity in thermally annealed Ta-Nb-Hf-Zr-Ti high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 695: 3530–3540
Guo S, Ng C, Lu J, et al. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109: 103505–103505
Joseph J, Jarvis T, Wu X, et al. Comparative study of the microstructures and mechanical properties of direct laser fabricated and arcmelted AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng-A, 2015, 633: 184–193
Yang T, Xia S, Liu S, et al. Precipitation behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys under ion irradiation. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 32146
Schuh B, Mendez-Martin F, Völker B, et al. Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCr-FeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater, 2015, 96: 258–268
Pickering E J, Muñoz-Moreno R, Stone H J, et al. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scripta Mater, 2016, 113: 106–109
Liu W H, He J Y, Huang H L, et al. Effects of Nb additions on the microstructure and mechanical property of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics, 2015, 60: 1–8
Kong K H, Kim K C, Kim W T, et al. Microstructural features of multicomponent FeCoCrNiSix alloys. Appl Micro, 2015, 45: 32–36
Jiang L, Lu Y, Dong Y, et al. Annealing effects on the microstructure and properties of bulk high-entropy CoCrFeNiTi0.5 alloy casting ingot. Intermetallics, 2014, 44: 37–43
Salishchev G A, Tikhonovsky M A, Shaysultanov D G, et al. Effect of Mn and V on structure and mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys based on CoCrFeNi system. J Alloys Compd, 2014, 591: 11–21
Chen Q, Lu Y, Dong Y, et al. Effect of minor B addition on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi multi-compenent alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2015, 25: 2958–2964
Sheng W, Yang X, Wang C, et al. Nano-crystallization of high-entropy amorphous NbTiAlSiWxNy films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Entropy, 2016, 18: 226
Fang S, Chen W, Fu Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of twinned Al0.5CrFeNiCo0.3C0.2 high entropy alloy processed by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater Des (1980–2015), 2014, 54: 973–979
Shun T T, Du Y C. Age hardening of the Al0.3CoCrFeNiC0.1 high entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 478: 269–272
Guo N N, Wang L, Luo L S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in-situ MC-carbide particulates-reinforced refractory high-entropy Mo0.5NbHf0.5ZrTi matrix alloy composite. Intermetallics, 2016, 69: 74–77
Stepanov N D, Yurchenko N Y, Tikhonovsky M A, et al. Effect of carbon content and annealing on structure and hardness of the CoCrFeNiMn-based high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 687: 59–71
Zhu J M, Fu H M, Zhang H F, et al. Microstructure and compressive properties of multiprincipal component AlCoCrFeNiCx alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509: 3476–3480
Wang Z, Baker I, Cai Z, et al. The effect of interstitial carbon on the mechanical properties and dislocation substructure evolution in Fe40.4Ni11.3Mn34.8Al7.5Cr6 high entropy alloys. Acta Mater, 2016, 120: 228–239
Stepanov N D, Shaysultanov D G, Chernichenko R S, et al. Effect of thermomechanical processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of the carbon-containing CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 693: 394–405
Wang P, Cai H, Zhou S, et al. Processing, microstructure and properties of Ni1.5CoCuFeCr0.5−xVx high entropy alloys with carbon introduced from process control agent. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 695: 462–475
Poletti M G, Fiore G, Gili F, et al. Development of a new high entropy alloy for wear resistance: FeCoCrNiW0.3 and FeCoCrNiW0.3 +5at.% of C. Mater Des, 2017, 115: 247–254
Xie J, Chen N, Shen J, et al. Atomistic study on the structure and thermodynamic properties of Cr7C3, Mn7C3, Fe7C3. Acta Mater, 2005, 53: 2727–2732
Takeuchi A, Inoue A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater Trans, 2005, 46: 2817–2829
Wang Y, Yang Y, Yang H, et al. Microstructure and wear properties of nitrided AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Mater Chem Phys, 2017
Liu Y, Ma S, Gao M C, et al. Erratum to: Tribological properties of AlCrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloy in different conditions. Metall Mat Trans A, 2016, 47: 3781–3781
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, T., Jiang, L., Zhang, C. et al. Effect of carbon addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 61, 117–123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9134-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-017-9134-6