Abstract
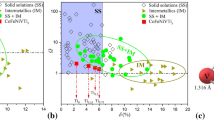
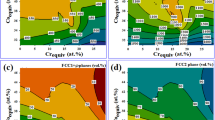
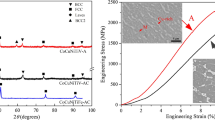
A series of CoCrFeNiMox (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2) high-entropy alloys were designed to develop a eutectic high-entropy alloy system and to acquire a superfine eutectic structure. The results show that for the CoCrFeNiMox alloys, with the increase of Mo content from 0.2 to 1.2, the microstructures shift from a typical dendrite structure to a hypoeutectic microstructure (x = 0.6), and then to a fully eutectic microstructure (x = 0.8) with a lamellar spacing only 110 nm, and finally culminate in the hypereutectic structure (x = 1.0, x = 1.2). The XRD results show that CoCrFeNiMox alloys have a single FCC phase when x is 0.2 or 0.4. When Mo content is over 0.6, it begins to separate Cr9Mo21Ni20 intermetallic compounds. The hardness of the CoCrFeNiMox alloys is increasing significantly from 172.8 to 763.7 HV with the increase of Mo content. Meanwhile, the fracture strength increased but the ductility decreases. Among these alloys, the CoCrFeNiMo0.6 alloy shows excellent integrated mechanical properties of compressive fracture strength and strain, which are 2051 Mpa and 23%, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 (2004).
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, and A.J.B. Vincent: Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 375–377, 213 (2004).
C. Huang, Y. Zhang, J. Shen, and R. Vilar: Thermal stability and oxidation resistance of laser clad TiVCrAlSi high entropy alloy coatings on Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206, 1389 (2011).
C-J. Tong, M-R. Chen, J-W. Yeh, S-J. Lin, S-K. Chen, T-T. Shun, and S-Y. Chang: Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 1263 (2005).
O. Senkov, S. Senkova, C. Woodward, and D. Miracle: Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater. 61, 1545 (2013).
K.M. Youssef, A.J. Zaddach, C. Niu, D.L. Irving, and C.C. Koch: A novel low-density, high-hardness, high-entropy alloy with close-packed single-phase nanocrystalline structures. Mater. Res. Lett. 3, 95 (2015).
T. Nagase, P.D. Rack, J.H. Noh, and T. Egami: In situ TEM observation of structural changes in nano-crystalline CoCrCuFeNi multicomponent high-entropy alloy (HEA) under fast electron irradiation by high voltage electron microscopy (HVEM). Intermetallics 59, 32 (2015).
J.W. Qiao, S.G. Ma, E.W. Huang, C.P. Chuang, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang: Microstructural characteristics and mechanical behaviors of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Sci. Forum 688, 419 (2011).
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, and R.O. Ritchie: A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 345, 1153 (2014).
H. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y. He, and H. Jiao: Microstructure and properties of 6FeNiCoSiCrAlTi high-entropy alloy coating prepared by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2259 (2011).
L. Wen, H. Kou, J. Li, H. Chang, X. Xue, and L. Zhou: Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 17, 266 (2009).
S. Xia, X. Yang, M. Chen, T. Yang, and Y. Zhang: The Al effects of Co-free and V-containing high-entropy alloys. Metals 7, 18 (2017).
S-K. Chen and Y-F. Kao: Near-constant resistivity in 4.2–360 K in a B2 Al2.08CoCrFeNi. AIP Adv. 2, 012111 (2012).
M.E. Glicksman: Principles of Solidification: An Introduction to Modern Casting and Crystal Growth Concepts (Springer Science & Business Media, New York, NY, 2010).
Y. Lu, Y. Dong, S. Guo, L. Jiang, H. Kang, T. Wang, B. Wen, Z. Wang, J. Jie, Z. Cao, H. Ruan, and T. Li: A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 4, 6200 (2014).
A.K. Mishra, S. Samal, and K. Biswas: Solidification behaviour of Ti–Cu–Fe–Co–Ni high entropy alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 65, 725 (2012).
S. Guo, C. Ng, and C.T. Liu: Anomalous solidification microstructures in Co-free AlxCrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 77 (2013).
L. Jiang, Z.Q. Cao, J.C. Jie, J.J. Zhang, Y.P. Lu, T.M. Wang, and T.J. Li: Effect of Mo and Ni elements on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the CoFeNixVMoy high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 649, 585 (2015).
Y. Tan, J. Li, J. Wang, and H. Kou: Seaweed eutectic-dendritic solidification pattern in a CoCrFeNiMnPd eutectic high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 85, 74 (2017).
F. He, Z. Wang, X. Shang, C. Leng, J. Li, and J. Wang: Stability of lamellar structures in CoCrFeNiNbx eutectic high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Mater. Des. 104, 259 (2016).
W.H. Liu, T. Yang, and C.T. Liu: Precipitation hardening in CoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 2 (2018).
X. Gao, Y. Lu, B. Zhang, N. Liang, G. Wu, G. Sha, J. Liu, and Y. Zhao: Microstructural origins of high strength and high ductility in an AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 141, 59 (2017).
Y. Lu, X. Gao, L. Jiang, Z. Chen, T. Wang, J. Jie, H. Kang, Y. Zhang, S. Guo, H. Ruan, Y. Zhao, Z. Cao, and T. Li: Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 124, 143 (2017).
F. He, Z. Wang, P. Cheng, Q. Wang, J. Li, Y. Dang, J. Wang, and C.T. Liu: Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 284 (2016).
Y. Lu, H. Jiang, S. Guo, T. Wang, Z. Cao, and T. Li: A new strategy to design eutectic high-entropy alloys using mixing enthalpy. Intermetallics 91, 124 (2017).
Z. Ding, Q. He, and Y. Yang: Exploring the design of eutectic or near-eutectic multicomponent alloys: From binary to high entropy alloys. Sci. China: Technol. Sci. 61, 159–167 (2017).
Y. Dong, L. Jiang, H. Jiang, Y. Lu, T. Wang, and T. Li: Effects of annealing treatment on microstructure and hardness of bulk AlCrFeNiMo0.2 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 82, 91–97 (2015).
E. ASTM: E9–89a, standard test methods of compression testing of metallic materials at room temperature. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 3 (ASTM International, Philadelphia, PA, 2000), pp. 1–9.
T-T. Shun, L-Y. Chang, and M-H. Shiu: Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater. Charact. 70, 63 (2012).
W.H. Liu, Z.P. Lu, J.Y. He, J.H. Luan, Z.J. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Liu, M.W. Chen, and C.T. Liu: Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater. 116, 332 (2016).
H. Jiang, K. Han, D. Qiao, Y. Lu, Z. Cao, and T. Li: Effects of Ta addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 43–48 (2018).
L. Jiang, Y. Lu, Y. Dong, T. Wang, Z. Cao, and T. Li: Effects of Nb addition on structural evolution and properties of the CoFeNi2V0.5 high-entropy alloy. Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 119, 291 (2015).
Z. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Yang, J. Wang, and C.T. Liu: Atomic-size effect and solid solubility of multicomponent alloys. Scr. Mater. 94, 28 (2015).
L. Liu, L.J. He, J.G. Qi, B. Wang, Z.F. Zhao, J. Shang, and Y. Zhang: Effects of Sn element on microstructure and properties of SnxAl2.5FeCoNiCu multi-component alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 654, 327 (2016).
S. Guo and C.T. Liu: Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci.: Mater. Int. 21, 433 (2011).
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue: Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46, 2817 (2005).
E.J. Pickering and N.G. Jones: High-entropy alloys: A critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 61, 183 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51601086, 51405215, and 51702143), Liaoning Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2015020204), and Doctoral Initiating Project of Liaoning Province Foundation for Natural Sciences, China (Grant No. 201601342).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Liu, L., Zhang, Y. et al. A superfine eutectic microstructure and the mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMox high-entropy alloys. Journal of Materials Research 33, 3258–3265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.177
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.177