Abstract
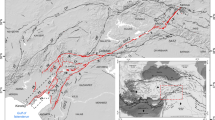
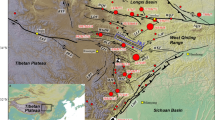
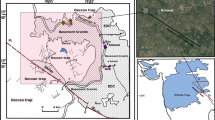
The kinematic characteristics of the Sanguankou-Niushoushan fault (SGK-NSSF) are of great significance to the understanding of the extension of the arc tectonic belt in the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau. Using field surveys and various data collection methods, including large-scale geological mapping, measurement of typical topographies, and dating of sedimentary strata, it was determined that the SGK-NSSF exhibits obvious dextral strike-slip characteristics and thus is not a sinistral strike-slip fault, as believed by previous researchers. The results of this study show that the geological boundaries for the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras were all dextrally dislocated by the fault, with the faulted displacements being similar. The maximum strike-slip displacement of the fault, after elimination of topographic effects, was found to be 961±6 m. The Sanguankou fault at the northern section exhibits obvious characteristics of more recent activities, with a series of small gullies having undergone synchronized dextral writhing after traversing the fault. The average horizontal slip rate of the fault since the late Quaternary was determined to be approximately 0.35 mm/a. The pre-existing fold structures formed during the late Pliocene were dislocated by the fault and became ex situ, indicating that dextral strike-slip of the fault could not have occurred prior to the late Pliocene. The maximum displacements and average slip rates were used to estimate the onset time of the dextral strike-slip activities of the fault as being after 2.7 Ma. In this study, the understanding of previous researchers concerning the extension in the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau was combined with analyses of the successive relationships between fold deformations and fault activities. This led to the finding that the extension in the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau reached the vicinity of the SGK-NSSF during the late Pliocene (∼2.7 Ma), causing regional uplift and fold deformations of the strata there. During the early Quaternary, the northeastern compression of the Tibet Plateau and the counterclockwise rotation of the Ordos block collectively resulted in the dextral strike-slip activities of the SGK-NSSF. This then formed the foremost margin of the arc tectonic belt extension in the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burchfiel B C, Deng Q D, Molnar P, Royden L, Wang Y P, Zhang P Z. 1989. Intracrustal detachment within zones of continental deformation. Geology, 17: 748–752
Burchfiel B C, Zhang P Z, Wang Y P, Zhang W Q, Song D M, Deng Q D, Molnar P, Royden L. 1991. Geology of the Haiyuan Fault zone, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China, and its relation to the evolution of the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 10: 1091–110
Chai C Z, Zhang W Q, Jiao D C. 1998. Quaternary structure feature in forward area of Tianjingshan fault (in Chinese). Earthq Res Chin, 14: 150–56
Chai C Z, Meng G K, Ma G R. 2011. Active Faults Exploration and Seismic Hazard Assessment in Yinchuan City (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press. 28–30
Chen H, Hu J M, Gong W B, Li L B. 2013. Cenozoic deformation and evolution of the Niushoushan-Luoshan fault zone in the northeast margin of the Tibet Plateau (in Chinese). Earth Sci Front, 20: 018–035
Deng Q D, Sung F M, Zhu S L, Li M L, Wang T L, Zhang W Q. 1984. Active faulting and tectonics of the Ningxia-Hui autonomous region, China. J Geophy Res, 89: 4427–4445
Deng Q D, Liao Y H. 1996. Paleoseismology along the range-front fault of Helan Mountains, North Central China. J Geophys Res, 101: 5873–5894
Deng Q D, Zhang W Q, Zhang P Z, Jiao D C, Song F M, Wang Y P, Burchfiel B C, Molnar P, Royden L, Zhu S F, Zhu S L, Chai C Z. 1989. Haiyuan Strike slip Fault zone and its compressional structures of the end (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 11: 1–14
Deng Q D, Zhang P Z, Ran Y K, Yang X P, Min W, Chu Q Z. 2003. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 46: 356–372
England P, Houseman G. 1985. Role of lithospheric strength heterogeneities in the tectonics of Tibet and neighbouring regions. Nature, 315: 297–301
England P, Molnar P. 1997. The field of crustal velocity in Asia calculated from Quaternary rates of slip on fault. Geophys J Int, 130: 551–582
Jiang H C, Ding Z L, Xiong S F. 2007. Magnetostratigraphy of the Neogene Sikouzi section at Guyuan, Ningxia, China. Palaeogeography, 243:223–234
Huo F C, Pan X S, You G L. 1989. Introduction to Geology of Ningxia (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press. 1–300
Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration (IGCEA), Earthquake Administration of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. 1990. Haiyuan Active Fault Zones (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press. 1–278
Lei Q Y, Chai C Z, Meng G K, Du P, Wang Y, Xie X F. 2008. Composite drilling section exploration of Yinchuan buried fault (in Chinese). Seismol Geo, 30: 250–262
Lei Q Y, Chai C Z, Meng G K, Wang Y, Meng G K. 2011. Activity characteristics of Luhuatai buried fault since late Quaternary revealed by drilling (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 33: 602–614
Lei Q Y, Chai C Z, Zheng W J, Du P, Xie X F, Wang Y, Cui J, Meng G K. 2014. Activity and slip rate in the northern section of the Yellow River fault by drilling (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 36: 464–477
Li C Y, Zhang P Z, Yin J H, Min W. 2009. Late Quaternary left-lateral slip rate of the Haiyuan fault, northeastern marigin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 28: 1–26
Li C Y. 2005. Quantitative studies on active faults in northeastern margins of the Tibetan Plateau (in Chinese). Ph D Thesis. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. 1–150
Li K Q. 1992. Petroleum Geology of China (Vo1.12) (in Chinese). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press. 362–371
Li Y X, Zhang J H, Guo L Q, Zhang Z F, Zhang J Q. 2005. Counter clock wise rotation and geodynamics of Ordos block (in Chinese). J Geog Geodyn, 25: 50–56
Li W L, Lu Y C, Ding G Y. 2001. Paleomagnetic evidence from loess for the relative motion between the Ordos and its adjacent blocks (in Chinese). Quat Sci, 21: 551–559
Liang H, Zhang K, Fu J L, Li Z B, Chen J, Lu K. 2013. The neotectonics in the Niushou Mountains, the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, China and its impact on the evolution of the Yellow River (in Chinese). Earth Sci Front, 20: 182–189
Liao Y H, Chai C Z, Zhang W X, Xu W J. 2000. The active features and slip rate of Lingwu faults in Late Quaternary (in Chinese). Earthq Res China, 16: 64–71
Liu J H, Zhang P Z, Zheng D W, Wan J L, Wang W T, Du P, Lei Q Y. 2010. Pattern and timing of late Cenozoic rapid exhumation and uplift of the Helan Mountain, China. Sci China Earth Sci, 53: 345–355
Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision. Science, 189: 4l9–426
Min W, Jiao D C, Chai C Z, Zhang P Z. 2003. Characteristics of the active Luoshan fault since late Pleistocene, north central China (in Italian). Anal Geofisi, 46: 997–1014
Min W, Chai C Z, Wang P, Yang P. 1992. Preliminary study on the Holocene active fault features at the eastern piedmont of the Luoshan Mountain (in Chinese). Earthq Res Chin, 8: 49–54
Ningxia Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (NBGMR). 1990. Regional geology of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House. 65–440
Peltzer G, Tapponnier P, Armijo R. 1989. Magnitude of Quaternary left lateral displacements along the north edge of Tibet. Science, 246: 1285–1289
Shen X H, Tian Q J, Ding G Y, Wei K B, Chen Z W. 2001. The late Cenozoic stratigraphic sequence and its implication to tectonic evolution, Hejiakouzi area, Ninxia Hui Autonomous Region (in Chinese). Earthq Res China, 17: 156–165
Shi W, Liu Y, Liu Y, Chen P, Chen L, Cen M, Huang X F, Li H Q. 2013. Cenozoic evolution of the Haiyuan fault zone in the northeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau (in Chinese). Earth Sci Front, 20: 001–017
Scholz C H. 2002. The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 175–243
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Dain A Y, Armijo R, Cobbold P. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology, 10: 611–616
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, Meyer B, Arnaud N, Wittlinger G, Yang J S. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294: 1671–1677
Tang X Y, Feng Q, Li D S. 1990. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of Bayanhot basin, western Inner Mongolia (in Chinese). Oil Gas Geol, 11: 127–135
The Research Group on Active Fault Systems around the Ordos Massif (RGAFSAO). 1988. Active Fault System Around Ordos Massif (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press. 28–30
Wang W T, Zhang P Z, Lei Q Y. 2013a. Deformational characteristics of the Niushoushan-Luoshan fault zone and its tectonic implications (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 35: 1–13
Wang W T, Kirby E, Zhang P Z, Zhen D W, Zhang G L, Chai C Z. 2013b. Tertiary basin evolution along the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Evidence for basin formation during Oligocene transtension. Geol Soc Am Bull, 142: 113–137
Wang W T, Zhang P Z, Kirby E, Wang L H, Zhang G L. 2011. A revised chronology for Tertiary sedimentation in the Sikouzi Basin: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the northeastern corner of the Tibetan plateau. Tectonophysics, 505: 100–114
Wang W T, Zhang P Z, Zheng D W, Pang J Z. 2014. Late Cenozoic tectonic deformation of the Haiyuan fault zone in the northeastern of Tibetan Plateau (in Chinese). Earth Sci Front, 21:266–274
Xu X W, Wen X Z, Ye J Q, Ma B Q, Chen J, Zhou R J, He H L, Tian Q J, He Y L, Wang Z C, Sun Z M, Feng X J, Yu G H, Chen L C, Chen G H, Yu S E, Ran Y K, Li X G, Li C X, An Y F. 2008. The Ms8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure (in Chinese). Seismol Geol, 30: 597–629
Yan L H, Wang L. 2002. Geo-thermal Resources in Yinchuan Basin (in Chinese). Yinchuan: Ningxia People Press. 1–169
Zhang J, Ma Z J, Ren W J. 2004. The tectonic characteristics of southern Helan Mountain and their relationships with the Guyuan-Qingtongxia fault (in Chinese). J Jinlin Univ (Earth Sci Ed), 34: 187–205
Zhang J, Cunningham D, Chen H Y. 2010. Sedimentary characteristics of Cenozoic strata in central-southern Ningxia, NW China: Implications for the evolution of the NE Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. J Asian Earth Sci, 39: 740–749
Zhang P Z, Deng Q D, Zhang G M, Ma J, Gan W J, Min W, Mao F Y, Wang Q. 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci, 46 (Suppl 1):13–24
Zhang P Z, Deng Q D, Zhang Z Q, Li H B. 2013. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China (in Chinese). Sci China Earth Sci, 43: 1607–1620
Zhang P Z, Molnar P, Burchfiel B C, Royden L, Wang Y P, Deng Q D, Song F M, Zhang W Q, Jiao D C. 1988. Bounds on the Holocene slip rate along the Haiyuan fault, north-central China. Quaternary Res, 30: 151–164
Zhang P Z, Burchiel B C, Molnar P, Zhang W Q, Jiao D C, Deng Q D, Wang Y P, Royden L, Song F M. 1990. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Ningxia-Hui Atonomous Region, China. Geol Soc Am Bull, 102: 1484–1498
Zhang P Z, Burchfiel B C, Molnar P, Zhang W Q, Jiao D C, Deng Q D, Wang Y P, Royden L, Song F M. 1991. Amount and style of late Cenozoic deformation in the Liupan Shan area, Ningxia Autonomous Region, China. Tectonics, 10: 1111–1129
Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, Wang M, Gan W J, Bürgmann R, Molnar P. 2004. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from Global Positioning System date. Geology, 32: 809–812
Zhang Y Q, Liao C Z, Shi W, Hu B. 2006. Neotectonic evolution of the peripheral zones of the Ordos Basin and geodynamic setting (in Chinese). Geol J Chin Univ, 12: 285–297
Zhang Y Q, Mercier J L, Vergely P. 1998. Extension in the graben systems around the Ordos (China), and its contribution to the extrusion tectonics of south China with respect to Gobi-Mongolia. Tectonophysics, 285: 41–75
Zhang Y Q, Vergely P, Mercier J L. 1999. Pliocene-Quaternary faulting pattern and left-slip propagation tectonics in North China. Episodes, 22: 84–88
Zhang W Q, Jiao D C, Chai C Z. 2015. Tianjingshan Active Fault (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press. 1–270
Zheng D W, Zhang P Z, Wan J L, Yan D Y, Zhang G L, Li C Y. 2005. Apatite fission track evidence for the thermal history of the Liupanshan basin (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 48: 157–164
Zheng D W, Zhang P Z, Wan J L. 2006. Rapid exhumation at ~8 Ma on the Liupan Shan thrust fault from apatite fission-track thermochronology: Implications for growth of the northeastern Tibetan plateau margin. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 248: 198–208
Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, Yuan D Y, Zhen D W. 2009. Deformation on the northern of the Tibetan plateau from GPS measurement and geologic rates of late Quaternary along the major fault (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 52: 2491–2508
Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, Zhang, Ge W P, Molnar P, Zhang H P. 2013a. Late Quaternary slip rate of the South Heli Shan Fault (northern Hexi Corridor, NW China) and its implications for northeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics, 32: 271–293
Zheng W J, Zhang H P, Zhang P Z, Molnar P, Liu X W, Yuan D Y. 2013b. Late Quaternary slip rates of the thrust faults in western Hexi Corridor (Northern Qilian Shan, China) and their implications for northeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau. Geosphere, 9: 342–354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, Q., Zhang, P., Zheng, W. et al. Dextral strike-slip of Sanguankou-Niushoushan fault zone and extension of arc tectonic belt in the northeastern margin of the Tibet Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 59, 1025–1040 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5272-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5272-1