Abstract
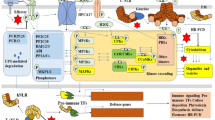
Fungal G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) play essential roles in sensing environmental cues including host signals. The study of GPCR in mediating fungus-insect interactions is still limited. Here we report the evolution of GPCR genes encoded in the entomopathogenic Metarhizium species and found the expansion of Pth11-like GPCRs in the generalist species with a wide host range. By deletion of ten candidate genes MrGpr1-MrGpr10 selected from the six obtained subfamilies in the generalist M. robertsii, we found that each of them played a varied level of roles in mediating appressorium formation. In particular, deletion of MrGpr8 resulted in the failure of appressorium formation on different substrates and the loss of virulence during topical infection of insects but not during injection assays when compared with the wild-type (WT) strain. Further analysis revealed that disruption of MrGpr8 substantially impaired the nucleus translocation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) Mero-Fus3 but not the MAPK Mero-Slt2 during appressorium formation. We also found that the defect of AMrGpr8 could not be rescued with the addition of cyclic AMP for appressorium formation. Relative to the WT, differential expression of the selected genes have also been detected in AMrGpr8. The results of this study may benefit the understanding of fungus-interactions mediated by GPCRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affeldt, K.J., Carrig, J., Amare, M., and Keller, N.P. (2014). Global survey of canonical Aspergillus flavus G protein-coupled receptors. mBio 5, e01501.
Blackwell, E., Halatek, I.M., Kim, H.J.N., Ellicott, A.T., Obukhov, A.A., and Stone, D.E. (2003). Effect of the pheromone-responsive Ga and phosphatase proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the subcellular localization of the Fus3 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol 23, 1135–1150.
Brown, N.A., Schrevens, S., van Dijck, P., and Goldman, G.H. (2018). Fungal G-protein-coupled receptors: mediators of pathogenesis and targets for disease control. Nat Microbiol 3, 402–414.
Bruno, K.S., Tenjo, F., Li, L., Hamer, J.E., and Xu, J.R. (2004). Cellular localization and role of kinase activity of PMK1 in Magnaporthe grisea. Eukaryot Cell 3, 1525–1532.
Cabrera, I.E., Pacentine, I.V., Lim, A., Guerrero, N., Krystofova, S., Li, L., Michkov, A.V., Servin, J.A., Ahrendt, S.R., Carrillo, A.J., et al. (2015). Global analysis of predicted G protein-coupled receptor genes in the filamentous fungus, Neurospora crassa. G3 5, 2729–2743.
Cen, K., Li, B., Lu, Y., Zhang, S., and Wang, C. (2017). Divergent LysM effectors contribute to the virulence of Beauveria bassiana by evasion of insect immune defenses. PLoS Pathog 13, e1006604.
Chen, X., Xu, C., Qian, Y., Liu, R., Zhang, Q., Zeng, G., Zhang, X., Zhao, H., and Fang, W. (2016). MAPK cascade-mediated regulation of pathogenicity, conidiation and tolerance to abiotic stresses in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Environ Microbiol 18, 1048–1062.
Chen, Y., Li, B., Cen, K., Lu, Y., Zhang, S., and Wang, C. (2018a). Diverse effect of phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic genes on phospholipid homeostasis, cell autophagy and fungal developments in Metarhizium robertsii. Environ Microbiol 20, 293–304.
Chen, Y., Cen, K., Lu, Y., Zhang, S., Shang, Y., and Wang, C. (2018b). Nitrogen-starvation triggers cellular accumulation of triacylglycerol in Metarhizium robertsii. Fungal Biol 122, 410–419.
DeZwaan, T.M., Carroll, A.M., Valent, B., and Sweigard, J.A. (1999). Magnaporthe grisea Pth11p is a novel plasma membrane protein that mediates appressorium differentiation in response to inductive substrate cues. Plant Cell 11, 2013–2030.
Dilks, T., Halsey, K., De Vos, R.P., Hammond-Kosack, K.E., and Brown, N. A. (2019). Non-canonical fungal G-protein coupled receptors promote Fusarium head blight on wheat. PLoS Pathog 15, e1007666.
Dos Reis, T.F., Mellado, L., Lohmar, J.M., Silva, L.P., Zhou, J.J., Calvo, A. M., Goldman, G.H., and Brown, N.A. (2019). GPCR-mediated glucose sensing system regulates light-dependent fungal development and mycotoxin production. PLoS Genet 15, e1008419.
Duan, Z.B., Gao, Q., Lv, D.D., Shi, S.H., Butt, T.M., and Wang, C.S. (2009). Appressorial differentiation and its association with cAMP in the insect pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae (in Chinese). Mycosystema 28, 712–717.
Fang, W., Pei, Y., and Bidochka, M.J. (2006). Transformation of Metarhizium anisopliae mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Can J Microbiol 52, 623–626.
Fang, W., Pava-ripoll, M., Wang, S., and St. Leger, R. (2009). Protein kinase A regulates production of virulence determinants by the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Fungal Genet Biol 46, 277–285.
Gao, Q., Shang, Y., Huang, W., and Wang, C. (2013). Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase contributes to triacylglycerol biosynthesis, lipid droplet formation, and host invasion in Metarhizium robertsii. Appl Environ Microbiol 79, 7646–7653.
Gao, Q., Lu, Y., Yao, H., Xu, Y.J., Huang, W., and Wang, C. (2016). Phospholipid homeostasis maintains cell polarity, development and virulence in metarhizium robertsii. Environ Microbiol 18, 3976–3990.
Gao, Q., Jin, K., Ying, S.H., Zhang, Y., Xiao, G., Shang, Y., Duan, Z., Hu, X., Xie, X.Q., Zhou, G., et al. (2011). Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet 7, e1001264.
Good, M., Tang, G., Singleton, J., Reményi, A., and Lim, W.A. (2009). The Ste5 scaffold directs mating signaling by catalytically unlocking the Fus3 MAP kinase for activation. Cell 136, 1085–1097.
Gruber, S., Omann, M., and Zeilinger, S. (2013). Comparative analysis of the repertoire of G protein-coupled receptors of three species of the fungal genus Trichoderma. BMC Microbiol 13, 108.
Hao, N., Behar, M., Elston, T.C., and Dohlman, H.G. (2007). Systems biology analysis of G protein and MAP kinase signaling in yeast. Oncogene 26, 3254–3266.
Hu, X., Xiao, G., Zheng, P., Shang, Y., Su, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, X., Zhan, S., St. Leger, R.J., and Wang, C. (2014). Trajectory and genomic determinants of fungal-pathogen speciation and host adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 16796–16801.
Huang, A., Lu, M., Ling, E., Li, P., and Wang, C. (2020). A M35 family metalloprotease is required for fungal virulence against insects by inactivating host prophenoloxidases and beyond. Virulence 11, 222–237.
Huang, W., Hong, S., Tang, G., Lu, Y., and Wang, C. (2019). Unveiling the function and regulation control of the DUF3129 family proteins in fungal infection of hosts. Phil Trans R Soc B 374, 20180321.
Isberg, V., Mordalski, S., Munk, C., Rataj, K., Harpsøe, K., Hauser, A.S., Vroling, B., Bojarski, A.J., Vriend, G., and Gloriam, D.E. (2017). GPCRdb: an information system for G protein-coupled receptors. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 2936.
Jiang, C., Cao, S., Wang, Z., Xu, H., Liang, J., Liu, H., Wang, G., Ding, M., Wang, Q., Gong, C., et al. (2019). An expanded subfamily of G-protein-coupled receptor genes in Fusarium graminearum required for wheat infection. Nat Microbiol 4, 1582–1591.
Jin, K., Han, L., and Xia, Y. (2014). MaMk1, a FUS3/KSS1-type mitogen-activated protein kinase gene, is required for appressorium formation, and insect cuticle penetration of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium acridum. J Invertebr Pathol 115, 68–75.
Kou, Y., Tan, Y.H., Ramanujam, R., and Naqvi, N.I. (2017). Structure-function analyses of the Pth11 receptor reveal an important role for CFEM motif and redox regulation in rice blast. New Phytol 214, 330–342.
Krogh, A., Larsson, B., von Heijne, G., and Sonnhammer, E.L.L. (2001). Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305, 567–580.
Kulkarni, R.D., Thon, M.R., Pan, H., and Dean, R.A. (2005). Novel G-protein-coupled receptor-like proteins in the plant pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Genome Biol 6, R24.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., and Tamura, K. (2018). MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35, 1547–1549.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., et al. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948.
Lu, Y., Xia, Y., Luo, F., Dong, C., and Wang, C. (2016). Functional convergence and divergence of mating-type genes fulfilling in Cordyceps militaris. Fungal Genet Biol 88, 35–43.
Martín, J.F., van den Berg, M.A., Ver Loren van Themaat, E., and Liras, P. (2019). Sensing and transduction of nutritional and chemical signals in filamentous fungi: Impact on cell development and secondary metabolites biosynthesis. Biotech Adv 37, 107392.
Meng, Y., Zhang, X., Guo, N., and Fang, W. (2019). MrSt12 implicated in the regulation of transcription factor AFTF1 by Fus3-MAPK during cuticle penetration by the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Fungal Genet Biol 131, 103244.
Ortiz-Urquiza, A., and Keyhani, N.O. (2013). Action on the surface: entomopathogenic fungi versus the insect cuticle. Insects 4, 357–374.
Ortiz-Urquiza, A., and Keyhani, N.O. (2015). Stress response signaling and virulence: insights from entomopathogenic fungi. Curr Genet 61, 239–249.
Ryder, L.S., and Talbot, N.J. (2015). Regulation of appressorium development in pathogenic fungi. Curr Opin Plant Biol 26, 8–13.
Sabnam, N., and Roy Barman, S. (2017). WISH, a novel CFEM GPCR is indispensable for surface sensing, asexual and pathogenic differentiation in rice blast fungus. Fungal Genet Biol 105, 37–51.
Sakulkoo, W., Osés-Ruiz, M., Oliveira Garcia, E., Soanes, D.M., Littlejohn, G.R., Hacker, C., Correia, A., Valent, B., and Talbot, N.J. (2018). A single fungal MAP kinase controls plant cell-to-cell invasion by the rice blast fungus. Science 359, 1399–1403.
Shang, Y., Chen, P., Chen, Y., Lu, Y., and Wang, C. (2015). MrSkn7 controls sporulation, cell wall integrity, autolysis, and virulence in Metarhizium robertsii. Eukaryot Cell 14, 396–405.
Shang, Y., Xiao, G., Zheng, P., Cen, K., Zhan, S., and Wang, C. (2016). Divergent and convergent evolution of fungal pathogenicity. Genome Biol Evol 8, 1374–1387.
Wang, C., and Wang, S. (2017). Insect pathogenic fungi: genomics, molecular interactions, and genetic improvements. Annu Rev Entomol 62, 73–90.
Wang, C., Zhang, S., Hou, R., Zhao, Z., Zheng, Q., Xu, Q., Zheng, D., Wang, G., Liu, H., Gao, X., et al. (2011). Functional analysis of the kinome of the wheat scab fungus Fusarium graminearum. PLoS Pathog 7, e1002460.
Wang, G., Wei, Z., and Wu, G. (2018). Role of Rab GTPases in the export trafficking of G protein-coupled receptors. Small GTPases 9, 130–135.
Wang, J.B., St Leger, R.J., and Wang, C. (2016). Advances in genomics of entomopathogenic fungi. Adv Genet 94, 67–105.
Wootten, D., Christopoulos, A., Marti-Solano, M., Babu, M.M., and Sexton, P.M. (2018). Mechanisms of signalling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19, 638–653.
Xu, J.R., and Hamer, J.E. (1996). MAP kinase and cAMP signaling regulate infection structure formation and pathogenic growth in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Genes Dev 10, 2696–2706.
Xu, X., Li, G., Li, L., Su, Z., and Chen, C. (2017). Genome-wide comparative analysis of putative Pth11-related G protein-coupled receptors in fungi belonging to Pezizomycotina. BMC Microbiol 17, 166.
Xue, C., Hsueh, Y.P., and Heitman, J. (2008). Magnificent seven: roles of G protein-coupled receptors in extracellular sensing in fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32, 1010–1032.
Yang, X., Feng, P., Yin, Y., Bushley, K., Spatafora, J.W., and Wang, C. (2018). Cyclosporine biosynthesis in Tolypocladium inflatum benefits fungal adaptation to the environment. mBio 9, e01211–01218.
Ying, S.H., Feng, M.G., and Keyhani, N.O. (2013). A carbon responsive G-protein coupled receptor modulates broad developmental and genetic networks in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Environ Microbiol 15, 2902–2921.
Zhang, A.X., Mouhoumed, A.Z., Tong, S.M., Ying, S.H., and Feng, M.G. (2019). BrlA and AbaA govern virulence-required dimorphic switch, conidiation, and pathogenicity in a fungal insect pathogen. mSystems 4.
Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Jiang, X., Wang, G., Luo, Z., Fan, Y., Wu, Z., and Pei, Y. (2010). Requirement of a mitogen-activated protein kinase for appressorium formation and penetration of insect cuticle by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl Environ Microbiol 76, 2262–2270.
Zhao, X., Mehrabi, R., and Xu, J.R. (2007). Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and fungal pathogenesis. Eukaryot Cell 6, 1701–1714.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Programs of China (2017YFD0200400 and 2017YFD0201202) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31501699).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, J., Shang, Y., Tang, G. et al. Identification of a key G-protein coupled receptor in mediating appressorium formation and fungal virulence against insects. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 466–477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1763-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1763-1