Abstract
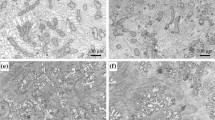
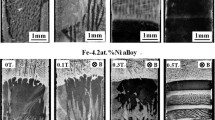
The influence of the rotating magnetic field (RMF) on the solidification process of Pb-Sn binary alloys is studied by comparing the solidification microstructures under the common condition and RMF condition. It is found that the RMF can completely eliminate the gravity induced macrosegregation, and result in dendrite fragmentation and promote solute diffusion velocity. These differences are regarded as the effect of complicated melt flow caused by RMF. Moreover, when the content of the primary phase is small, many spherical microstructures form under the RMF condition. The analyses indicate that these special microstructures are likely the conjunction action of melt flow and concentration and temperature field uniformity caused by RMF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang X D, Li T J, Fautrelle Y, et al. Two kinds of magnetic fields induced by one pair of rotating permanent magnets and their application in stirring and controlling molten metal flows. J Cryst Growth, 2005, 275: 1473–1479
Vives C. Elaboration of semisolid alloys by means of new electromagnetic rheocasting process. Metall Trans B, 1992, 23(2): 189–205
Flemings M C. Behavior of metal alloys in the semisolid state. Metall Trans B, 1991, 22(6): 269–293
Mao W M, Zhen Z S, Chen H T. Microstructures of AZ91D alloy solidified during electromagnetic stirring. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2005, 15(1): 72–76
Mao W M, Li S S, Zhao A M, et al. Microstructures of hypereutectic Al-24%Si alloy stirred by electromagnetic field. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (in Chinese), 2001, 11(5): 819–823
Zhang K, Liu G J, Xu J, et al. Semi-solid Al-7%Si alloy prepared by electromagnetic stirring-continuous casting technology and its solidification microstructures. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China (in Chinese), 2000, 10(1): 47–50
Zhang W Q, Yang Y S, Zhu Y F, et al. Structural transition and macro-segregation of Al-Cu eutectic alloy solidified in the electromagnetic centrifugal casting process. Metall Mater Trans A, 1998, 29(1): 404–408
Zhang W, Yang Y, Liu Q, et al. Effects of forced flow on morphology of Al-CuAl2 eutectic solidified with electromagnetic stirring. J Mater Sci Letts, 1997, 16(23): 1955–1957
Xu Z H. A study on solidified structures of Al-Si alloys under rotary magnetic field condition. Foundry (in Chinese), 2000, 49(2): 115–117
Li Z, Wu B Y. Mechanism and evolution of morphology of the primary phases for ZA-27 alloy in the rotating electromagnetic field. Foundry (in Chinese), 1997, 10: 1–5
Campanella T, Charbon C, Rappaz M. Grain refinement induced by electromagnetic stirring: A dendrite fragmentation criterion. Metall Mater Trans A, 2004, 35(10): 3201–3210
Yang Z, Seo P K, Kang C G. Grain size control of semisolid A356 alloy manufactured by electromagnetic stirring. J Mater Sci Tech, 2005, 21(2): 219–225
Smithells C J. Smithells Metals Reference Book. 6th ed. London: Butterworths, 1983. 14-1–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Chen, C., Hong, Z. et al. Effect of rotating magnetic field on the solidification microstructures of Pb-Sn alloys. SCI CHINA SER E 49, 274–282 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-006-0274-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-006-0274-4