Abstract
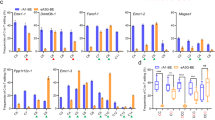
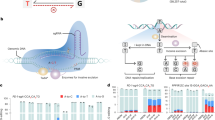
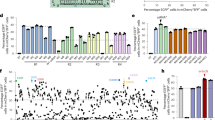
Cytidine base editor (CBE), which is composed of a cytidine deaminase fused to Cas9 nickase, has been widely used to induce C-to-T conversions in a wide range of organisms. However, the targeting scope of current CBEs is largely restricted to protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequences containing G, T, or A bases. In this study, we developed a new base editor termed “nNme2-CBE” with excellent PAM compatibility for cytidine dinucleotide, significantly expanding the genome-targeting scope of CBEs. Using nNme2-CBE, targeted editing efficiencies of 29.0%–55.0% and 17.3%–52.5% were generated in human cells and rabbit embryos, respectively. In contrast to conventional nSp-CBE, the nNme2-CBE is a natural high-fidelity base editing platform with minimal DNA off-targeting detected in vivo. Significantly increased efficiency in GC context and precision were determined by combining nNme2Cas9 with rationally engineered cytidine deaminases. In addition, the Founder rabbits with accurate single-base substitutions at Fgf5 gene loci were successfully generated by using the nNme2-CBE system. These novel nNme2-CBEs with expanded PAM compatibility and high fidelity will expand the base editing toolset for efficient gene modification and therapeutic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors state that all data necessary for confirming the conclusions presented in this article are represented fully within the article or can be provided by the authors upon request.
References
Agudelo, D., Carter, S., Velimirovic, M., Duringer, A., Rivest, J.F., Levesque, S., Loehr, J., Mouchiroud, M., Cyr, D., Waters, P.J., et al. (2020). Versatile and robust genome editing with Streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR1-Cas9. Genome Res 30, 107–117.
Amrani, N., Gao, X.D., Liu, P., Edraki, A., Mir, A., Ibraheim, R., Gupta, A., Sasaki, K.E., Wu, T., Donohoue, P.D., et al. (2018). NmeCas9 is an intrinsically high-fidelity genome-editing platform. Genome Biol 19, 214.
Anzalone, A.V., Randolph, P.B., Davis, J.R., Sousa, A.A., Koblan, L.W., Levy, J.M., Chen, P.J., Wilson, C., Newby, G.A., Raguram, A., et al. (2019). Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 576, 149–157.
Bae, S., Park, J., and Kim, J.S. (2014). Cas-OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 30, 1473–1475.
Billon, P., Bryant, E.E., Joseph, S.A., Nambiar, T.S., Hayward, S.B., Rothstein, R., and Ciccia, A. (2017). CRISPR-mediated base editing enables efficient disruption of eukaryotic genes through induction of STOP codons. Mol Cell 67, 1068–1079.e4.
Brinkman, E.K., Chen, T., Amendola, M., and van Steensel, B. (2014). Easy quantitative assessment of genome editing by sequence trace decomposition. Nucleic Acids Res 42, e168.
Chatterjee, P., Jakimo, N., and Jacobson, J.M. (2018). Minimal PAM specificity of a highly similar SpCas9 ortholog. Sci Adv 4, eaau0766.
Deng, J., Chen, M., Liu, Z., Song, Y., Sui, T., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2019). The disrupted balance between hair follicles and sebaceous glands in Hoxc13-ablated rabbits. FASEB J 33, 1226–1234.
Doman, J.L., Raguram, A., Newby, G.A., and Liu, D.R. (2020). Evaluation and minimization of Cas9-independent off-target DNA editing by cytosine base editors. Nat Biotechnol 38, 620–628.
Edraki, A., Mir, A., Ibraheim, R., Gainetdinov, I., Yoon, Y., Song, C.Q., Cao, Y., Gallant, J., Xue, W., Rivera-Pérez, J.A., et al. (2019). A compact, high-accuracy Cas9 with a dinucleotide PAM for in vivo genome editing. Mol Cell 73, 714–726.e4.
Esvelt, K.M., Mali, P., Braff, J.L., Moosburner, M., Yaung, S.J., and Church, G.M. (2013). Orthogonal Cas9 proteins for RNA-guided gene regulation and editing. Nat Methods 10, 1116–1121.
Kluesner, M.G., Nedveck, D.A., Lahr, W.S., Garbe, J.R., Abrahante, J.E., Webber, B.R., and Moriarity, B.S. (2018). EditR: a method to quantify base editing from Sanger sequencing. CRISPR J 1, 239–250.
Gaudelli, N.M., Komor, A.C., Rees, H.A., Packer, M.S., Badran, A.H., Bryson, D.I., and Liu, D.R. (2017). Programmable base editing of A•T to G•C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 551, 464–471.
Gehrke, J.M., Cervantes, O., Clement, M.K., Wu, Y., Zeng, J., Bauer, D.E., Pinello, L., and Joung, J.K. (2018). An APOBEC3A-Cas9 base editor with minimized bystander and off-target activities. Nat Biotechnol 36, 977–982.
Grünewald, J., Zhou, R., Garcia, S.P., Iyer, S., Lareau, C.A., Aryee, M.J., and Joung, J.K. (2019). Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors. Nature 569, 433–437.
Housley, D.J.E., and Venta, P.J. (2006). The long and the short of it: evidence that FGF5 is a major determinant of canine ‘hair’-itability. Anim Genet 37, 309–315
Huang, T.P., Zhao, K.T., Miller, S.M., Gaudelli, N.M., Oakes, B.L., Fellmann, C., Savage, D.F., and Liu, D.R. (2019). Circularly permuted and PAM-modified Cas9 variants broaden the targeting scope of base editors. Nat Biotechnol 37, 626–631.
Jakimo, N., Chatterjee, P., Nip, L., and Jacobson, J.M. (2018). A Cas9 with complete PAM recognition for adenine dinucleotides. bioRxiv, 429654.
Jin, S., Zong, Y., Gao, Q., Zhu, Z., Wang, Y., Qin, P., Liang, C., Wang, D., Qiu, J.L., Zhang, F., et al. (2019). Cytosine, but not adenine, base editors induce genome-wide off-target mutations in rice. Science eaaw7166.
Kim, D., Kim, D.E., Lee, G., Cho, S.I., and Kim, J.S. (2019). Genome-wide target specificity of CRISPR RNA-guided adenine base editors. Nat Biotechnol 37, 430–435.
Kim, S., Bae, T., Hwang, J., and Kim, J.S. (2017a). Rescue of high-specificity Cas9 variants using sgRNAs with matched 5′ nucleotides. Genome Biol 18, 218.
Kim, Y.B., Komor, A.C., Levy, J.M., Packer, M.S., Zhao, K.T., and Liu, D. R. (2017b). Increasing the genome-targeting scope and precision of base editing with engineered Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusions. Nat Biotechnol 35, 371–376.
Kleinstiver, B.P., Sousa, A.A., Walton, R.T., Tak, Y.E., Hsu, J.Y., Clement, K., Welch, M.M., Horng, J.E., Malagon-Lopez, J., Scarfò, I., et al. (2019). Engineered CRISPR-Cas12a variants with increased activities and improved targeting ranges for gene, epigenetic and base editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 276–282.
Knott, G.J., and Doudna, J.A. (2018). CRISPR-Cas guides the future of genetic engineering. Science 361, 866–869.
Koblan, L.W., Doman, J.L., Wilson, C., Levy, J.M., Tay, T., Newby, G.A., Maianti, J.P., Raguram, A., and Liu, D.R. (2018). Improving cytidine and adenine base editors by expression optimization and ancestral reconstruction. Nat Biotechnol 36, 843–846.
Komor, A.C., Kim, Y.B., Packer, M.S., Zuris, J.A., and Liu, D.R. (2016). Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533, 420–424.
Komor, A.C., Zhao, K.T., Packer, M.S., Gaudelli, N.M., Waterbury, A.L., Koblan, L.W., Kim, Y.B., Badran, A.H., and Liu, D.R. (2017). Improved base excision repair inhibition and bacteriophage Mu Gam protein yields C:G-to-T:A base editors with higher efficiency and product purity. Sci Adv 3, eaao4774.
Lee, J.K., Jeong, E., Lee, J., Jung, M., Shin, E., Kim, Y.H., Lee, K., Jung, I., Kim, D., Kim, S., et al. (2018). Directed evolution of CRISPR-Cas9 to increase its specificity. Nat Commun 9, 3048.
Levy, J.M., Yeh, W.H., Pendse, N., Davis, J.R., Hennessey, E., Butcher, R., Koblan, L.W., Comander, J., Liu, Q., and Liu, D.R. (2020). Cytosine and adenine base editing of the brain, liver, retina, heart and skeletal muscle of mice via adeno-associated viruses. Nat Biomed Eng 4, 97–110.
Li, X., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, B., Wang, X., Wei, J., Lu, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Huang, X., et al. (2018). Base editing with a Cpf1-cytidine deaminase fusion. Nat Biotechnol 36, 324–327.
Lin, Q., Zong, Y., Xue, C., Wang, S., Jin, S., Zhu, Z., Wang, Y., Anzalone, A.V., Raguram, A., Doman, J.L., et al. (2020). Prime genome editing in rice and wheat. Nat Biotechnol 38, 582–585.
Liu, Z., Chen, M., Chen, S., Deng, J., Song, Y., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2018). Highly efficient RNA-guided base editing in rabbit. Nat Commun 9, 2717.
Liu, Z., Chen, S., Shan, H., Chen, M., Song, Y., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2019a). Highly precise base editing with CC context-specificity using engineered human APOBEC3G-nCas9 fusions. bioRxiv, 658351.
Liu, Z., Chen, S., Shan, H., Jia, Y., Chen, M., Song, Y., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2020). Efficient base editing with high precision in rabbits using YFE-BE4max. Cell Death Dis 11, 36.
Liu, Z., Shan, H., Chen, S., Chen, M., Song, Y., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2020). Highly efficient base editing with expanded targeting scope using SpCas9-NG in rabbits. FASEB J 34, 588–596.
Liu, Z., Shan, H., Chen, S., Chen, M., Zhang, Q., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2019b). Improved base editor for efficient editing in GC contexts in rabbits with an optimized AID-Cas9 fusion. FASEB J 33, 9210–9219.
Martin, A.S., Salamango, D.J., Serebrenik, A.A., Shaban, N.M., Brown, W. L., and Harris, R.S. (2019). A panel of eGFP reporters for single base editing by APOBEC-Cas9 editosome complexes. Sci Rep 9, 497.
Mendell, J.R., Shilling, C., Leslie, N.D., Flanigan, K.M., al-Dahhak, R., Gastier-Foster, J., Kneile, K., Dunn, D.M., Duval, B., Aoyagi, A., et al. (2012). Evidence-based path to newborn screening for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol 71, 304–313.
Meng, X., Hu, X., Liu, Q., Song, X., Gao, C., Li, J., and Wang, K. (2018). Robust genome editing of CRISPR-Cas9 at NAG PAMs in rice. Sci China Life Sci 61, 122–125.
Nishimasu, H., Shi, X., Ishiguro, S., Gao, L., Hirano, S., Okazaki, S., Noda, T., Abudayyeh, O.O., Gootenberg, J.S., Mori, H., et al. (2018). Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease with expanded targeting space. Science 361, 1259–1262.
Oetting, W.S., and King, R.A. (1999). Molecular basis of albinism: mutations and polymorphisms of pigmentation genes associated with albinism. Hum Mutat 13, 99–115.
Rees, H.A., and Liu, D.R. (2018). Base editing: precision chemistry on the genome and transcriptome of living cells. Nat Rev Genet 19, 770–788.
Richter, M.F., Zhao, K.T., Eton, E., Lapinaite, A., Newby, G.A., Thuronyi, B.W., Wilson, C., Koblan, L.W., Zeng, J., Bauer, D.E., et al. (2020). Phage-assisted evolution of an adenine base editor with improved Cas domain compatibility and activity. Nat Biotechnol 38, 883–891.
Ryu, S.M., Koo, T., Kim, K., Lim, K., Baek, G., Kim, S.T., Kim, H.S., Kim, D.E., Lee, H., Chung, E., et al. (2018). Adenine base editing in mouse embryos and an adult mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat Biotechnol 36, 536–539.
Thuronyi, B.W., Koblan, L.W., Levy, J.M., Yeh, W.H., Zheng, C., Newby, G.A., Wilson, C., Bhaumik, M., Shubina-Oleinik, O., Holt, J.R., et al. (2019). Continuous evolution of base editors with expanded target compatibility and improved activity. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1070–1079.
Villiger, L., Grisch-Chan, H.M., Lindsay, H., Ringnalda, F., Pogliano, C.B., Allegri, G., Fingerhut, R., Häberle, J., Matos, J., Robinson, M.D., et al. (2018). Treatment of a metabolic liver disease by in vivo genome base editing in adult mice. Nat Med 24, 1519–1525.
Wang, X., Li, J., Wang, Y., Yang, B., Wei, J., Wu, J., Wang, R., Huang, X., Chen, J., and Yang, L. (2018). Efficient base editing in methylated regions with a human APOBEC3A-Cas9 fusion. Nat Biotechnol 36, 946–949.
Xu, Y., Liu, H., Pan, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Yao, B., Li, N., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2020). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated disruption of fibroblast growth factor 5 in rabbits results in a systemic long hair phenotype by prolonging anagen. Genes 11, 297.
Xue, C., Zhang, H., Lin, Q., Fan, R., and Gao, C. (2018). Manipulating mRNA splicing by base editing in plants. Sci China Life Sci 61, 1293–1300.
Yang, B., Yang, L., and Chen, J. (2019). Development and application of base editors. CRISPR J 2, 91–104.
Yang, D., Xu, J., Zhu, T., Fan, J., Lai, L., Zhang, J., and Chen, Y.E. (2014). Effective gene targeting in rabbits using RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. J Mol Cell Biol 6, 97–99.
Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Li, T., Chen, K., Qiu, J.L., and Gao, C. (2017). Perfectly matched 20-nucleotide guide RNA sequences enable robust genome editing using high-fidelity SpCas9 nucleases. Genome Biol 18, 191.
Zhou, C., Sun, Y., Yan, R., Liu, Y., Zuo, E., Gu, C., Han, L., Wei, Y., Hu, X., Zeng, R., et al. (2019). Off-target RNA mutation induced by DNA base editing and its elimination by mutagenesis. Nature 571, 275–278.
Zong, Y., Song, Q., Li, C., Jin, S., Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Qiu, J.L., and Gao, C. (2018). Efficient C-to-T base editing in plants using a fusion of nCas9 and human APOBEC3A. Nat Biotechnol 36, 950–953.
Zuo, E., Sun, Y., Wei, W., Yuan, T., Ying, W., Sun, H., Yuan, L., Steinmetz, L.M., Li, Y., and Yang, H. (2019). Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos. Science eaav9973.
Zuo, E., Sun, Y., Yuan, T., He, B., Zhou, C., Ying, W., Liu, J., Wei, W., Zeng, R., Li, Y., et al. (2020). A rationally engineered cytosine base editor retains high on-target activity while reducing both DNA and RNA off-target effects. Nat Methods 17, 600–604.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Peiran Hu and Nannan Li for their assistance at the Embryo Engineering Center for critical technical assistance. This study was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Stem Cell and Translational Research (2019YFA0110700), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT_16R32), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA16030501, XDA16030503), and Key Research & Development Program of Guangzhou Regenerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory (2018GZR110104004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as mean±standard error of the mean (s. e.m.) of at least three individual determinations for all experiments. Data were analyzed by Student’s t-test via GraphPad prism software 8.0.1. A probability value smaller than 0.05 (P<0.05) was considered statistically significant. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Chen, S., Jia, Y. et al. Efficient and high-fidelity base editor with expanded PAM compatibility for cytidine dinucleotide. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1355–1367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1775-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1775-2