Abstract
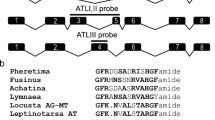
Ion transport peptide (ITP) and a longer ITP-like (ITPL) are alternatively spliced insect neuropeptides involved in the regulation of development and water homeostasis. Using in situ hybridisation and immunohistochemistry, we determined site- and stage-specific expression of each peptide in Bombyx mori. Each peptide was differentially expressed, except for the prominent overlapping expression of both peptides in six pairs of the brain neurosecretory cells Ia2. After metamorphosis, ITP appeared in the male-specific neurons of the abdominal neuromere 9 (MAN9) that innervate the reproductive organs. ITPL was detected in a pair of dorsolateral interneurons (IN-DL) in each thoracic and abdominal ganglion, and in the thoracic neurosecretory cells (NS-VTL2) which terminate in the vicinity of the prothoracic gland. Feeding larvae showed ITPL expression in the abdominal neurosecretory cells M5. ITPL was also expressed in the peripheral L1 neurons that project axons into the thoracic and abdominal transverse nerves. Our results suggest that ITP and ITPL exhibit different sex- and stage-specific functions that may include regulation of reproduction and steroid production. For future functional studies, we identified an upstream regulatory region controlling ITP/ITPL expression in the brain and L1 neurons, and prepared stable transgenic line pITP-Gal4.2 using the piggyBac system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audsley N, McInthosh C, Phillips JE (1992a) Isolation of a neuropeptide from locust corpus cardiacum which influences ileal transport. J Exp Biol 173:261–274
Audsley N, McInthosh C, Phillips JE (1992b) Actions of ion-transport peptide from locust corpus cardiacum on several hindgut transport processes. J Exp Biol 173:275–288
Bednár B, Roller L, Čižmár D, Mitrová D, Žitňan D (2017) Developmental and sex-specific differences in expression of neuropeptides derived from allatotropin gene in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Cell Tissue Res 368:259–275
Begum K, Li B, Beeman RW, Park Y (2009) Functions of ion transport peptide and ion transport peptide-like in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:717–725
Čižmár D, Roller L, Pillerová M, Sláma K, Žitňan D (2019) Multiple neuropeptides produced by sex-specific neurons control activity of the male accessory glands and gonoducts in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Sci Rep 9:2253
Chung JS, Dircksen H, Webster SG (1999) A remarkable, precisely timed release of hyperglycemic hormone from endocrine cells in the gut is associated with ecdysis in the crab Carcinus maenas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(23):13103–13107
Dai L, Žitňan D, Adams MA (2007) Strategic expression of ion transport peptide gene products in central and peripheral neurons of insects. J Comp Neurol 500:353–367
Daubnerová I, Roller L, Žitňan D (2009) Transgenesis approaches for functional analysis of peptidergic cells in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162(1):36–42
Davis NT, Homberg U, Dircksen H, Levine RB, Hildebrand JG (1993) Crustacean cardioactive peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta and changes in their immunoreactivity during postembryonic development. J Comp Neurol 338:612–627
Dircksen H, Tesfai LK, Albus C, Nässel DR (2008) Ion transport peptide splice forms in central and peripheral neurons throughout postembryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Neurol 509:23–41
Dircksen H (2009) Insect ion transport peptides are derived from alternatively spliced genes and differentially expressed in the central and peripheral nervous system. J Exp Biol 212:401–412
Drexler AL, Harris CC, Pena MG, Asuncion-Uchi M, Chung S, Webster S, Fuse M (2007) Molecular characterization and cell-specific expression of an ion transport peptide in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 329:391–408
Endo H, Nagasawa H, Watanabe T (2000) Isolation of a cDNA encoding a CHH-family peptide from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:355–361
Gáliková M, Dircksen H, Nässel DR (2018) The thirsty fly: ion transport peptide (ITP) is a novel endocrine regulator of water homeostasis in Drosophila. PLoS Genet 14(8):e1007618
Johard HAD, Yoishii T, Dircksen H, Cusumano P, Rouyer F, Helfrich-Förster C, Nässel DR (2009) Peptidergic clock neurons in Drosophila: Ion transport peptide and short neuropeptide F in subsets of dorsal and ventral lateral neurons. J Comp Neurol 516:59–73
Kegler G, Reichweis B, Weese S, Gaus G, Peter-Katalimić J, Keller R (1989) Amino acid sequence of the crustacean hyperglycemic hormone (CHH) from the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. FEBS Lett 255:10–14
Kim YJ, Zitnan D, Cho KH, Schooley DA, Mizoguchi A, Adams ME (2006) Central peptidergic ensembles associated with organization of an innate behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(38):14211–14216
Lacombe C, Grève P, Martin G (1999) Overview on the sub-grouping of the crustacean hyperglycemic hormone family. Neuropeptides 33(1):71–80
Li B, Predel R, Neupert S, Hauser F, Tanaka Y, Cazzamali G, Williamson M, Arakane Y, Verleyen P, Schoofs L, Schachtner J, Grimmelikhuijzen CJ, Park Y (2008) Genomics, transcriptomics, and peptidomics of neuropeptides and protein hormones in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Genome Res 18:113–122
Long D, Lu W, Zhang Y, Bi L, Xiang Z, Zhao A (2015) An efficient strategy for producing a stable, replaceable, highly efficient transgene expression system in silkworm. Bombyx Mori Sci Rep 5:8802. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08802
Lu D, Lee K-L, Horodyski FM, Witten JL (2002) Molecular characterization and cell-specific expression of a Manduca sexta FLRFamide gene. J Comp Neurol 446:377–396
Meredith J, Ring M, Macinus A, Marschall J, Cheng NN, Theilmann D, Brock HW, Phillips JE (1996) Locust ion transport peptide (ITP): primary structure, cDNA and expression in a baculovirus system. J Exp Biol 199:1053–1061
Namiki S, Kanzaki R (2019) Morphology and physiology of olfactory neurons in the lateral protocerebrum of the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Sci Rep 9:16604
Nagai C, Mabashi-Asazuma H, Nagasawa H, Nagata S (2014) Identification and characterization of receptors for ion transport peptide (ITP) and ITP-like (ITPL) in the silkworm Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem 289:32166–32177
Park D, Veenstra JA, Park JH, Taghert PH (2008) Mapping peptidergic cells in Drosophila: where DIMM fits. PLoS ONE 3:e1896
Pfeiffer BD, Ngo TT, Hibbard KL, Murphy C, Jenett A, Truman JW, Rubin GM (2010) Refinement of tools for targeted gene expression in Drosophila. Genetics 186(2):735–755
Roller L, Yamanaka N, Watanabe K, Daubnerová I, Žitňan D, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2008) The unique evolution of neuropeptide genes in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1147–1157
Roller L, Čižmár D, Gáliková Z, Bednár B, Žitňan D (2016) Molecular cloning, expression and identification of the promoter regulatory region for the neuropeptide trissin in the nervous system of the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Cell Tissue Res 364:499–512
Roller L, Daubnerová I, Mizoguchi A, Satake H, Tanaka Y, Stano M, Klucar L, Žitňan D (2022) Expression analysis of peptidergic enteroendocrine cells in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Cell Tissue Res 389:385–407
Sun L, Zhang Z, Zhang R, Yu Y, Yang F, Tan A (2020) Molecular disruption of iontransport peptide receptor results in impaired water homeostasis and developmental defects in Bombyx mori. Front Physiol 11:424
Takemura SY, Aso Y, Hige T, Wong A, Lu Z, Xu CS, Rivlin PK, Hess H, Zhao T, Parag T et al (2017) A connectome of a learning and memory center in the adult Drosophila brain. eLife 6:e26975
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C et al (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Wall JB, Taghert PH (1991) Segment-specific modifications of a neuropeptide phenotype in embryonic neurons of the moth, Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 309:375–390
Webster SG, Keller R, Dircksen H (2012) The CHH-superfamily of multifunctional peptide hormones controlling crustacean metabolism, osmoregulation, moulting, and reproduction. Gen Comp Endocrinol 175:217–233
Wasserthal W, Wasserthal LT (1980) Multinucleate neurons with neurohaemal and synapsing axons at the heart and alary muscles of the butterfly Caligo beltrao Illiger (Lepidoptera). Cell Tissue Res 212:351–362
Yamanaka N, Žitňan D, Kim Y-J, Adams ME, Hua Y-J, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Suzuki A, Satake H, Mizoguchi A, Asaoka K, Tanaka Y, Kataoka H (2006) Regulation of insect steroid hormone biosynthesis by innervating peptidergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8622–8627
Yamanaka N, Roller L, Žitňan D, Satake H, Mizoguchi A, Kataoka H, Tanaka Y (2011) Bombyx orcokinins are brain-gut peptides involved in the neuronal regulation of ecdysteroidogenesis. J Comp Neurol 519:238–246
Yu B, Li D-T, Wang S-L, Xu H-J, Bao Y-Y, Yhang C-X (2016) Ion transport peptide (ITP) regulates wing expansion and cuticle melanism in the brown planthopper. Nilaparvata Lugens Insect Mol Biol 25(6):778–787
Žitňan D, Adams ME (2005) Neuroendocrine regulation of insect ecdysis. Coprehensive Molecular Insect Science (LI Gilbert, K Iatrou, SS Gill, eds.), Vol 3, pp. 1–60
Hermann-Luibl C, Yoshii T, Senthilan PR, Dircksen H, Helfrich-Förster C. (2014) The ion transport peptide is a new functional clock neuropeptide in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurosci 34(29):9522-36
Daubnerová I, Roller L, Satake H, Yhang C, Kim Y-J, Žitňan D (2021) Identifcation and function of ETH receptor networks in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Sci Rep 11(1): 1-23
Shiomi K, Kajiura Z, Nakagaki M, Yamashita O (2003) Baculovirus-Mediated Efficient Gene transfer into the central nervous system of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Biotechnol Sericology 72: 149–155
Reese MG (2001) Application of a time-delay neural network to promoter annotation in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Comput Chem 26(1): 51–6
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to C.J.P. Grimmelikhuijzen, Y-J. Kim, A. Mizoguchi and J.A. Veenstra for providing valuable antisera.
Funding
This study was supported by the Slovak grant agency, Agentúra na podporu výskumu a vývoja, (APVV-16–0395, APVV-18–0201, APVV-21–0431).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animal
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
441_2023_3752_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Supplementary file1 Fig. S1 Detection of ITP/ITPL transcripts using ISH probe followed by IH staining with ITP antibody in Ia2 cells of the larval brain. Note very strong ISH labelling in cell bodies that suppressed IH staining (arrows). ITP-IR in axonal projections from these cells are clearly visible (arrowheads) (TIFF 2957 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Klöcklerová, V., Gáliková, Z., Roller, L. et al. Differential expression of ITP and ITPL indicate multiple functions in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Cell Tissue Res 392, 715–731 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03752-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-023-03752-y