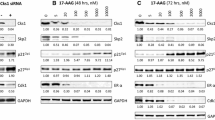
Abstract
The stability of Ikaros family zinc finger protein 1 (Ikaros), a critical hematopoietic transcription factor, can be regulated by cereblon (CRBN) ubiquitin ligase stimulated by immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma. However, other stabilization mechanisms of Ikaros have yet to be elucidated. In this study, we show that the pharmacologic inhibition or knockdown of Hsp90 downregulates Ikaros in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 but not autophagy inhibitor chloroquine could suppress the Hsp90 inhibitor STA-9090-induced reduction of Ikaros, which is accompanied with the increased ubiquitination of Ikaros. Moreover, Ikaros interacts with E3 ubiquitin-ligase C terminal Hsc70 binding protein (CHIP), which mediates the STA-9090-induced ubiquitination of Ikaros. In addition, the knockdown of Ikaros effectively inhibits the proliferation of leukemia cells, but this phenomenon could be rescued by Ikaros overexpression. Collectively, our findings indicate that the interplay between HSP90 and CHIP regulates the stability of Ikaros in AML cells, which provides a novel strategy for AML treatment through targeting the HSP90/Ikaros/CHIP axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablain, J., Nasr, R., Bazarbachi, A., and de Thé, H. (2011). The drug-induced degradation of oncoproteins: an unexpected Achilles’ heel of cancer cells? Cancer Discov 1, 117–127.
Bansal, H., Bansal, S., Rao, M., Foley, K.P., Sang, J., Proia, D.A., Blackman, R.K., Ying, W., Barsoum, J., Baer, M.R., et al. (2010). Heat shock protein 90 regulates the expression of Wilms tumor 1 protein in myeloid leukemias. Blood 116, 4591–4599.
Beer, P.A., Knapp, D.J.H.F., Kannan, N., Miller, P.H., Babovic, S., Bulaeva, E., Aghaeepour, N., Rabu, G., Rostamirad, S., Shih, K., et al. (2014). A dominant-negative isoform of IKAROS expands primitive normal human hematopoietic cells. Stem Cell Rep 3, 841–857.
Bottardi, S., Mavoungou, L., Pak, H., Daou, S., Bourgoin, V., Lakehal, Y. A., Affarel, B., and Milot, E. (2014). The IKAROS interaction with a complex including chromatin remodeling and transcription elongation activities is required for hematopoiesis. PLoS Genet 10, e1004827.
Bottardi, S., Mavoungou, L., and Milot, E. (2015). IKAROS: a multifunctional regulator of the polymerase II transcription cycle. Trends Genets 31, 500–508.
Cao, Z., Li, G., Shao, Q., Yang, G., Zheng, L., Zhang, T., and Zhao, Y. (2016). CHIP: A new modulator of human malignant disorders. Oncotarget 7, 29864–29874.
Chan, S.M. (2019). The making of a leukemic stem cell: a novel role for IKZF2 in AML stemness and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 24, 5–6.
Churchman, M.L., Qian, M., te Kronnie, G., Zhang, R., Yang, W., Zhang, H., Lana, T., Tedrick, P., Baskin, R., Verbist, K., et al. (2018). Germline genetic IKZF1 variation and predisposition to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 33, 937–948.e8.
Clappier, E., Grardel, N., Bakkus, M., Rapion, J., De Moerloose, B., Kastner, P., Caye, A., Vivent, J., Costa, V., Ferster, A., et al. (2015). IKZF1 deletion is an independent prognostic marker in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and distinguishes patients benefiting from pulses during maintenance therapy: results of the EORTC Children’s Leukemia Group study 58951. Leukemia 29, 2154–2161.
Csermely, P., Schnaider, T., So”ti, C., Prohászka, Z., and Nardai, G. (1998). The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family. Pharmacol Ther 79, 129–168.
de Rooij, J.D.E., Beuling, E., van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M., Obulkasim, A., Baruchel, A., Trka, J., Reinhardt, D., Sonneveld, E., Gibson, B.E.S., Pieters, R., et al. (2015). Recurrent deletions of IKZF1 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 100, 1151–1159.
Edkins, A.L. (2015). CHIP: a co-chaperone for degradation by the proteasome. Subcell Biochem 78, 219–242.
Errico, A. (2014). Haematological cancer: Ikaros—not a myth for myeloma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11, 65.
Fan, M., Park, A., and Nephew, K.P. (2005). CHIP (carboxyl terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein) promotes basal and geldanamycin-induced degradation of estrogen receptor-a. Mol Endocrinol 19, 2901–2914.
Fang, J., Liu, X., Bolanos, L., Barker, B., Rigolino, C., Cortelezzi, A., Oliva, E.N., Cuzzola, M., Grimes, H.L., Fontanillo, C., et al. (2016). A calcium- and calpain-dependent pathway determines the response to lenalidomide in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Med 22, 727–734.
Flandrin, P., Guyotat, D., Duval, A., Cornillon, J., Tavernier, E., Nadal, N., and Campos, L. (2008). Significance of heat-shock protein (HSP) 90 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 13, 357–364.
Garcia-Carbonero, R., Carnero, A., and Paz-Ares, L. (2013). Inhibition of HSP90 molecular chaperones: moving into the clinic. Lancet Oncol 14, e358–e369.
Gopalakrishnan, R., Matta, H., Tolani, B., Triche Jr, T., and Chaudhary, P. M. (2016). Immunomodulatory drugs target IKZF1-IRF4-MYC axis in primary effusion lymphoma in a cereblon-dependent manner and display synergistic cytotoxicity with BRD4 inhibitors. Oncogene 35, 1797–1810.
Gowda, C.S., Song, C., Ding, Y., Kapadia, M., and Dovat, S. (2016). Protein signaling and regulation of gene transcription in leukemia: role of the Casein Kinase II-Ikaros axis. J Invest Med 64, 735–739.
Hong, D.S., Banerji, U., Tavana, B., George, G.C., Aaron, J., and Kurzrock, R. (2013). Targeting the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (HSP90): lessons learned and future directions. Cancer Treat Rev 39, 375–387.
Hoter, A., El-Sabban, M., and Naim, H. (2018). The HSP90 family: structure, regulation, function, and implications in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 19, 2560.
Kronke, J., Udeshi, N.D., Narla, A., Grauman, P., Hurst, S.N., McConkey, M., Svinkina, T., Heckl, D., Comer, E., Li, X., et al. (2014). Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells. Science 343, 301–305.
Lallemand-Breitenbach, V., Jeanne, M., Benhenda, S., Nasr, R., Lei, M., Peres, L., Zhou, J., Zhu, J., Raught, B., and de Thé, H. (2008). Arsenic degrades PML or PML-RARa through a SUMO-triggered RNF4/ubiquitin-mediated pathway. Nat Cell Biol 10, 547–555.
Lu, G., Middleton, R.E., Sun, H., Naniong, M.V., Ott, C.J., Mitsiades, C.S., Wong, K.K., Bradner, J.E., and Kaelin, W.G. (2014). The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins. Science 343, 305–309.
Ma, S., Pathak, S., Mandal, M., Trinh, L., Clark, M.R., and Lu, R. (2010). Ikaros and Aiolos inhibit pre-B-cell proliferation by directly suppressing c-Myc expression. Mol Cell Biol 30, 4149–4158.
Macias-Garcia, A., Heizmann, B., Sellars, M.L., Marchal, P., Dali, H., Pasquali, J.L., Muller, S., Kastner, P., and Chan, S. (2016). Ikaros is a negative regulator of B1 cell development and function. J Biol Chem 291, 9073–9086.
Nelson, N., Xiang, S., Zhang, X., Gilvary, D., Djeu, J., Husain, K., Malafa, M., Vohra, N., Pilon-Thomas, S., and Ghansah, T. (2015). Murine pancreatic adenocarcinoma reduces Ikaros expression and disrupts T cell homeostasis. PLoS ONE 10, e0115546.
Popescu, M., Gurel, Z., Ronni, T., Song, C., Hung, K.Y., Payne, K.J., and Dovat, S. (2009). Ikaros stability and pericentromeric localization are regulated by protein phosphatase 1. J Biol Chem 284, 13869–13880.
Prinsloo, E., Kramer, A.H., Edkins, A.L., and Blatch, G.L. (2012). STAT3 interacts directly with Hsp90. IUBMB Life 64, 266–273.
Qin, D.J., Tang, C.X., Yang, L., Lei, H., Wei, W., Wang, Y.Y., Ma, C.M., Gao, F.H., Xu, H.Z., and Wu, Y.L. (2015). Hsp90 is a novel target molecule of CDDO-Me in inhibiting proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. PLoS ONE 10, e0132337.
Tsuchiya, M., Nakajima, Y., Hirata, N., Morishita, T., Kishimoto, H., Kanda, Y., and Kimura, K. (2014). Ubiquitin ligase CHIP suppresses cancer stem cell properties in a population of breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 452, 928–932.
Tsukahara, F., and Maru, Y. (2010). Bag1 directly routes immature BCR-ABL for proteasomal degradation. Blood 116, 3582–3592.
Wang, Z., Hu, Y., Xiao, D., Wang, J., Liu, C., Xu, Y., Shi, X., Jiang, P., Huang, L., Li, P., et al. (2017). Stabilization of Notch1 by the Hsp90 chaperone is crucial for T-cell leukemogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 23, 3834–3846.
Yagi, T., Hibi, S., Takanashi, M., Kano, G., Tabata, Y., Imamura, T., Inaba, T., Morimoto, A., Todo, S., and Imashuku, S. (2002). High frequency of Ikaros isoform 6 expression in acute myelomonocytic and monocytic leukemias: implications for up-regulation of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-XL in leukemogenesis. Blood 99, 1350–1355.
Yan, S., Sun, X., Xiang, B., Cang, H., Kang, X., Chen, Y., Li, H., Shi, G., Yeh, E.T.H., Wang, B., et al. (2010). Redox regulation of the stability of the SUMO protease SENP3 via interactions with CHIP and Hsp90. EMBO J 29, 3773–3786.
Yang, M., Wang, C., Zhu, X., Tang, S., Shi, L., Cao, X., and Chen, T. (2011). E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP facilitates Toll-like receptor signaling by recruiting and polyubiquitinating Src and atypical PKCζ. J Exp Med 208, 2099–2112.
Yim, K.H., Prince, T.L., Qu, S., Bai, F., Jennings, P.A., Onuchic, J.N., Theodorakis, E.A., and Neckers, L. (2016). Gambogic acid identifies an isoform-specific druggable pocket in the middle domain of Hsp90β. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E4801–E4809.
Yoshida, T., Ng, S.Y.M., and Georgopoulos, K. (2010). Awakening lineage potential by Ikaros-mediated transcriptional priming. Curr Opin Immunol 22, 154–160.
Zeidner, J., and Foster, M. (2017). Immunomodulatory drugs: IMiDs in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Curr Drug Targets 18, 304–314.
Zhu, Y.X., Braggio, E., Shi, C.X., Kortuem, K.M., Bruins, L.A., Schmidt, J. E., Chang, X.B., Langlais, P., Luo, M., Jedlowski, P., et al. (2014). Identification of cereblon-binding proteins and relationship with response and survival after IMiDs in multiple myeloma. Blood 124, 536–545.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0505200), Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai (19ZR1428700, 20ZR1430600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272886, 81570118, 81570112, 81700157, 81700475). We thank professor Jing Yi for her valuable suggestions and providing CHIP plasmids. We thank the excellent technique support from Core Facility of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Jin, J., Ji, Y. et al. Hsp90/C terminal Hsc70-interacting protein regulates the stability of Ikaros in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1481–1490 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1860-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1860-2