Abstract
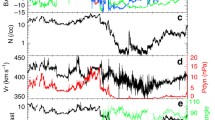
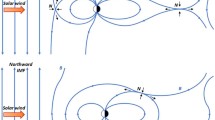
By analyzing hot ion and electron parameters together with magnetic field measurements from Cluster, an event of magnetopause crossing of the spacecraft has been investigated. At the latitude of about 40° and magnetic local time (MLT) of 13:20 during the southward interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), a transition layer was observed, with the magnetospheric field configuration and cold dense plasma features of the magnetosheath. The particle energy-time spectrograms inside the layer were similar to but still a little different from those in the magnetosheath, obviously indicating the solar wind entry into the magnetosphere. The direction and magnitude of the accelerated ion flow implied that reconnection might possibly cause such a solar wind entry phenomenon. The bipolar signature of the normal magnetic component B N in magnetopause coordinates further supported happening of reconnection there. The solar wind plasma flowed toward the magnetopause and entered the magnetosphere along the reconnected flux tube. The magnetospheric branch of the reconnected flux tube was still inside the magnetosphere after reconnection and supplied the path for the solar wind entry into the dayside magnetosphere. The case analysis gives observational evidence and more details of how the reconnection process at the dayside low latitude magnetopause caused the solar wind entry into the magnetosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnstone A D, Burge S, Carter P J, et al. PEACE: a plasma electron and current experiment. Space Sci Rev, 1997, 79(1–2): 351
Akasofu S I. Energy coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere. Space Sci Rev, 1981, 28(1): 121–190
Hasegawa H, Fujimoto M, Phan T D, et al. Transport of solar wind into magnetosphere through rolled-up Kelvin-Helmholtz vortices. Lett Nature, 2004, 430(6): 755–758
Baumjohann W, Paschmann G. Solar wind magnetosphere coupling: Process and observations. Phys Scripta, 1987, 18(1): 61
Burton R K, McPherron R L, Russell C T. An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst. J Geophys Res, 1975, 80(31): 4204
Fujomoto M, Terasawa T. Anomalous ion mixing within an MHD scale Kelvin-Helmholtz votex. J Geophys Res, 1995, 100(A7): 12025–12033
Fujimoto M, Nishida A, Mukai T, et al. Plasma entry from the flanks of the near-Earth magnetotail: GEOTAIL observations in the dawn-side LLBL and the plasma sheet. J Geomag Geoelectr, 1996, 48(6): 711–727
Gonzalez W D. A unified view of solar wind-magnetospheric coupling functions. Planet Space Sci, 1990, 38(5): 627
Perreault P, Akasofu S I. A study of geomagnetic storms. Geophys J R Astron Soc, 1978, 54(4): 547
Treumann R A, LaBelle J, Bauer T M. Diffussion processes: an observational perspective. In: Song P, Sonnerup B U O, Thomas M F, eds. Physics of the Magnetopause. Washington D C: American Geophysical Union, 1995. 331
Yeh T, Akasofu S I. A theoretic derived energy coupling function for the magnetosphere. Space Sci Rev, 1981, 29(4): 425–429
Dungey J W. Interplanetary magnetic filed and auroral zones. Phys Rev Lett, 1961, 6(2): 47
Hasegawa H, Fujimoto M, Saito Y, et al. Dense and stagnant ions in the low-latitude-boundary-region under northward interplanetary magnetic field. Geophys Res Lett, 2004, 31(6): L06802
Reiff P H, Hill T W, Burch J L. Solar wind plasma injection at the dayside magnetospheric cusp. J Geophys Res, 1977, 82(3): 479–491
Song P, Russell C T. Model of the formation of the low-latitude boundary layer for strongly northward interplanetary magnetic field. J Geophys Res, 1992, 97(A2): 1411–1420
Axford W I, Hines C O. A unifying theory of high-latitude geophysical phenomena and geomagnetic storms. Can J Phys, 1961, 39(10): 1433
Mishin V V. Velocity boundary layers in the distant geotail and the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability. Planet Space Sci, 2004, 53(1–3): 157–160
LaBelle J, Treumann R A. Plasma waves at the dayside magnetopause. Space Sci Rev, 1988, 47(1–2): 175
Manuel J R, Samson J C. The spatial development of the low-latitude boundary layer. J Geophys Res, 1993, 98(A10): 17367–17385
Winske D, Thomas V A, Omidi N. Diffussion at the magnetopause: a theoretical perspective. In: Song P, Sonnerup B U O, Thomas M F, eds. Physics of the Magnetopause. Washington D C: American Geophysical Union, 1995. 321
Chandler M O, Avanov L A. Observations at low latitudes of magnetic merging signatures within a flux transfer event during a northward interplanetary magnetic field. J Geophys Res, 2003, 108(A10): 1358. doi:10.1029/2003JA009852
Milan S E, Provan G, Hubert B. Magnetic flux transport in the Dungey cycle: A survey of dayside and nightside renconnction rates. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112(A1): A01209. doi: 10.1029/2006JA011642
Yan G Q, Shen C, Liu Z X, et al. Solar wind transport into magnetosphere caused by magnetic reconnection at high latitude magnetopause during northward IMF: Cluster-DSP conjunction observations. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2008, 51(10): 1677–1684
Haerendel G, Paschmann G. Entry of solar wind plasma into the magnetosphere. In: Hultqvist B, Stenflo L, eds. Physics of the Hot Plasma in the Magnetosphere. New York: Plenum Press, 1975. 23
Paschmann G, Haerendel G, Sckopke N, et al. Plasma and magnetic field characteristics of the distant polar cusp near local noon: The entry layer. J Geophys Res, 1976, 81(16): 2883
Escoubet C P. The Cluster mission. Ann Geophys, 2001, 19(10–12): 1197–1200
Rème H, Aoustin C, Bosqued J M, et al. First multispacecraft ion measurement in and near the Earth’s magnetosphere with the identical Cluster ion spectro-metry (CIS) experiment. Ann Geophys, 2001, 19(10–12): 1303–1354
Balogh A, Carr C M, Acuna M H, et al. The Cluster magnetic field investigation: overview of in-flight performance and initial results. Ann Geophys, 2001, 19(10–12): 1207–1217
Sonnerup B U O, Cahill L J. Magnetopause structure and attitude from Explorer 12 observations. J Geophys Res, 1967, 72(1): 171–183
Sonnerup B U O, Cahill L J. Theory of the magnetopause current layer. J Geophys Res, 1968, 73(5): 1757–1770
Phan T D, Paschmann G, Baumjohann W, et al. The magnetosheath region adjacent to the dayside magnetopause: AMPTE/IRM observations. J Geophys Res, 1994, 99(A1): 121–141
Dunlop M W, Taylor M G G T, Davies J A, et al. Coordinated Cluster/Double Star observations of dayside reconnection signatures. Ann Geophys, 2005, 23(11): 2867–2875
Lee L C, Fu Z F. A theory of magnetic flux transfer at the earth’s magnetopause. Geophys Res Lett, 1985, 12(2): 105–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2006CB806305), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40621003, 40620130094, 40674094 and 40731054), the Hundred Talents Program of the CAS, and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, G., Liu, Z., Shen, C. et al. Solar wind entry via flux tube into magnetosphere observed by Cluster measurements at dayside magnetopause during southward IMF. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52, 2104–2111 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0088-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0088-2