Abstract
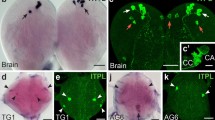
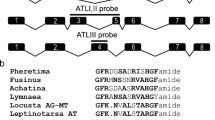
Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH), a neuropeptide hormone stimulating the prothoracic glands to synthesize ecdysone, plays an important role in regulating postembryonic development in insects. The cDNA encoding PTTH was isolated and sequenced from the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Spe). The deduced amino acid sequence is composed of a signal peptide, a peptide (65 amino acids) of unknown function, and a mature PTTH molecule (111 amino acids). The Spe-PTTH shows similarities (45.5%–70.3%) to other known PTTHs reported in Lepidoptera species, but 7 cysteine residues and the hydrophobic regions were conserved. Whole-mount immunocytochemistry by using an antiserum against recombinant Helicoverpa armigera PTTH showed that Spe-PTTH was synthesized in two pairs of neurosecretory cells in the S. exigua brain. Northern blot analysis demonstrates the presence of a 1.2-kb transcript in the brain. The Spe-PTTH mRNA is detectable at high levels at the wandering larval stage, early pupal stage, and pharate adult stage, suggesting that the Spe-PTTH gene might be correlated with molting, metamorphosis, and reproduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams C M Physiology of insect biology II. Interaction between the pupal brain and prothoracic glands in the metamorphosis in the giant silkworm, Platysamia cecropia. Biol Bull, 1947, 93: 89–98
Kataoka H, Nagasawa H, Isogai I. Isolation and partial characterization of a prothoracicotropic hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Agric Biol Chem, 1987, 51: 1067–1076
Kawakami A, Kataoka H, Oka T, et al. Molecular cloning of the Bombyx mori prothoracicotropic hormone. Science, 1990, 247(4948): 1333–1335
Sauman I, Reppert S M. Molecular characterization of prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) from the giant silkmoth Antheraea pernyi: Developmental appearance of PTTH-expressing cells and relationship to circadian clock cells in central brain. Dev Biol, 1996, 178(2): 418–429
Sehnal F, Hansen I, Scheller K. The cDNA-structure of the prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) of the silkmoth Hyalophora cecropia. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2002, 32(2): 233–237
Shionoya M, Matsubayashi H, Asahina M, et al. Molecular cloning of the prothoracicotropic hormone from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2003, 33(8): 795–801
Xu W H, Rinehart J P, Denlinger D L. Structural characterization and expression analysis of prothoracicotropic hormone in the corn earworm, Helicoverpa zea. Peptides, 2003, 24(9): 1319–1325
Xu W H, Denlinger D L. Molecular characterization of prothoracicotropic hormone and diapause hormone in Heliothis virescens during diapause, and a new role for diapause hormone. Insect Mol Biol, 2003, 12(5): 509–516
Wei Z J, Zhang Q R, Kang L, et al. Molecular characterization and expression of prothoracicotropic hormone during development and pupal diapause in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J Insect Physiol, 2005, 51(6): 691–700
Nagata S, Namiki T, Ko R, et al. A novel type of receptor cDNA from the prothoracic glands of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2006, 70(2): 554–558
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroforms extraction. Anal Biochem, 1987, 162: 156–159
Chen J, Liu J, Guo L, et al. Inducible expression pattern of rice Bowman-Birk inhibitor gene Os WIP1-2 and its protease inhibitory activity. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(9): 895–899
Zhang T Y, Sun J S, Zhang L B, et al. Cloning and expression of the cDNA encoding the FXPRL family of peptides and a functional analysis of their effect on breaking pupal diapause in Helicoverpa armigera. J Insect Physiol, 2004, 50(1): 25–33
Sun J S, Chen F S, Xu W H. Localization, expression, and secretion pathway of diapause hormone in embryo and larva of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(13): 1386–1391
Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Plewniak F, et al. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res, 1997, 25(24): 4876–4882
Ding S X, Zhuang X, Guo F, et al. Molecular phylogenetic relationships of China Seas groupers based on cytochromeb gene fragment sequences. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci, 2006, 49(3): 235–242
Ishibashi J, Kataoka H, Isogai A, et al. Assignment of disulfide bond location in prothoracicotropic hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: A homodimeric peptide. Biochemistry, 1994, 33(19): 5912–5919
Liu J, Shi G P, Zhang W Q, et al. Cathepsin L function in insect molting: molecular cloning and functional analysis in cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol Biol, 2006, 15(6): 823–834
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, People’s Republic of China (Grant No. 2006CB102001)
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this article have been submitted to Gen-Bank and have been assigned the accession number AY628763
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Su, J., Shen, J. et al. Molecular characterization and developmental expression of the gene encoding the prothoracicotropic hormone in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua . SCI CHINA SER C 50, 466–472 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0060-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0060-y